




Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: THE HINDU
Scientists have developed an RNA-based antiviral that effectively combats the cucumber mosaic virus in plants.
Farmers worldwide face a massive challenge from plant viruses, unlike bacteria or fungi, which farmers can control with chemicals like pesticides, no simple cure exists for viral infections in plants.
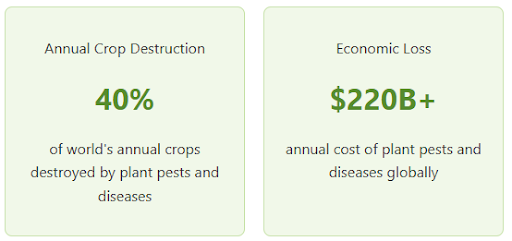
The United Nations’ Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) reports that pests and diseases destroy 40% of global crops yearly, costing over $220 billion. Plant viruses alone cause losses of more than $30 billion annually. One such virus, the Cucumber Mosaic Virus (CMV), is a major threat.
It infects over 1,200 plant species, including crops like cucumbers, pumpkins, bananas, cereals, and even medicinal plants.
In India, CMV causes 25-30% yield losses in banana plantations and up to 70% infection rates in pumpkins, cucumbers, and melons.
Infected plants show mosaic-like discoloration, stunted growth, and produce fruits that are not fit for sale.
It spreads through small insects called aphids, with nearly 90 aphid species capable of transmitting it, making outbreaks hard to control.
Scientists at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg in Germany have developed a new RNA-based antiviral to protect plants from CMV. RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) is a molecule that plays a key role in how living organisms, including plants, function. The researchers use RNA to strengthen a plant’s natural defense system, similar to how our immune system fights viruses.
Plants have a natural defense called RNA silencing. When a virus attacks, it introduces double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), which alerts the plant’s immune system.
To fix this, scientists developed two RNA-based techniques: Host-Induced Gene Silencing (HIGS) and Spray-Induced Gene Silencing (SIGS).
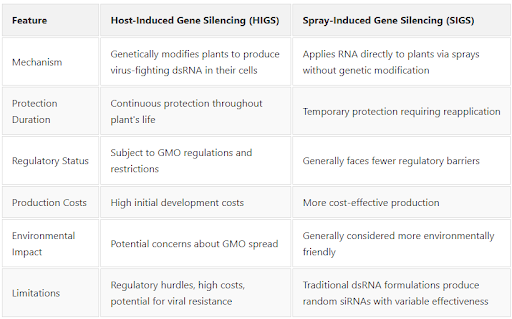
The German researchers improved SIGS by creating effective dsRNA, a specially designed RNA molecule packed with highly functional siRNAs. Unlike traditional dsRNA, which produces random siRNAs, effective dsRNA ensures the plant generates siRNAs that precisely target the CMV’s genetic material. This triggers a stronger and more targeted immune response.
In lab tests on a model plant, Nicotiana benthamiana, the effective dsRNA reduced the CMV viral load by nearly 80%, with some plants achieving complete protection. It worked better than traditional dsRNA because it produced more effective siRNAs. The method also proved effective against multiple CMV strains, making it versatile.
Must Read Articles:
RNA Editing|RNA|DNA|RNA vs DNA
RNA-BASED THERAPEUTICS MEDICINE
Source:
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. In the question given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Mark your answer as per the codes provided: Assertion (A): RNA viruses exhibit a higher rate of mutation compared to DNA viruses. Reason (R): RNA-dependent RNA polymerases lack proofreading mechanisms. Which of the options given below is correct? A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation for A. B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation for A. C) A is true, but R is false. D) A is false, but R is true. Answer: A Explanation: Assertion (A): RNA viruses exhibit a higher rate of mutation compared to DNA viruses. This statement is true. Research shows that RNA viruses have mutation rates 100 to 1000 times higher than DNA viruses. Reason (R): RNA-dependent RNA polymerases lack proofreading mechanisms. This statement is also true. Unlike DNA polymerases, RNA-dependent RNA polymerases, the enzymes responsible for replicating the genetic material of RNA viruses, do not have an inherent proofreading ability to correct errors during replication. Because the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase makes more errors during replication and lacks the ability to fix them, RNA viruses accumulate mutations at a much faster rate compared to DNA viruses. Therefore, the Reason (R) is the correct explanation for the Assertion (A). |







© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved