



The Poshan Tracker app’s glitches in Haryana disrupt beneficiary registration, affecting pregnant women and lactating mothers. Facial recognition and Aadhaar e-KYC issues, coupled with poor internet and digital illiteracy, exclude vulnerable groups. Aspirants, understand these UPSC-relevant challenges in governance, digital inclusion, and nutrition schemes to boost your preparation.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: THE HINDU
Anganwadi workers, providing nutrition and health services, are facing technical difficulties to register beneficiaries (pregnant women, new mothers, and children) on the Poshan Tracker app.
The Ministry of Women and Child Development launched the Poshan (Prime Minister's Overarching Scheme for Holistic Nourishment) Abhiyaan in 2018.
It aims to improve the nutrition levels for young children (0-6 years old), adolescent girls, pregnant women, and mothers who are breastfeeding.
|
Malnutrition in India As per the National Family Health Survey (NHFS-5)
|
|
Positive Impact of the Poshan Abhiyaan According to the World Bank report, between 2015-16 and 2019-21, in 11 focus states, child stunting decreased from an average of 41% to 37%, and child wasting fell from 22% to 20%. The proportion of undernourished women also decreased from 24.5% to 20.3%. |
Access to Quality Services => Providing essential health services through schemes like Integrated Child Development Scheme (ICDS) , National Health Mission (NHM), and Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY), especially during the first 1,000 days of a child’s life.
Cross-Sectoral Convergence => Coordinating efforts across multiple ministries, including water and sanitation under the Swachh Bharat Mission and drinking water access through the National Drinking Water Mission.
Jan Andolan => Community engagement is key to driving mass awareness and encouraging behavioral change around nutrition.
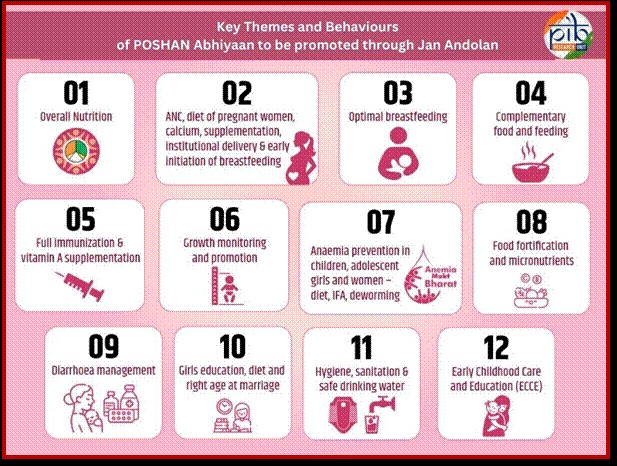 Leveraging Technology => Tools like the Poshan Tracker application allow real-time data collection and intervention.
Leveraging Technology => Tools like the Poshan Tracker application allow real-time data collection and intervention.
Mandatory Facial Recognition and Aadhaar e-KYC => Since July 1, 2025, the government requires beneficiaries to register on the app using facial recognition and Aadhaar e-KYC to prove their identity. Children must also register using their parents' or guardians' Aadhaar details.
Aadhaar Mismatches => The app does not accept beneficiary names that are misspelled on their Aadhaar cards.
Poor Internet Connectivity => In many rural areas, weak or unreliable internet connections make it difficult for the app to function properly.
Lack of Digital Skills and Training => Some anganwadi workers do not know how to use smartphones or the app and depend on others for help. They have not received specific training for using these digital tools.
The government merged several existing nutrition programs, including the Supplementary Nutrition Programme and the original Poshan Abhiyaan, into Mission POSHAN 2.0. It was announced in the Union Budget 2021-22.
Its goals include developing human capital, tackling malnutrition, promoting nutrition awareness, and infrastructure upgrades for Anganwadi Centre (AWCs).
Both Poshan Abhiyaan and Mission POSHAN 2.0 receive their funding from the central government, with contribution from State governments, and also receive International support from UNICEF and the World Bank.
Integrated Services => Combining health, nutrition, education, and sanitation services. Provide digital skill to ground workers.
Community-Led Initiatives => Empowering local communities, and frontline workers to drive change. Awareness campaign with local leaders and Celebrities.
Technology for Monitoring => Utilizing digital platforms for real-time data collection and program oversight.
Public-Private Partnerships => Engaging various stakeholders to support nutrition initiatives.
|
FAQ Q. What is the objective of the Poshan Abhiyaan? The Poshan Abhiyaan aims to improve nutrition levels for young children, adolescent girls, pregnant women, and breastfeeding mothers, specifically tackling malnutrition in a focused way. Q. What are the key targets for reduction under Poshan Abhiyaan? It targets a 2% annual reduction in stunting, under-nutrition, and low birth weight, alongside a 3% annual reduction in anemia. Q. What is Mission POSHAN 2.0, and how does it relate to the original Abhiyaan? Mission POSHAN 2.0 is a merged program (announced in Union Budget 2021-22) that includes the original Poshan Abhiyaan, aiming for holistic human capital development, malnutrition reduction, and Anganwadi Centre upgrades. |
Must Read Articles:
Source: THE HINDU
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Analyze the 'double burden of malnutrition' in India, where undernutrition coexists with overnutrition and rising rates of diet-related non-communicable diseases. What policy interventions are required to address this paradox? 250 words |




© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved