Description

Copyright infringement is not intended
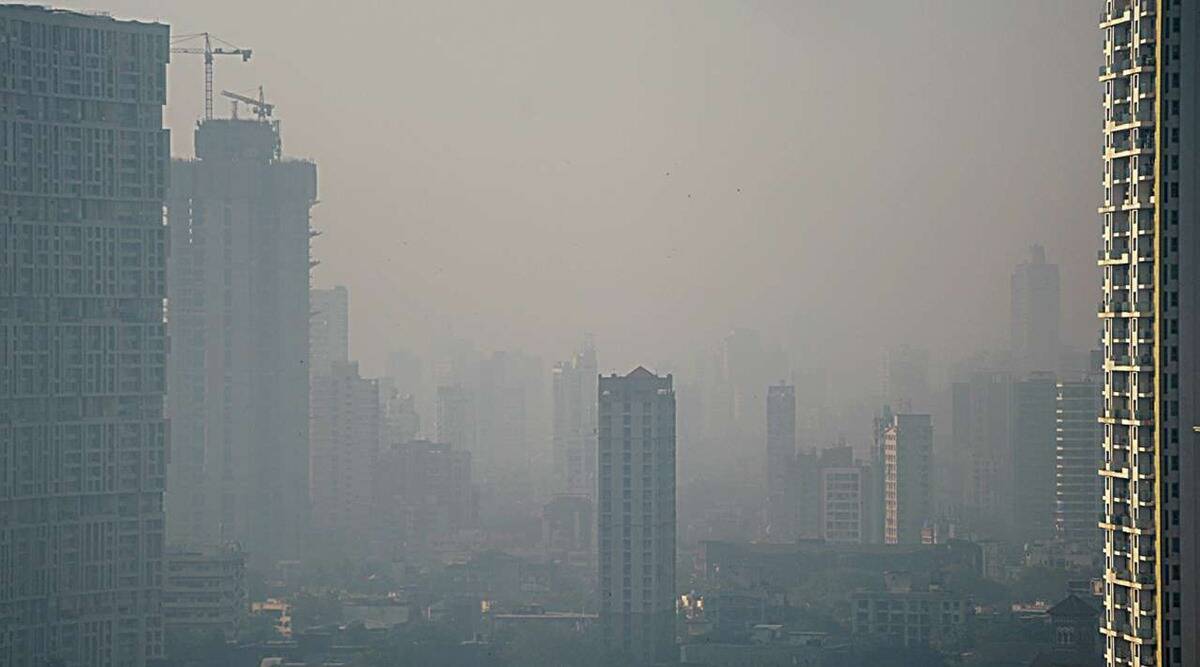
Context: Colaba and Mazagaon in South Mumbai have emerged as the most polluted localities in the city, with the air quality index (AQI) exceeding 330 — indicating “very poor” air — as per data from the System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting And Research (SAFAR).
Reasons for Poor Air Quality:
Sea Salt
- The sea salt in water vapour tends to react with other pollutants like PM 2.5, and sulphur oxides from vehicles that are already present in the air, to create secondary pollutants.
- When wind speeds are slow, these secondary pollutants add to the pollution load.
- Beig added that PM2.5 (a prominent pollutant in Mumbai) is highly susceptible to sea salt particles.
No breeze
- The sea breeze over Mumbai has been low or stagnant. Thus, emissions from road and metro construction activities and vehicular movement are getting trapped in the air, raising the AQI.
Urban Canyon Effect
- Levels of traffic-related air pollution can be substantially elevated along a road surrounded by tall buildings. This is called the Urban Canyon Effect.
- The canyon effect occurs when tall buildings flank both sides of city streets, restricting air movement. Eventually, this increases the concentration of pollutants in the ambient air.
Inversion layer
- In the Inversion layer of the atmosphere there is a temperature inversion, with the layer tending to prevent the air below it from rising, thus trapping any pollutants that are present.
- This occurs most often when a warm, less dense air mass moves over a dense, cold air. The inversion layer does not allow pollutants to escape, thus trapping them closer to the ground.
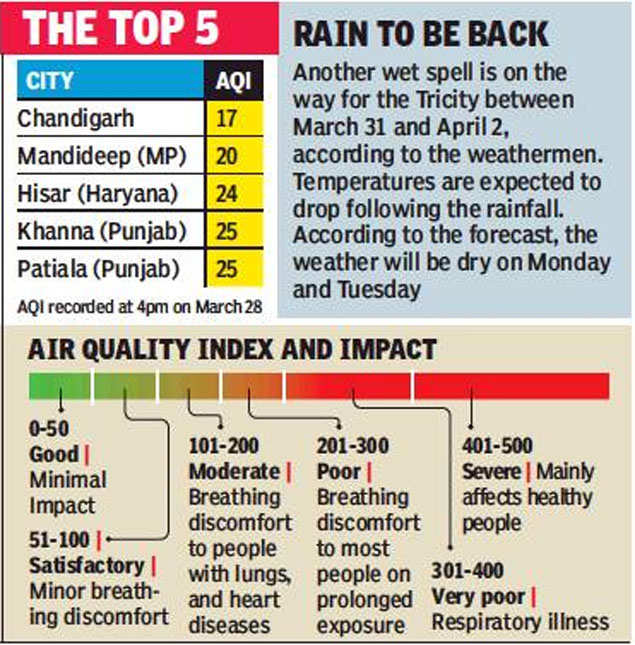
What is Air Quality Index?
- AQI is a mean of pollutants such as particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulphur dioxide (SO2) and carbon monoxide (CO) emissions as a single value.
- The higher the AQI value, the greater the level of air pollution and the greater the health concern.
- AQI is recorded by SAFAR, an organisation that integrates the measurement of air quality with weather forecasts.
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/why-mumbai-colaba-mazagaon-are-witnessing-very-poor-air-quality-7628071/











