



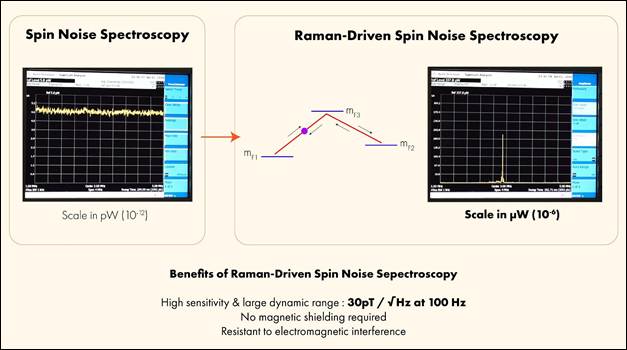
Researchers at Raman Research Institute (RRI) have introduced Raman-Driven Spin Noise Spectroscopy (RDSNS), an innovative all-optical quantum magnetometry method. This technique uses laser light to analyze quantum jitters in Rubidium atoms, allowing precise, non-contact measurement of magnetic fields. RDSNS enhances dynamic range without losing sensitivity, promising faster, more portable, and accurate magnetometers for diverse applications.
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: PIB
Researchers at the Raman Research Institute (RRI) have developed a new technology to measure the invisible forces of magnetism—from inside the human brain to the depths of outer space—without requiring bulky shielding.
A magnetometer is a special device that measures changes in magnetic fields. For example, geologists use magnetometers to find minerals underground because different rocks have different magnetic properties. Doctors also use them in advanced medical imaging to see what's happening inside the human body.
Many powerful magnetometers, known as "Optically Pumped Atomic Magnetometers (OPAMs)" or "Spin Exchange Relaxation Free (SERF) magnetometers," work by observing how light interacts with small atoms.
When the light passes through, a weak magnetic field makes the light "twist" or change its direction of vibration. Scientists call this "polarization rotation."
By precisely measuring how much the light twists, the magnetometers can figure out the strength of the magnetic field.
While current high-tech magnetometers are very sensitive, they face a few big challenges:
It is an innovative method for measuring magnetic fields. Researchers at the Raman Research Institute (RRI) developed this technique.
It is a "quantum" method, uses the fundamental properties of atoms at their smallest level to make its measurements.
How does it work?
Shining Lasers => Researchers shine powerful laser light onto a collection of Rubidium atoms.
Listening to Jitters => The laser light acts like a highly sensitive microphone, picking up on the tiny, random wobbles (spin noise) of the atoms.
Detecting Shifts => When a magnetic field is present, it affects these atomic wobbles. The pattern of the spin noise shifts in predictable ways.
Measuring the Field => By carefully analyzing these subtle shifts in the spin noise using the lasers, the researchers can accurately determine the strength of the magnetic field.
Source:
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Which of the following is a key application of magnetometers? A) Measuring the speed of sound B) Detecting non-magnetic metals at long distances C) Geophysical surveys and aircraft navigation D) Determining the chemical composition of liquids Answer: C Explanation: Magnetometers are widely used in geophysical surveys (e.g., mineral exploration, archaeology, unexploded ordnance detection) and play a crucial role in aircraft navigation systems as digital compasses. |







© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved