



Gujarat has initiated India's first tribal genome sequencing project, involving 2,000 individuals from 17 districts. The project aims to identify common genetic issues in tribal communities, enabling personalized treatments and supporting government health policies like the National Sickle Cell Anemia Elimination Mission. UPSC GS II & III

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: THE HINDU
Gujarat has become the first Indian State to launch a genome sequencing initiative focused exclusively on tribal communities.
It is launched by Gujarat to study the complete genetic code (genome) of 2,000 individuals from tribal communities across 17 districts in the State.
It aims to pinpoint specific genetic problems or risks that are common in these groups.
|
What is the Genome India Project? It is a research initiative, launched in 2020, led by the Bangalore-based Indian Institute of Science's Centre for Brain Research and involves over 20 universities across the country to collect samples, compile data, conduct research, and create an ‘Indian reference genome' grid. It is funded by Department of Biotechnology (DBT) to sequence at least 10,000 Indian genomes in phase 1, with the goal to develop diagnostic indicators for several high-priority diseases and other uncommon and genetic disorders.
The data is stored at the Indian Biological Data Centre (IBDC) in Faridabad; India's first national repository for life science data from publicly funded research . |
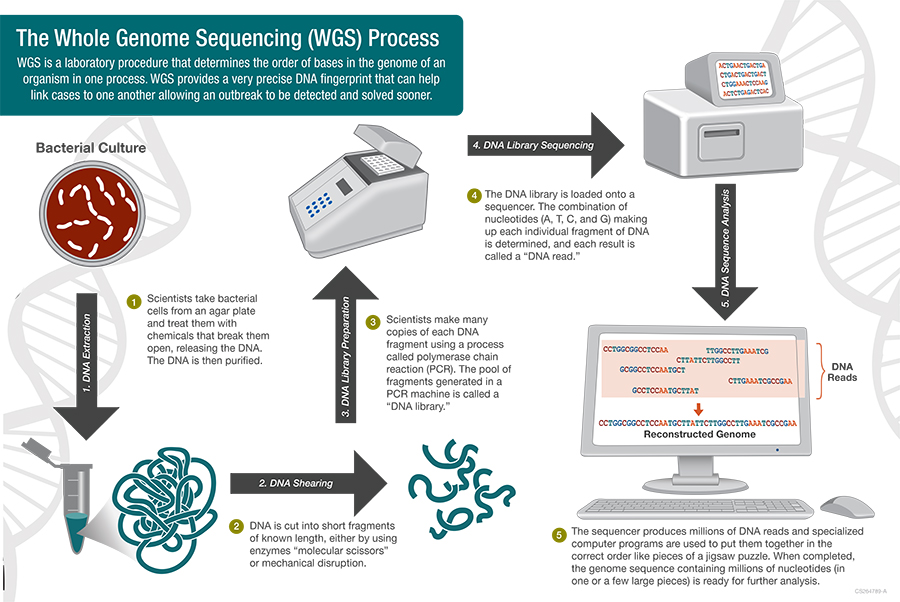
Tribal populations have lived in isolated areas, and they tend to marry within their own communities (endogamy). Over many generations, this can lead to unique genetic differences or a higher prevalence of certain genetic conditions. Understanding these specific genetic variations is key for creating health plans that truly work for them.
Tribal communities experience a higher burden of specific genetic disorders. This project focuses on the early detection and treatment of conditions like:
Understand human genetics better.
Designing new drugs and vaccines that are more effective for specific populations.
Genetic data can shed light on human migration patterns and the historical ancestry of these communities.
|
What is "benefit sharing"? It means that if the research leads to new discoveries, medicines, or commercial products, the communities who contributed their genetic data should also share in the benefits. This prevents exploitation and ensures fairness, as their unique genetic resources made the research possible. |
It directly supports initiatives like the National Sickle Cell Anemia Elimination Mission.
Informed Consent => For tribal communities, who may have different languages or cultural understandings, it is crucial to explain everything clearly and respectfully, ensuring they truly understand before agreeing.
Private Genetic Information => Concerns about keeping the information private and secure to prevent misuse or discrimination.
National Health Mission (NHM) => Improve healthcare access and quality across India, with specific components and funding for tribal areas.
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY) => National health insurance scheme that provides financial protection to vulnerable families, including many from tribal communities.
Tribal Sub-Plan (TSP) / Schedule Tribe Component (STC) => Certain percentage of funds from various ministries are specifically allocated for the development and welfare of Scheduled Tribes, including health.
Research & Data Collection => Organizations like the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) conduct studies on tribal health issues to inform policy.
|
FAQ What is the objective of Gujarat's Tribal Genome Project? The project aims to identify genetic health risks and enable precision healthcare for tribal populations by sequencing 2,000 genomes for early detection and targeted treatment of inherited diseases. Which specific genetic disorders will the project focus on? The initiative will primarily focus on early detection and treatment of genetic disorders such as sickle cell anaemia, thalassaemia, and certain hereditary cancers prevalent in tribal communities. What makes Gujarat's Tribal Genome Project unique in India? Gujarat is the first Indian State to launch a genome sequencing initiative focused exclusively and comprehensively on its tribal communities. |
Must Read Articles:
About India's Genome India Database
Genome India Project Completed
Source: THE HINDU
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. What are the key ethical concerns associated with large-scale genomic data collection under the Genome India Project? How can these be addressed? 150 words |







© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved