Description
GS PAPER III: Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
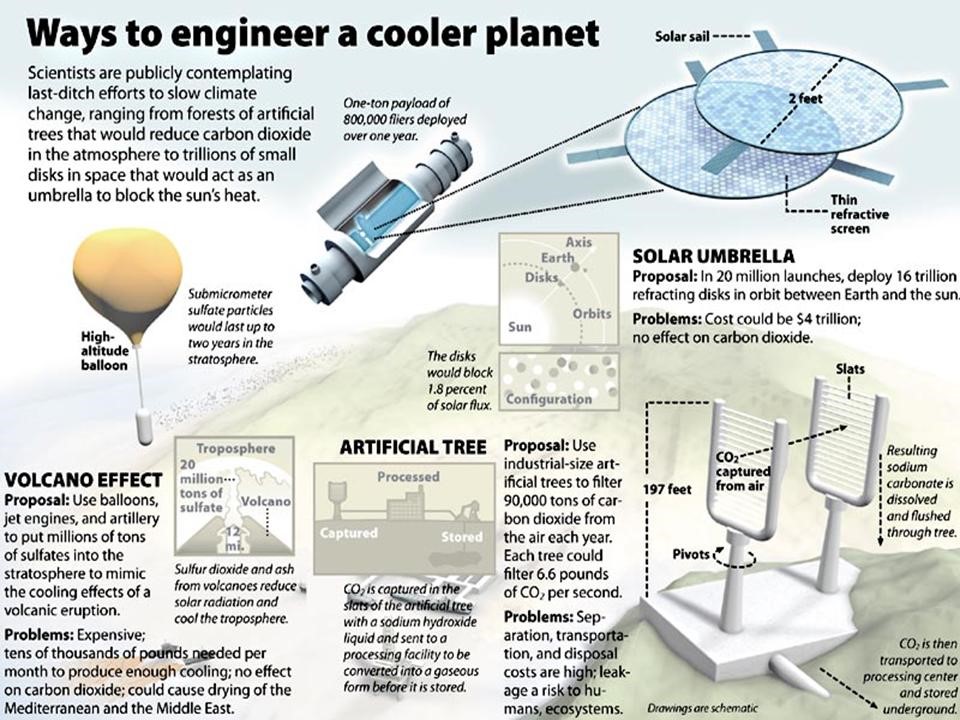
What is geoengineering ?
- Climate engineering or climate intervention, commonly referred to as geoengineering, is the deliberate and large-scale intervention in the Earth's climate system.
- The most prominent subcategories of climate engineering are solar radiation management and carbon dioxide removal.
Why in news?
- Engineers from Purdue University in the US have created the whitest paint.
- This ‘Whitest ever’ paint can reflect 99 per cent of sunlight.
- Buildings coated with this paint may be able to cool them off enough to reduce the need for air conditioning, the researchers have said.
What is the whitest paint?
- The white paint older formulation was made of calcium carbonate, while the new one is made up of barium sulphate, which makes it more white.
- The newer paint is whiter and keeps the surface areas it is painted on cooler than the formulation before this could.
- If this new paint was used to cover a roof area of 1,000 square feet, it may be able to get a cooling power of 10 kilowatts.
- Most ovens use up about 2.3 kilowatts to run for an hour and a 3 ton 12 Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) air conditioner uses up about 3 kilowatts to run for an hour.
- The team has also claimed that this paint may be the closest equivalent to the blackest black paint called “Vantablack” that is able to absorb up to 99.9 per cent of visible light.
How this works?
- Whenever an object is seen by the eye, it is either because of sunlight or the artificial light in the room.
- This light is made up of seven different colours (Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red or VIBGYOR).
- Specifically, light is made up of wavelengths of different colours.
- The colour of any object or thing is determined by the wavelength the molecules are not able to absorb. Whichever wavelength of colour is not absorbed by an object, will be the colour that the eye sees.
What determines which wavelength of light will be reflected and absorbed?
- This is dependent on how electrons are arranged in an atom (the building block of life, an atom is made up of electrons, protons and neutrons.
- In contrast, if an object is black, it is because it has absorbed all the wavelengths and therefore no light is reflected from them.
- This is the reason that darker objects, as a result absorbing all wavelengths tend to heat up faster (during absorption the light energy is converted into heat energy).
So, what makes the paint so white?
- There are two features, one is the paint’s high concentration of a chemical compound called barium sulfate, which is also used to make photo paper and cosmetics white.
- The second feature is different sized particles of this chemical compound, which means different sizes scatter different amounts of light.
- In this way, a varying size of particles of the compound make sure that the paint can scatter more of the light spectrum from the sun.
- This paint can keep surfaces 19 degrees Fahrenheit cooler than their ambient surroundings at night.
- It can also cool surfaces 8 degrees Fahrenheit below their surroundings under strong sunlight during noon hours.
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/white-paint-research-sunlight-weather-7276431/