



Operation Crystal Fortress dismantled a major transnational meth cartel, seizing 328 kg of meth and advancing India’s Drug-Free India goal. It highlights rising synthetic drug threats and shows how multi-agency action, tech tools like NIDAAN, NCORD coordination and demand-reduction drives strengthen India’s anti-narcotics strategy.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: The Hindu
Operation Crystal Fortress, a joint Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) and Delhi Police Special Cell operation, dismantled a transnational methamphetamine cartel, by seizing 328 kg of methamphetamine worth approximately ₹262 crore from a New Delhi residence.
Drug addiction refers to the harmful or hazardous use of psychoactive substances, including alcohol and illicit drugs, which can lead to dependence syndrome.
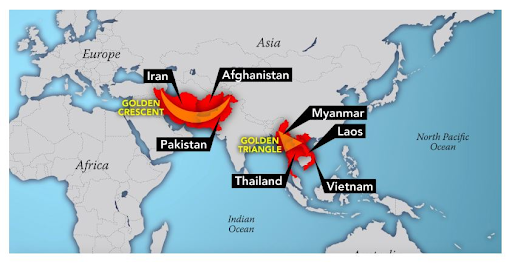
India's geographical location between the "Golden Crescent" (Afghanistan, Iran, Pakistan) and the "Golden Triangle" (Myanmar, Laos, Thailand) makes it vulnerable as both a transit route and an end market for illicit drugs.
Findings of 'Magnitude of Substance Use in India' report (2019) by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) and AIIMS.
|
Substance Category |
Key Statistics (Population aged 10-75) |
Individuals Requiring Help/Treatment |
|
Alcohol |
16 crore people (14.6%) are current users. |
2.9 crore people suffer from alcohol dependence. |
|
Cannabis (Bhang, Ganja, Charas) |
3.1 crore people (2.8%) are users. |
Approximately 72 lakh individuals need help for cannabis use problems. |
|
Opioids (Opium, Heroin, Pharmaceuticals) |
2.26 crore people (2.06%) are users. Heroin is the most common opioid used. |
Around 77 lakh individuals require treatment for opioid use problems. |
|
Inhalants |
Prevalence is higher among children and adolescents (1.17%) than adults. |
An estimated 4.6 lakh children and 18 lakh adults need help. |
|
Injecting Drugs |
Approximately 8.5 lakh people inject drugs (PWID). |
They face high risk of HIV and Hepatitis B & C infections. |
Geographical Hotspots: States like Punjab, Mizoram, Nagaland, and Arunachal Pradesh show a high prevalence of opioid use. Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, and Delhi are hotspots for cannabis use.
Synthetic Drugs: There is a sharp increase in the seizure and use of synthetic drugs like Methamphetamine ('Ice') and Fentanyl due to their high potency and low cost.
Youth Vulnerability: Adolescents and young adults (18-35 years) are the most vulnerable demographic. Early exposure and peer pressure are risk factors.
Injecting Drug Use: A high-risk behaviour concentrated in states like Punjab, Delhi, Mizoram, and Uttar Pradesh, acting as a major vector for blood-borne diseases.
The Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act, 1985: Prohibits the production, sale, purchase, transport, and consumption of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances, except for medical and scientific purposes.
Prevention of Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (PITNDPS) Act, 1988: Provides for preventive detention of persons involved in drug trafficking to disrupt their operations.
Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB): The apex coordinating and drug law enforcement agency. It works to implement the provisions of the NDPS Act and coordinates with national and international agencies.
Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO): Regulates the quality of drugs and cosmetics, and also monitors the misuse of pharmaceutical products.
Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan (NMBA) by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) to create a drug-free India.
National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction (NAPDDR) is a centrally sponsored scheme by MoSJE that provides financial assistance to state governments and NGOs for:
India is a signatory to three key UN conventions on drug control and actively collaborates with international bodies like the UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) and Interpol.
Cross-Border Trafficking: Porous borders with the Golden Crescent and Golden Triangle regions remain a primary challenge.
Synthetic Drugs & Darknet: The rise of new psychoactive substances (NPS) and their sale through the darknet complicates enforcement.
Inadequate Rehabilitation: Gap exists between the number of people needing help and the availability of quality treatment and rehabilitation facilities.
Social Stigma: Stigma prevents individuals and families from seeking timely help, leading to a hidden epidemic.
Inter-Agency Coordination: Ensuring seamless intelligence sharing and operational synergy among various central and state agencies is challenging.
Strengthen Law Enforcement: Enhance surveillance using technology like drones and AI-based analytics to monitor trafficking routes and destroy illicit cultivation. Improve inter-agency coordination through platforms like the NCORD (Narco Coordination Centre) mechanism.
Intensify Prevention & Awareness: Integrate drug abuse education into the school curriculum. Leverage social media to run sustained campaigns targeting youth.
Enhance Health Infrastructure: Treat addiction as a public health issue, not just a crime. Expand access to affordable de-addiction and mental health services, especially in rural areas. Focus on a "Whole Person Recovery" model that includes aftercare and skill development.
Community Participation: Promote a "Jan Andolan" (people's movement) by involving communities, civil society, and religious leaders in prevention and reintegration efforts.
Data-Driven Policy: Conduct regular national surveys on substance use to formulate evidence-based policies and monitor the effectiveness of interventions.
A successful strategy for combating drug problems requires combining strong law enforcement to curb supply with comprehensive prevention, treatment, and rehabilitation for demand reduction, supported by political will and community engagement.
Source: The Hindu
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Operation Crystal Fortress, recently in the news, is targeted the trafficking of which substance: A) Heroin originating from the Golden Crescent B) Cocaine smuggled through maritime routes C) Methamphetamine, a synthetic drug D) Opium cultivated domestically Answer: C Explanation: "Operation Crystal Fortress", is joint operation by the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) and Delhi Police's Special Cell dismantled a transnational cartel and resulted in the seizure of approximately 328-329 kg of high-quality methamphetamine in Delhi. |
Operation Crystal Fortress was a successful, intelligence-led joint operation by the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) and Delhi Police Special Cell. It dismantled a major transnational drug cartel, leading to the seizure of 328 kg of methamphetamine in New Delhi.
The National Integrated Database on Arrested Narco-offenders (NIDAAN) is a one-stop solution for all narcotics offenders' data. It helps law enforcement agencies connect cases, identify networks, and track the history of individuals involved in the drug trade.
The NMBA is a campaign launched by the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment in vulnerable districts across India. It focuses on demand reduction through community-outreach programs involving awareness generation, prevention, and rehabilitation of drug users.






© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved