Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
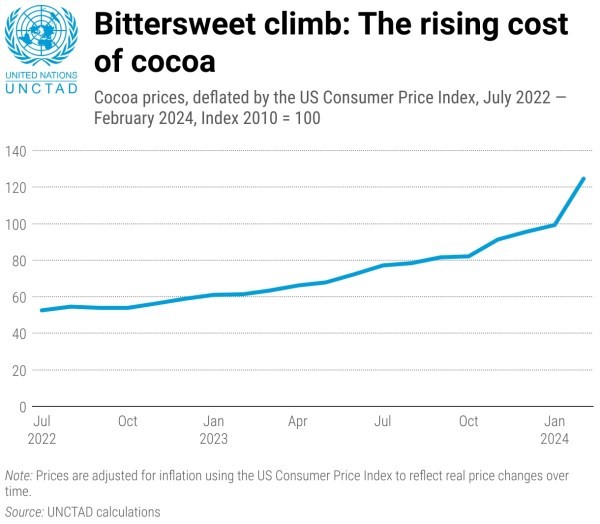
- Cocoa bean prices, crucial for chocolate production, surged to a record $12,000 per ton in April, quadrupling last year's rate.
Chocolate Industry
- The chocolate industry is currently facing a significant crisis as the prices of cocoa beans, its most crucial raw material, have soared to unprecedented levels.
- Due to the exorbitant prices of cocoa beans, cocoa processors, who transform these beans into butter and liquor for chocolate production, have been compelled to curtail their operations.
Factors Behind Rising Cocoa Prices:
El Niño and Climate Change:
- The emergence of El Niño, a weather phenomenon characterized by abnormal warming of Pacific Ocean waters, has triggered heavier rainfall in West Africa, where a substantial portion of the world's cocoa beans are cultivated.
- This increased rainfall has created favorable conditions for the spread of black pod disease, a fungal infection that causes cocoa pods to rot on the trees, significantly diminishing yields.
- Climate change exacerbates the situation by causing erratic rainfall patterns and extreme weather events, making cocoa trees more susceptible to diseases and environmental stressors.
- Experts predict that the effects of climate change could render some cocoa-growing regions unsuitable for cultivation in the future.
Low Income of Cocoa Farmers:
- Most cocoa beans are sourced from West African countries, where cocoa farmers struggle to earn a liveable income, often falling below the poverty line.
- The dire financial situation of cocoa farmers hampers their ability to invest in land, leading to decreased productivity and resilience against climate change.
- To make ends meet, some farmers resort to employing slave and child labour or selling their land to illegal miners, further exacerbating social and environmental issues.
Impact on Cocoa Farmers:
Ghanaian Farmers' Plight:
- In Ghana, a significant cocoa-producing country, up to 90% of farmers cannot afford basic necessities, highlighting the severity of the situation.
- Over recent years, farmers' incomes have seen a significant decline, with women particularly affected by the downturn.
- The lack of financial resources prevents farmers from investing in land improvement or adopting sustainable agricultural practices, perpetuating a cycle of poverty and vulnerability.
Corporate Profits vs. Farmer Exploitation:
Profit Disparity:
- Despite the soaring cocoa prices and subsequent chocolate sales, major chocolate companies such as Lindt, Mondelēz, Nestlé, and Hershey’s continue to generate substantial profits.
- However, these companies have not taken adequate measures to address the plight of cocoa farmers or improve their living standards, raising ethical concerns about their business practices.
Exploitation Concerns:
- The focus on maintaining low consumer prices has historically led to the exploitation of cocoa farmers, who bear the brunt of the industry's cost-cutting measures.
- Research suggests that the chocolate industry's profitability is sustained by the underpaid labor of West African farmers, particularly children, highlighting systemic issues of exploitation and injustice.
Moving Forward:
- Urgent action is needed to address the root causes of cocoa bean scarcity and farmer exploitation within the chocolate supply chain.
- Without meaningful intervention, the industry risks perpetuating social and environmental injustices, leading to further price hikes and human rights abuses.
Cocoa Consumption in India
Cocoa Cultivation in India:
- Geographical Distribution:
- Primarily grown as an intercrop in Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Kerala.
- Requires about 40-50% shade for optimal growth.
- Majority of cocoa cultivated in coconut groves, followed by arecanut, oil palm, and rubber plantations.
- Andhra Pradesh's Cocoa Fields:
- Concentrated in west Godavari, east Godavari, and Krishna districts.
Cocoa Production in India:
Area and Production
- In India Cocoa is being cultivated in the States of Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu in an area of 1,03,376 ha with total production of 27,072 MT.
- Andhra Pradesh ranks first in area with 39,714 ha and production of 10,903 MT.
- The highest productivity is also in Andhra Pradesh which is 950 kg/ha.
- The average productivity of cocoa in Indian is 669 Kg/ha.
Export
- Cocoa is an export oriented commodity. In India, at present there are 10 multinational companies engaged in the field of cocoa industry and exports products like Beans, chocolates, cocoa butter, cocoa powder and cocoa based products to other countries. India earns foreign exchange worth Rs. 1108cores through exports of cocoa bean and its products.
Import
- The demand of chocolate industry and confectionaries in India is 50,000 MT of dry bean per annum.
- The current domestic production of cocoa beans is not sufficient to meet the demand of the industry.
- Hence India is importing a lion share of its requirement from other cocoa growing countries worth Rs.2021crores.
Chocolate Consumption in India:
- According to the International Cocoa Organisation, India’s per capita consumption of chocolate is between 100 gm and 200 gm a year, much lower than Japan, which consumes around 2 kg of chocolate per person per year, and even Europe, where the consumption lies between 5 kg and 10 kg a year.

Government Support and Challenges in Cocoa Cultivation
Perceived Lack of Government Support:
- Despite high demand for cocoa beans, farmers express frustration over the government's lack of encouragement for cocoa cultivation.
- The absence of guidance from research institutes or governmental initiatives, with farming practices relying solely on peer-to-peer knowledge sharing.
Progressive Initiatives in Andhra Pradesh:
- Andhra Pradesh emerges as the leading cocoa-producing state in India.
- Farmers in districts like west Godavari exhibit progressiveness in adopting cocoa cultivation without significant government intervention.
- The National Horticulture Mission provides a subsidy of Rs 20,000 per hectare to cocoa farmers in Andhra Pradesh for the first three years since 2005, fostering growth in cocoa cultivation.
Challenges in Implementation:
- Directorate of Cashewnut and Cocoa Development (DCCD), acknowledges challenges in meeting cocoa cultivation targets.
- Despite the mission's objective of adding 20,000 hectares annually, only a quarter of this target is achieved due to resource constraints and competing priorities within the horticulture department.
Historical Efforts and Partnerships:
- Cadbury's historical efforts in the 1960s saw experimental cocoa planting in Kerala as part of promoting the crop.
- Cadbury continues to promote cocoa cultivation through its 'Cocoa Life' initiative, collaborating with Kerala Agricultural University and Tamil Nadu Agricultural University for research.
- Seedling distribution at subsidized rates and research partnerships with institutions like the Central Plantation Crops Research Institute in Kasargod, Kerala, contribute to cocoa cultivation advancements.
Cocoa Cultivation in India:
Geographical Advantage:
- South India's proximity to the Equator provides ideal climatic conditions for cocoa cultivation.
- Significant potential for cocoa planting exists in irrigated coconut, arecanut, and oil palm areas, with only a fraction of these areas currently utilized for cocoa cultivation.
Challenges Hindering Growth:
- Lack of awareness about cocoa cultivation among farmers.
- Weather-related uncertainties and competition from other crops pose challenges.
- Arecanut farmers in coastal Karnataka express concerns about potential yield declines if shifting to cocoa cultivation.
Market Dynamics and Price Trends:
Local Production and Demand:
- Mondelez India sources a third of its cocoa locally, highlighting the potential for domestic production.
- Local industry demand and a 30% import duty on cocoa products may shield against drastic price falls.
Price Volatility and Future Outlook:
- Recent years witnessed stability in cocoa bean prices in India, around Rs 200/kg.
- Predictions of a surplus in global cocoa production, particularly in the Ivory Coast, leading to a drop in cocoa futures prices.
- Despite price fluctuations, local demand and government support could stabilize prices for Indian cocoa farmers.
Untapped Potential and Expansion Efforts:
Quality and Scope:
- Indian cocoa beans are recognized for their quality, comparable to the best globally.
- While Kerala may be saturated, states like Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka have yet to fully exploit their cocoa-growing potential.
Exploration Beyond South India:
- Introduction of cocoa cultivation in regions like Assam and Nagaland to diversify cocoa production.
- Despite being an in-demand intercrop with relatively stable prices, cocoa cultivation in India still awaits broader recognition and support.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Evaluate the current state of India's chocolate industry, focusing on production, consumption patterns, and socio-economic implications. Propose strategies to enhance the global competitiveness of India's chocolate industry.
|