



Antimatter is a type of matter with opposite electric charge and reversed quantum numbers. It is produced naturally in high-energy astrophysical phenomena and particle accelerators. However, it is extremely rare in the observable universe, with most of the cosmos consisting of matter. Antimatter could be used in medical imaging, propulsion, weapons, and future energy sources.
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: THE HINDU
Scientists at the Large Hadron Collider (CERN) have discovered that the laws of physics treat matter and antimatter differently in baryons, the building blocks of the visible universe.
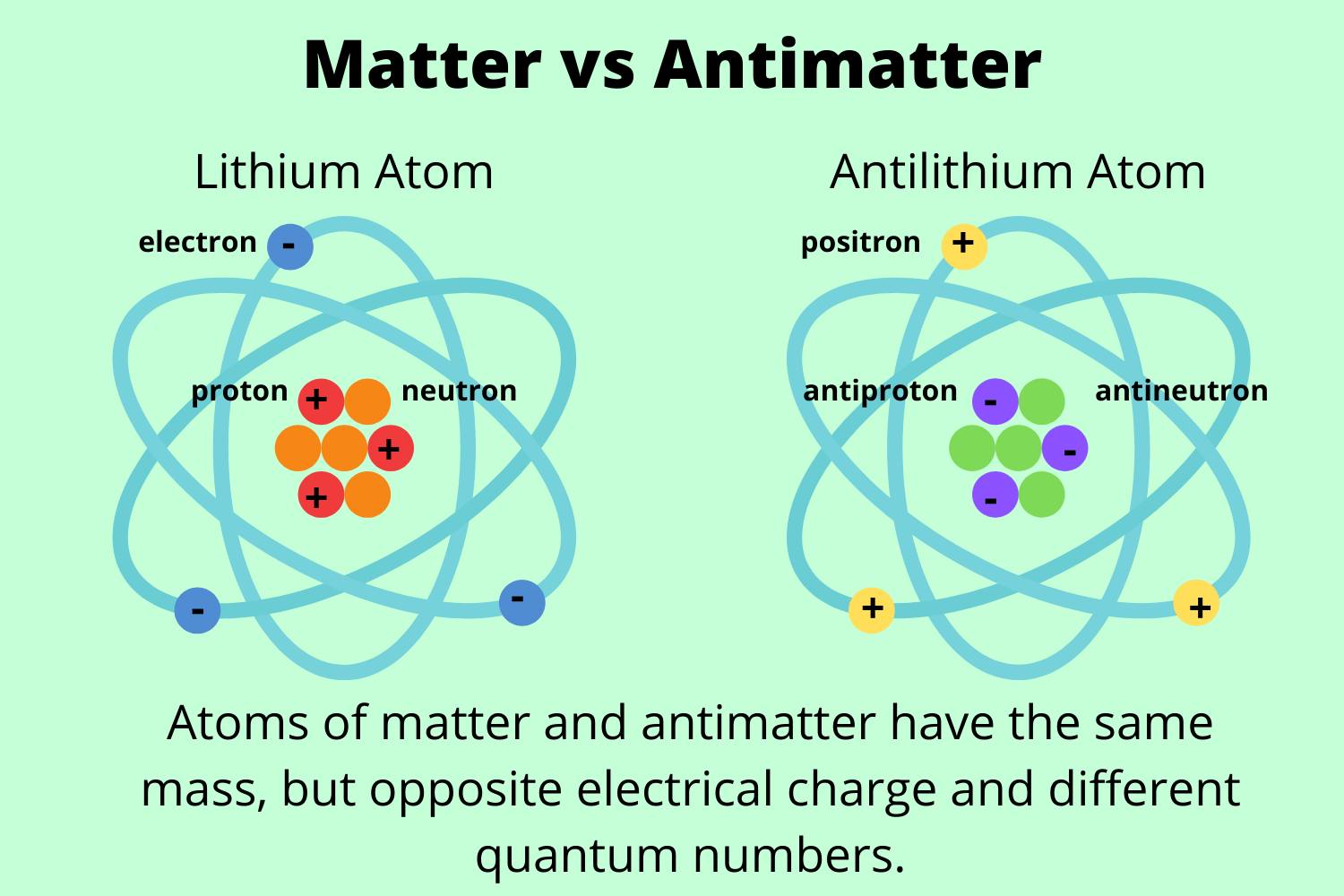
Antimatter consists of antiparticles, which are nearly identical to their corresponding matter particles but carry an opposite electric charge and other reversed quantum numbers. For example, the antiparticle of an electron (which has a negative charge) is a positron (a positively charged electron).
 What Are the Key Properties of Antimatter?
What Are the Key Properties of Antimatter?Opposite Charge => Opposite electric charge of their matter counterparts.
Identical Mass => Exact same mass as its corresponding particle.
Annihilation => When a particle meets its antiparticle, they mutually annihilate, converting their entire mass into pure energy in the form of photons (light particles). This process holds to Einstein's famous equation, E=mc².
Gravitational Interaction => Scientists generally assume that antimatter interacts with gravity in the same way as matter—it "falls down." However, direct experimental verification has been challenging.
Production => Naturally in some high-energy astrophysical phenomena, like lightning strikes, cosmic rays interacting with Earth's atmosphere, and certain radioactive decays.
Scientists can create and study antimatter in laboratories, however, it is extremely rare in the observable universe. Most of the cosmos, including stars, planets, and galaxies, consists almost entirely of matter.
Cosmic Rays => A tiny fraction of cosmic rays are antiprotons or positrons, likely formed in high-energy processes in distant astrophysical objects.
Antimatter Galaxies? => No conclusive evidence of large regions or galaxies made of antimatter.
Big Bang Prediction => Universe's early moments have produced matter and antimatter in nearly equal amounts.
Annihilation => If matter and antimatter appeared in perfect symmetry, they would have completely annihilated each other as the universe cooled, leaving behind a universe full of only radiation, with no stars, planets, or life.
Medical Imaging => Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans use positrons (antimatter electrons) for diagnostic imaging.
Propulsion => A tiny amount of antimatter could provide enormous thrust, potentially enabling faster interstellar travel.
Weapons => Due to its high energy density, antimatter has been theoretically considered for weapons.
Future Energy Sources
Advanced Propulsion Systems for spacecraft
Cancer Treatment Research
|
FAQ What is antimatter? Antimatter is composed of antiparticles that have the same mass as their corresponding matter particles but possess opposite fundamental charges and properties. How is antimatter created naturally in the universe? Antimatter is naturally produced in high-energy cosmic events like cosmic ray interactions with the atmosphere, during radioactive beta-plus decay, and briefly during the Big Bang. Can antimatter be used as a energy source? While antimatter-matter annihilation releases immense energy, its production and containment are currently extremely challenging and energy-intensive, making practical energy generation speculative for now. |
Must Read Articles:
Einstein's General Relativity and Antimatter
Source: THE HINDU
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Which of the following techniques utilizes antimatter? A) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) B) Computed Tomography (CT) scan C) Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scan D) X-ray imaging Answer: C Explanation: PET scans use antimatter to emit positrons, which annihilate with body electrons, producing gamma rays for imaging. |







© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved