Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: www.hindustantimes.com
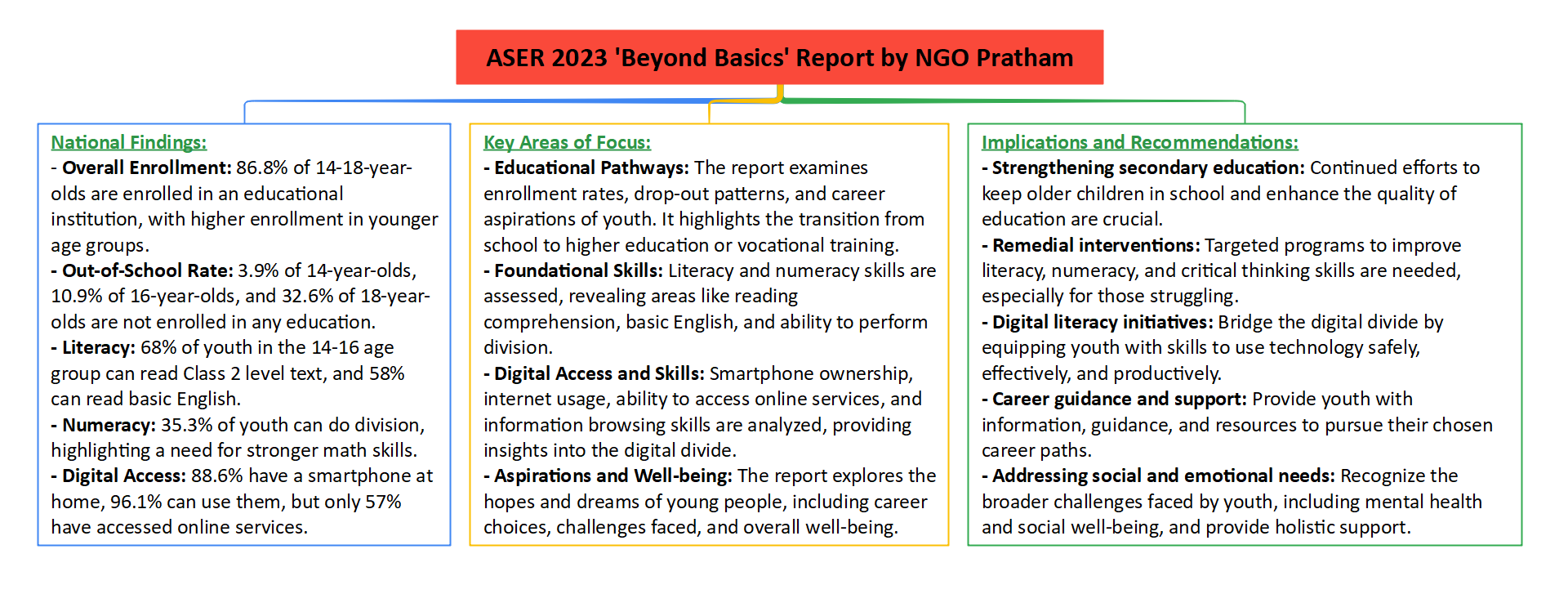
Context: The Annual Status of Education Report-2023 (ASER) 'Beyond Basics' conducted by the non-profit organization Pratham provides insights into the educational status and digital access of 14 to 18-year-old youth.
Key Findings of the Report
- 42% of children in the age group of 14-18 in rural India cannot read easy sentences in English.
- More than half of them struggle with simple division problems.
Survey Coverage
- The ASER 2023 survey covered 28 districts across 26 states, reaching a total of 34,745 youths in the age group 14-18.
- One rural district was surveyed in each major state, except for Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh, where two rural districts were surveyed.
- The survey explores four key domains: Activity, Ability, Awareness and Digital Aptitude, and Aspirations.
Literacy and Numeracy Skills
- About 25% of children in this age group cannot read a Std II level text fluently in their regional language.
- Only 43.3% of 14-18-year-olds can correctly solve division problems (3-digit by 1-digit), a skill usually expected in Std III/IV.
English Reading Skills by Gender
- Across enrollment categories, females (76%) perform better than males (70.9%) in reading a Std II level text in their regional language. However, males outperform females in arithmetic and English reading.

Aspirations and Education
- Over 60% of young people in the 14-18 age group aspire to continue studying to the undergraduate level or higher.
- More than 86.8% of youngsters in this age group are enrolled in educational institutions.
- In Std XI or higher, more than half are enrolled in the Arts/Humanities stream (55.7%), followed by STEM (31.7%) and Commerce (9.4%).
Gendered Work Aspirations
- Work aspirations are highly gendered. Boys often aspire to join the army (13.8%) or police (13.6%), while girls commonly aspire to become teachers (16%) or doctors (14.8%).
Vocational Training
- Only 5.6% of surveyed youth report taking vocational training or other related courses currently.
Conclusion
- The ASER-2023 report paints a concerning picture of English reading proficiency, literacy, and numeracy skills among children in rural India, while also highlighting aspirations, enrollment patterns, and the gendered nature of work aspirations. The findings emphasize the need for targeted interventions to improve foundational skills and bridge educational gaps in rural areas.
Must Read Articles:
ASER REPORT: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/aser-report-32
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. How has the education system in India evolved over the years, and what are the current challenges and potential solutions to ensure equitable access to quality education across different regions and socio-economic backgrounds?
|










