



Bharat Taxi, India’s first cooperative ride-hailing platform, launches as a swadeshi alternative to Uber and Ola. Built on platform cooperativism, it makes drivers owner-members with zero commission and profit sharing. Backed by Amul and IFFCO, it promotes a fairer gig economy aligned with social security reforms.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: NEWSONAIR
The Government of India has launched Bharat Taxi, as an alternative to private cab aggregators like Uber and Ola.
It is India’s first national-level cooperative ride-hailing platform.
It is a government-backed initiative designed to provide a fair, transparent alternative to private aggregators like Uber and Rapido.
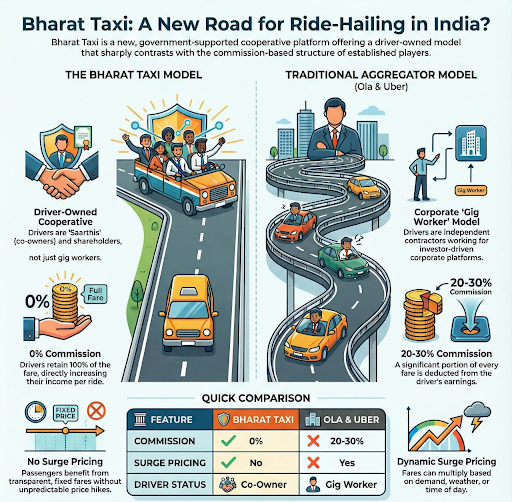
Ownership Structure: It is operated by the Sahakar Taxi Cooperative Limited, a multi-state cooperative where drivers are shareholders and co-owners.
Zero-Commission Model: Drivers retain 100% of the fare, avoiding the high commission fees charged by private platforms.
Pricing: The platform eliminates surge pricing, offering transparent, fixed fare structures to improve passenger reliability.
Government Support: Promoted by the Ministry of Cooperation and developed with the National e-Governance Division (NeGD).
The conventional gig economy model, dominated by private platforms like Uber and Ola, has faced criticism for creating poor working conditions. A cooperative model addresses these core issues:
Technological Competition: Building a strong, user-friendly, and efficient app to compete with sophisticated, AI-driven global rivals is a major hurdle.
Customer and Driver Acquisition: Attracting both customers and drivers away from existing platforms requires aggressive marketing, consistent service quality, and compelling incentives.
Scaling Operations: Expanding across multiple cities while upholding the democratic principles of a cooperative model will be operationally complex.
Navigating Regulations: Platform must navigate diverse state-level transport regulations and licensing requirements.
Bharat Taxi aims to create a fairer, worker-centric gig economy in India, however, its success depends on strong technology, effective governance, and government backing.
If successful, the Bharat Taxi model could serve as a template for other sectors, advancing the goal of an inclusive and prosperous digital India.
Source: NEWSONAIR
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. With reference to 'Bharat Taxi', consider the following statements: 1. It is India's first national-level private ride-hailing aggregator. 2. It operates on a zero-commission, driver-owned cooperative model. 3. It is primarily funded by foreign venture capital to compete with Uber and Ola. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 3 only (b) 2 only (c) 2 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Answer: B Explanation: Statement 1 is incorrect: Bharat Taxi is India's first national-level cooperative-driven ride-hailing initiative, not a private one. It is backed by the Union Ministry of Cooperation and various cooperative bodies. Statement 2 is correct: It operates on a zero-commission, driver-owned cooperative model where drivers become co-owners and shareholders, retaining a greater share of their earnings. Statement 3 is incorrect: Bharat Taxi is not funded by foreign venture capital. It operates as an independent service provider and is aligned with the government's goal to support the cooperative sector. |
Bharat Taxi is India's first national-level, cooperative-based cab service. It functions as a "Swadeshi" alternative to private aggregators like Uber and Ola, where the drivers are also the owners and members of the cooperative.
The primary difference is its business model. Unlike Uber and Ola which are profit-driven corporations that charge a commission (20-30%) from drivers, Bharat Taxi is a driver-owned cooperative. It plans to operate on a zero-commission basis initially, with profits being distributed among the driver-members.
Platform Cooperativism is a model that integrates the traditional cooperative business structure (democratic member ownership and control) with the technology of the digital platform economy. It aims to create fairer and more equitable online platforms for workers.






© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved