Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
An incident involving military activity between Taiwan and China in the Taiwan Strait.
Details
- Taiwan detected 11 Chinese military aircraft and 10 naval ships breaching the sensitive median line of the Taiwan Strait.
- The breach occurred between 6 a.m. on Monday (Aug. 28) and 6 a.m. on Tuesday (Aug. 29).
- One Harbin BZK-005 drone breached the median line in Taiwan's Air Defence Identification Zone (ADIZ) in the northeastern sector.
- The drone circled Taiwan and crossed the median line again in the southwest corner of the ADIZ, heading back towards China.
- Two Chengdu J-10 fighter aircraft also entered the area's southwest corner.
Taiwan's Response
- Taiwan scrambled its aircraft, naval ships, and land-based missiles to track Chinese military activity.
- The response was aimed at monitoring and countering the PLA (People's Liberation Army) activity near Taiwan.

Increased Chinese Military Activity
- Beijing had dispatched 362 military planes and 194 naval ships on operations near Taiwan earlier in the month.
- In March alone, China sent 325 military aircraft and 101 naval vessels around Taiwan.
- China has been increasingly using grey zone tactics, involving routine aircraft entry into Taiwan's ADIZ.
Grey Zone Tactics
- Grey zone tactics involve efforts to achieve security objectives without resorting to direct and substantial use of force.
- These tactics fall beyond steady-state deterrence and assurance, seeking to achieve objectives through unconventional means.
Background
- China has been engaging in heightened military activity near Taiwan since September 2020.
- Taiwan responds to breaches of its airspace and ADIZ with defensive measures and tracking.
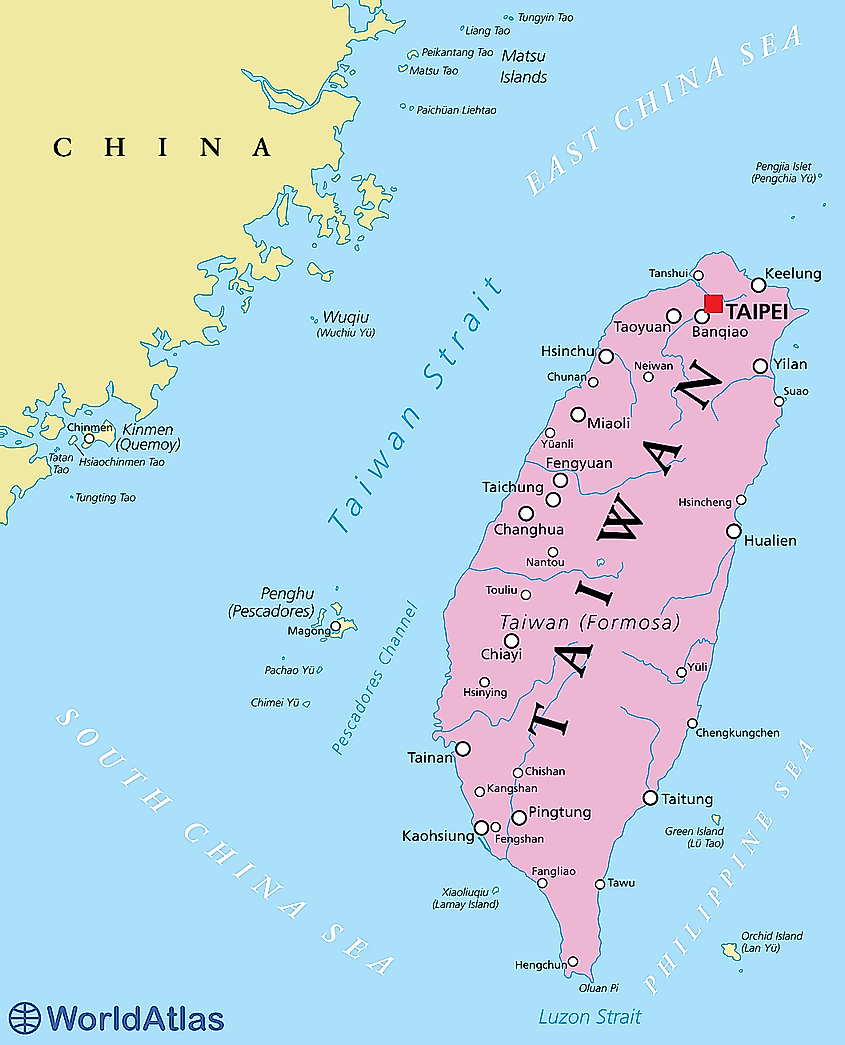
About Taiwan Strait
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
- The Taiwan Strait is a narrow body of water located between the island of Taiwan and the southeastern coast of China.
- It has immense geopolitical significance due to its role in shaping the relationships and tensions between Taiwan, China, and the broader international community.
Geographical Location and Dimensions
- The Taiwan Strait stretches approximately 180 kilometers (112 miles) in width at its widest point and narrows down to about 130 kilometers (81 miles) at its narrowest point.
- It separates the island of Taiwan from the Chinese mainland's Fujian Province.
Historical Context
- The strait's history dates back centuries and has been a vital maritime route for trade, cultural exchanges, and military activities.
- Throughout history, control over the Taiwan Strait has been a point of contention between different dynasties and empires.
Modern Geopolitical Tensions
- The Taiwan Strait is a focal point of tension between the People's Republic of China (PRC) and the Republic of China (ROC, commonly referred to as Taiwan).
- The PRC claims Taiwan as a part of its territory and seeks reunification under the "One China" policy.
- The ROC maintains its own government, military, and economy, considering itself a sovereign state.
International Implications
- The Taiwan Strait has garnered global attention due to its potential to trigger a significant conflict with far-reaching consequences.
- The United States, in accordance with the Taiwan Relations Act, provides defensive weaponry and support to Taiwan, signaling its commitment to the island's security.
Cross-Strait Relations
- Cross-Strait relations refer to interactions between the PRC and ROC.
- Economic and cultural exchanges have increased over the years, but political tensions persist.
Peaceful Resolution Efforts
- International organizations and countries advocate for peaceful resolution of the Taiwan issue.
- Diplomatic efforts aim to prevent conflicts and encourage dialogue between the parties involved.
Impact on Regional Stability
- The stability of the Taiwan Strait has direct implications for regional stability in East Asia.
- Neighboring countries closely monitor the situation and adapt their policies accordingly.
Economic Significance
- The Taiwan Strait facilitates maritime trade routes for both China and Taiwan, contributing to their economies.
- Ports along the strait are vital hubs for shipping and commerce.
Global Trade and Shipping Routes
- The Taiwan Strait is part of crucial international shipping routes that connect the Pacific Ocean to the South China Sea.
Tourism and Cultural Exchanges
- Both sides of the strait promote tourism and cultural exchanges, allowing people to connect and learn about each other's societies.
Environmental Concerns
- Environmental challenges, such as pollution and maritime accidents, can affect the strait due to heavy shipping and naval activities.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q) Discuss the geopolitical significance of the Taiwan Strait in shaping East Asian dynamics and its implications on regional stability and international relations. (150 words)
|

https://theprint.in/world/taiwan-retaliates-as-chinese-warplanes-cross-straits-median-line/1737443/











