Description
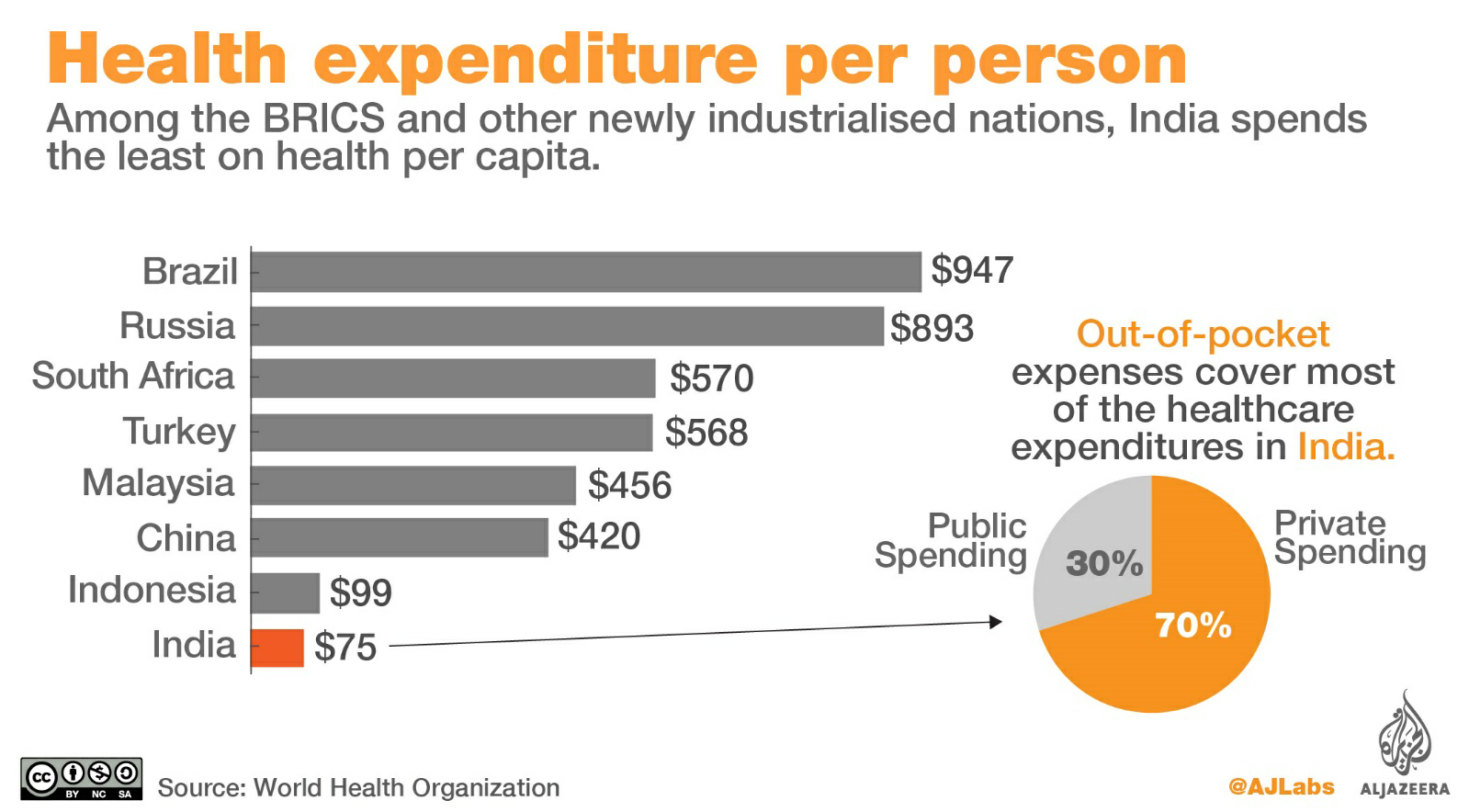
Figure 3: No Copyright Infringement Intended
Context:
- In order to create a common rate structure for hospitals, India's Insurance Regulatory Development Authority (IRDAI) must either propose its own regulatory agency to the medical sector or allow hospital regulation.
- The inflation rate for hospitalization is currently around 10- 15%, and it was found that the rates are changing regularly.
Important point About (problems related to the hospital's current fee structure):
- Different tariffs: Hospitals change rates on a regular basis. There is no agency that regulates pricing and classification. When Covid struck the country last year, patients were overcharged by several hospitals.
- Health insurance premium: If the insurance company keeps paying at the hospital's request, the health insurance business will not be successful in the long run. The industry has already recorded a large number of bills.
- Individual hospital integration process: Today, healthcare systems and private insurers have separate hospital integration processes that replicate different activities and contribute to inefficiencies and duplications.
- No infrastructure to regulate hospitals: IRDAI currently does not have the infrastructure to regulate hospitals. Hospital regulation is a difficult task for IRDAI, as medical care is a government The Indian Insurance Regulatory Development Bureau (IRDAI) is a legal entity established under the Parliamentary Law.
Suggestions of the Panel:
- Even with rising penetration, general and medical inflation must be taken into account, and medical inflation far exceeds CPI (Consumer Price Index) inflation, so a correction cycle is needed from a price perspective.
- IRDAI has proposed a harmonization of its own common hospital registration, inclusion process, hospital classification, and packaging costs to facilitate standardization and effective use of medical infrastructure under insurance programs.
- It is advisable to have a common integrated portal that can be used by all systems / insurers with standardized integration standards (and) it is very difficult to focus specifically on standard safety and quality parameters.
Need to regulate Health Sector:
- Healthcare has become one of India's largest sectors in terms of sales and employment.
- Population growth, income growth, infrastructure growth, heightened awareness, insurance policy, and the rise of India as a hub for medical tourism and clinical trials are contributing to the development of India's medical sector.
- As the demand in this area grows, it becomes important to provide modern medical facilities.
- Government-funded health insurance allows the poor in India to receive timely care without the burden of paying for themselves.
Importance of health insurance:
- This is a mechanism that pools India's high capital expenditures (OOPE) to provide better financial protection from health shocks.
- Health insurance prepayment has proven to be an important tool for pooling risk and protecting against catastrophic (and often poor) costs from health shocks.
- In addition, prepaid pool funds can improve medical
- The state of life is unevenly distributed: Since independence, people's life expectancy has increased from 35 to 65 years. However, living conditions are unevenly distributed in different parts of the country. India's health problems remain a major concern.
- Low government spending: The low government health costs limit the capacity and quality of public sector health services.
- A considerable population is overlooked: At least 30% or 40 million people do not have financial protection for their health.










