



India won its seventh unopposed election to the UN Human Rights Council for 2026–2028, reaffirming its commitment to multilateralism and balanced dialogue. It vows to uphold all human rights, including the Right to Development, and act as a bridge-builder and strong voice for the Global South.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: NEWSONAIR
India re-elected unanimously to the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) for 2026-2028, its seventh term.
The UNHRC is an inter-governmental body within the United Nations framework dedicated to the global promotion and protection of human rights.
Formation: Established by the UN General Assembly (UNGA) in 2006, it succeeded the UN Commission on Human Rights, which had faced criticism for its politicization.
Mission: It addresses human rights violations, offers recommendations, and facilitates dialogue on thematic and country-specific human rights issues.
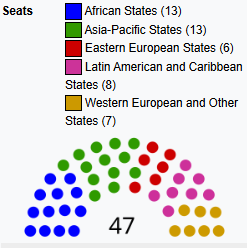
Structure
Shaping Global Human Rights
India gains a crucial platform to influence international human rights standards, ensuring alignment with its core values of democracy, pluralism, and justice.
Championing the Global South
Membership allows India to advocate for the interests of developing nations, promoting a balanced, cooperative, and non-intrusive approach to human rights that respects national sovereignty.
Countering Biased Narratives
A seat on the Council empowers India to directly address and challenge critiques of its human rights record that it perceives as biased or politically motivated, whether from other states or international NGOs.
Showcasing Indian Democratic Model
Opportunity for India to present its unique position as a large, diverse, and developing democracy that effectively upholds fundamental freedoms and democratic principles amidst complex societal and economic challenges.
The UN Human Rights Council is crucial for human rights. India's seventh term, starting in 2026, is a key opportunity to strengthen the Council, advocate for reforms reducing politicization, and foster a cooperative, effective, and context-sensitive approach.
Source: NEWSONAIR
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. The election of members to the UN Human Rights Council requires: A) A simple majority vote in the UN General Assembly. B) A two-thirds majority vote of the members present and voting in the UN General Assembly. C) An absolute majority vote in the UN General Assembly. D) Unanimous consent from the regional group, followed by ratification by the Security Council. Answer: C Explanation: Members of the UNHRC are elected directly and individually by a secret ballot by the majority of the members of the UN General Assembly. A candidate needs to secure an absolute majority, which is a minimum of 97 votes, to be elected. |
The UN Human Rights Council is an intergovernmental body within the United Nations system responsible for strengthening the promotion and protection of human rights around the globe. It is based in Geneva, Switzerland.
The Council is composed of 47 Member States elected for staggered three-year terms by an absolute majority vote in the UN General Assembly. This means a candidate must receive at least 97 votes from the 193 UN members.
The UPR is a unique mechanism of the Council that periodically reviews the human rights records of all 193 UN Member States. It is a state-led process where peers assess and make recommendations to the country under review.






© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved