Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Bharat Biotech's intranasal Covid vaccine -- BBV154 has been approved by the Union Health Ministry as a booster dose for those above 18 years of age. The approval for the vaccine comes amid a spurt in Covid cases in China and some other countries.
Details
- The needle-free vaccine will be available at private centres. It will be introduced on the Co-WIN platform soon.
- Being needless, the intranasal vaccine will be India’s first such booster dose. It can be administered to those above 18 years.
- The advantage of this vaccine is that it will provide a very broad spectrum of immunity and also local immunity, which is in the nasal passage itself, lowering the rate of infection in people who take this. The rate of transmission will also come down. In that sense, the nasal vaccine could be more effective than the others.
What is an Intranasal Vaccine?
- Vaccines are usually given through different routes, with the most common being injectable shots delivered into the muscles (intramuscular) or the tissue just between the skin and the muscles (subcutaneous).
- Other routes of delivery, especially in some vaccines for infants, include administering the liquid solution orally instead of injecting. In the intranasal route, the vaccine is sprayed into the nostrils and inhaled.
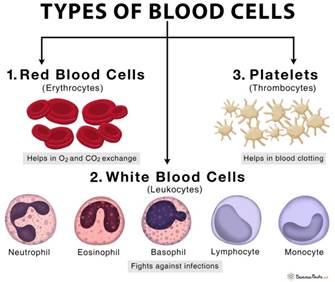
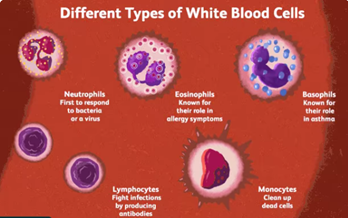
Blood Cells and Immunity
- The cells in our body deploy powerful countermeasures against viral infection. Antibodies, made by types of blood cells called B cells, are molecules that recognise and attach to parts of the virus. Other cells called T cells seek out and destroy virus-infected cells, removing the source of infection.
Working of vaccines in general
- Generally, vaccines trigger a response in the blood. B cells, churn out antibodies — including a particularly potent disease-fighter called IgG — to roam the body in search of the virus.
- T cells, either help B cells produce antibodies or seek out and destroy the infected cells.
.jpg)
Intra-Nasal Vaccine
- Vaccines that are injected through the nose or mouth tap into another set of immune cells that hang around mucosal tissues.
- The B cells that reside theremake another type of antibody, called IgA, that plays a large role in destroying the airway pathogens.
- In addition to this, the T cells that are residing nearby will be able to memorise the pathogens that it encountered and will lifelong scout the areas where these were first encountered.
- The effectiveness of an intranasal vaccine was first seen in the 1960s when polio doses replaced its injected predecessor.
- It targeted the body’s immune response in the gut, where the virus thrives and many people who took the oral vaccine seemed to cancel out the infections even before they felt symptoms.
Decoding Blood Cells
.jpg)
https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/bharat-biotechs-intranasal-covid-vaccine-approved-by-govt-to-be-available-on-co-win-soon/article66296120.ece