Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- In Union Budget 2023-24, Union Finance Minister Mrs Nirmala Sitharaman announced the revamping of Credit Guarantee Scheme for Micro & Small Enterprises with effect from 01.04.2023.
- Step taken: An infusion of Rs 9,000 crore to the corpus to enable additional collateral-free guaranteed credit of Rs. 2 lakh crore and the reduction in the cost of the credit by about 1 per cent.
Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE)
- Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE) is jointly set up by Ministry of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSME), Government of India and Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) in Aug’2000 to catalyse flow of institutional credit to Micro & Small Enterprises (MSEs).
- Credit Guarantee Scheme (CGS) was launched to
- strengthen credit delivery system and to facilitate flow of credit to the MSE sector,
- create access to finance for unserved, under-served and underprivileged,
- making availability of finance from conventional lenders to new generation entrepreneurs.
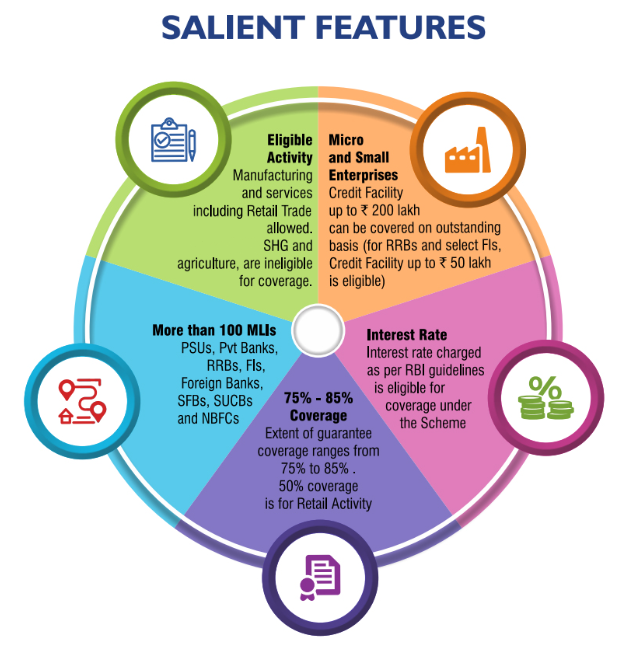
Eligibility:
- Under CGTMSE, guarantee cover is provided by the trust for the credit facilities to an extent of Rs 200 lakh that have been sanctioned without any collateral security and/or third party guarantees to all new and existing Micro and Small Enterprises (both Mfg as well as services) except Educational & Training Institutions.
- CGTMSE has recently modified the scheme by introducing Hybrid Security product wherein loans sanctioned to MSE units with partial collateral coverage can be covered under the credit guarantee scheme (CGS) of CGTMSE i.e., A portion of loan which is not covered by collateral security (Max. of Rs 2.00 Crs) sanctioned to MSE units can be covered under CGTMSE.
- Retail Trade activity is eligible for coverage under CGTMSE with exposure limit for coverage being fixed at maximum of Rs 1.00 Cr.
Loans sanctioned under Agriculture segment and SHGs are also not eligible to cover under CGTMSE.
Extent of guarantee:
The extent of guarantee provided by the trust is based on the category of the borrowers/location of the unit and amount of credit facility being covered under guarantee. The same is as under:
|
Category
|
Maximum extent of guarantee where credit facility is
|
|
|
Upto Rs 5 lakh
|
Above Rs 5 lakh & upto Rs 50 lakh
|
Above Rs 50 lakh & upto Rs 200 lakh
|
|
Micro Enterprise
|
85% of the amount in default subject to a maximum of Rs 4.25 lakh
|
75% of the amount in default subject to a maximum of Rs 37.50 lakh
|
75% of the amount in default subject to a maximum of
Rs 150 lakh
|
|
Women Entrepreneurs/ Units located in NE region(incl. Sikkim) {other than credit facilities upto Rs 5 lakh to Micro Enterprises}
|
80% of the amount in default subject to a maximum of Rs 40 lakh
|
|
All other categories of borrowers
|
75% of the amount in default subject to a maximum of Rs 37.50 lakh
|
|
Retail Trade Activity
[Max of Rs 1.00 Cr]
|
50% of the amount in default subject to maximum of Rs 50 lakh
|
- Credit facilities sanctioned beyond Rs 200 lakh to a single eligible borrower can also be covered under CGTMSE. However, the limit that shall be covered under guarantee will be restricted to Rs 200 lakh only even though the credit facility sanctioned is above Rs 200 lakh.
- Guarantee Fees: The guarantee fees vary from 1% to 2% p.a. (plus risk premium) depending on type of account. As on date banks Risk premium is 15%.
Recent steps taken and changes made in CGTMSE
- Consequent upon this, the following significant steps have been taken:
- The corpus of Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro & Small Enterprises (CGTMSE) has been infused with a sum of Rs. 8,000 crore on 30.03.2023.
- CGTMSE has issued guidelines regarding reduction of annual guarantee fee for loans upto Rs. 1 crore from a peak rate of 2% per annum to as low as 0.37% per annum. This will reduce the overall cost of credit to the Micro & Small Enterprises to a great extent.
- The limit on ceiling for guarantees has been enhanced from Rs. 2 crore to Rs. 5 crore.
- For settlement of claims in respect of guarantees for loan outstanding upto Rs. 10 lakh, initiation of legal proceedings will no longer be required.
Note: CGTMSE created a new landmark by touching the milestone figure of approving guarantees worth Rs. 1 lakh crore during FY 2022 - 23.

Importance of providing Credit Guarantees to MSMEs
- Indian MSMEs find it difficult to get finance due to weak creditor and property rights, informal economy, lack of appropriate accounting records, and information asymmetry. Furthermore, the administrative cost of lending to MSMEs is relatively higher because of their smaller loan sizes. Collecting information on MSME’s creditworthiness requires more resources as a percentage of the underlying loan. Therefore, lending institutions may not always find it economically rational to lend to MSMEs.
- Therefore, banks’ lending decisions are generally dependent on collateral. However, many first-generation MSMEs, who may be having huge potential (and many ingenious ideas!), may not have the capability to fulfill the collateral requirements of banks. Therefore, because of a lack of funds, many individuals and MSEs with enormous potential cannot start or scale up their businesses. Due to credit rationing, profitable projects of micro and small enterprises may not see the light of the day, resulting in suboptimal investment and employment in the economy.
- Providing credit guarantees to lending institutions can play an increasingly important role in bridging this credit gap and facilitating the growth of credit to the MSME sector. By providing guarantees to the lending institutions and covering part of the default risk, credit guarantee institutions lower the lender’s risk as guarantees secure repayment of all or part of the loan in case of default.
- Credit Guarantee not only enables micro and small businesses without collateral to obtain loans but also leads to overall credit enhancement in the economy as many of the MSMEs without collateral would not have otherwise got credit from the lending institutions. Credit guarantee also encourages lending institutions to save on capital provisioning as the provision of guarantees reduces the capital adequacy ratio.
- By providing a guarantee for a percentage of a financial institution’s loan portfolio, the capital adequacy requirements against the portion of the portfolio that is guaranteed are correspondingly lower, which further leads to credit enhancement in the economy.
- Furthermore, since the entire risk of default is not borne by lending institutions after the provision of credit guarantees, lending institutions need not to charge a higher interest rate to take care of the risk associated with lending to SMEs. Thus, providing credit guarantees at nominal guarantee fees also allows lending institutions to extend loans at a cheaper rate to MSMEs.
Significance of CGTMSE Scheme in this respect
- Over the past 20 years, CGTMSE has been instrumental in providing guarantee cover to collateral and/or third party guarantee free credit facilities extended by eligible Member Lending Institution [MLIs] to MSEs.
- In India by way of extending loan guarantees to lenders and thereby instilling confidence and risk aversion amongst the lenders, Credit Guarantee Trust for MSMEs (CGTMSE) has played an increasingly important role in facilitating the growth of credit to MSME sector.

Way Ahead
- Some more tweaks in the CGTMSE scheme can also be undertaken to improve the efficacy of the scheme further.
- The signup for the Guarantee cover amongst member lending institutions is still very low.
- Guarantee fee charged by CGTMSE from member lending institutions is believed to be high by many banks. Therefore, rationalising fee for claiming guarantee cover will go a long way in covering a bigger share of MSEs loans under the guarantee scheme.
- The Recent SBI report also suggests reducing the annual guarantee fees to 0.50% of the loan amount across all the slabs and making CGTMSE coverage mandatory for all SME loans up to Rs 2 crore.
- Moreover, the report also suggests increasing the limit for non-collateralized loans under CGTMSE to INR 20 lakh from the current INR 10 lakh for micro and small units for all activities under the manufacturing, services, and trade sector.
- Furthermore, by encouraging State Financial Corporation (SFC) to provide first and/or second loss guarantee to lending institutions instead of directly financing MSMEs out of their balance sheet, there can be multiple times disbursal of credit with the same amount of outlay incurred by them.
- At present, besides providing guarantees, the SFCs also provide financial assistance to MSMEs in various forms, such as directly providing term loans, direct subscription to the debentures or the equity, and seed capital.
- Sincere efforts need to be put into increasing the share of guarantees provided by SFCs to lending institutions out of the total expenditure incurred by them.
- Moreover, setting up a state-level credit guarantee trust for MSMEs on the lines of CGTMSE, which is at the national level, can also fulfill state-specific requirements, and provide MSMEs with easy access to funds, & banks with higher reliability.
Important Article: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/eclgs
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Providing credit guarantees to lending institutions can play an increasingly important role in bridging the credit gap faced by Indian MSMEs and facilitating the growth of credit to the MSME sector. Elucidate.
|

https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1912500











