




Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
About
Origin
Merger with Ganga
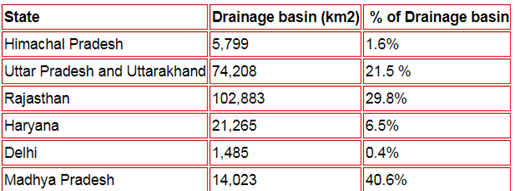
Catchment
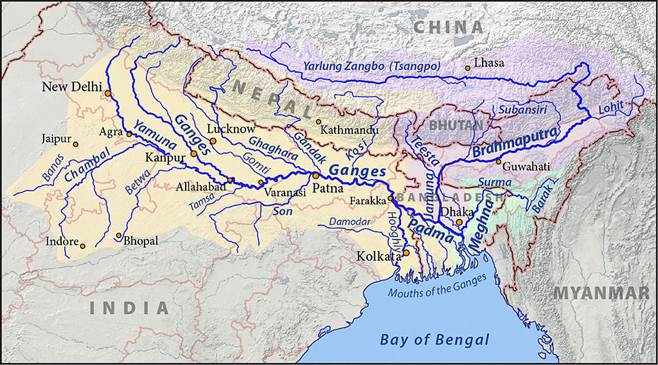
Important cities through which Yamuna passes
Tributaries of Yamuna
The main Yamuna and Tons are fed by glaciers, viz., the Bandar Punch Glacier and its branches and originates from the Great Himalayan range.
Tons River
The Tons is the longest tributary of the Yamuna River and its flows through Garhwal, the western part of the Himalayan state of Uttaranchal. The river originates at an elevation of 3900 m and joins the Yamuna below Kalsi near Dehradun, Uttarakhand. It is one of the most major perennial Indian Himalayan rivers. It is the biggest tributaries of the Yamuna.
Giri River
The river Giri is an important tributary of the Yamuna River. It is the main source of water in the South-Eastern Himachal Pradesh. The Giri is famous in the Jubbal, Rohru hills that rises from Kupar peak just above Jubbal town after flowing across the heart of Shimla hills and then flows down in the southeastern direction dividing the Sirmaur district into equal parts that are known as Cis-Giri and Trans-Giri region and joins Yamuna upstream of Paonta below Mokkampur.
Hindon River
Hindon River is an important tributary of Yamuna River. In fact, this river is sand-witch between two major rivers: Ganga on the left and Yamuna on the right. Hindon originates from upper Shiwalik (Lower Himalayas). It is a purely rain fed river with catchment area of about 7,083 sq. km. This river has a total run of about 400 km.
Betwa River
The Betwa River is a tributary of Yamuna River. The Betwa river originates at an elevation of 470 m in the Bhopal District in Madhya Pradesh. After traversing a distance of 590 km, the river joins the Yamuna River near Hamirpur. The total catchment area of the Betwa River is 46,580 sq km of which 31,971 sq km (68.64%) lies in M.P. and 14,609 sq km (31.36%) lies in U.P. The basin is saucer shaped with sandstone hills around the perimeter. The river has 14 principle tributaries out of which 11 are completely in Madhya Pradesh and 3 lies partly in Madhya Pradesh and partly in Uttar Pradesh. The Halali and Dhasan River are the important tributaries of the Betwa River.
Dhasan River
The Dhasan River is a right bank tributary of the Betwa River. The river originates in Begumganj tehsil of Raisen district in Madhya Pradesh state in central India. The river forms the southeastern boundary of the Lalitpur District of Uttar Pradesh state. Total length of the river is 365 km, out of which 240 km lies in Madhya Pradesh, 54 km common boundary between Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh and 71 km in Uttar Pradesh.
Ken River
Ken is an inter-state river, flowing through the state of Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. The river originates near the village Ahirgawab in Jabalpur District of Madhya Pradesh at an altitude of 550 m above near sea level and joins the Yamuna River, near Chilla village of U.P.
It forms the common boundary between Panna and Chattarpur district of M.P. and Banda district (U.P.). The river has a total length of 427 km, out of which 292 km lies in M.P., 84 km in U.P. and 51 km forms the common boundary.
The important tributaries of the Ken River are Sonar, Bearma, Kopra, Bewas, Urmil, Mirhasan, Kutni, Kali, Gurne, Patan, Siameri, Chandrawal, Banne, etc, among others. The longest tributary is Sonar which is 227 km in length and lies wholly in M.P..
Sind River
River Sind is one of the second largest right bank tributaries of Yamuna. It rises at a height of 543 m above sea level in Vidisha District of Madhya Pradesh. It flows generally in north- east direction for a distance of 415 km before joining Yamuna 20 km upstream of Auraiya. Important tributaries of Sind are Parwati and Kunwari on its left bank and Pahuj on the right bank.
River Chambal
The Chambal River, called Charmanvati in ancient times, is the largest of the rivers flowing through Rajasthan state. This tributary of Yamuna is 960km long. The total area drained by the Chambal up to its confluence with the Yamuna is 143,219 sq km out of which 76,854 sq km lies in M.P. state, 65,264 sq km in Rajasthan state and 1,101 sq km in Uttar Pradesh.
River Chambal, the biggest tributary of Yamuna rises in Vindhyan range near Mhow in Indore District of Madhya Pradesh.
Chambal basin is bound on north by the ridge separating it from Luni and Yamuna basins, on the south by Vindhyan range and on the west by Aravali range, on east lies the ridge separating it from Kunwari and Sind rivers of Yamuna basin Chambal basin.
Dams on Chambal
Tributaries of Chambal River
Kali Sindh:
It’s originated in the northern slopes of Vindhya Hills. Flowing in the M.P., it enters in the Rajasthan near Bindha village in Jhalwara District. After flowing 145 km in Rajasthan its joins Chambal River near Nonera village of Kota District.
Parwan River:
The Parwan originate in the Malwa Plateau and after flowing for about 186 km in M.P., it enters Rajasthan near Kharibor village in Jhalwara District. Its joins Kali Sindh near Ramgarh village in Kota district.
Parwati River:
The Parwati river originates in the northern slopes of the Vindhyan hills in M.P. where it forms a boundary between MP and Rajasthan for about 18 km, and then enters Rajasthan near Chatarpura village in Baran District. The river catchment in Rajasthan is situated in Kota and Jhalawar District. Major tributaries of the Parwati River are Lhasi, Berni, Bethli, Andheri, Retri, Dubraj, Bilas and Kunu.
Banas River
The Banas River originates in the Khamnor hills of the Aravali range (about 5km from Kumbhalgarh) and flows along its entire length through Rajasthan. Banas is a major tributary of the Chambal River, the two rivers meeting near village Rameshwar in Khandar Block in Sawai Madhopur District. The main tributaries of the Banas River are Berach and Menali on the right bank and Kothari, Khari, Dai, Dheel, Sohadara, Morel and Kalisil on the left bank.
The Banas River itself has many big tributaries. The Berach river originates in the hills northeast of Udaipur city. It flows northeast in Udaipur, Chittorgarh and Bhilwara district before joining Banas near Bigod village in Mandalgarh Tehsil of Bhilwara District. The Berch flow in a hilly region up to Badgaon reservoir and then through plains. This river receives flow from Ayar, Wagli Wagon, Gambhiri and Orai Rivers.
Sipra River
The Sipra River is also call Ksipra (Markandeya). It flows in the state of Madhya Pradesh. The river is famous for the sanctity associated with it.
https://epaper.thehindu.com/Home/ShareArticle?OrgId=GO09VSOC1.1&imageview=0





© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved