Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context: The genetic causes of Raynaud’s phenomenon have been probed by researchers at Queen Mary University of London’s Precision Healthcare Research Institute (PHURI) and Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin’s Berlin Institute of Health (BIH).
Findings of the research
The researchers discovered variations in two genes that predisposed participants to
Raynaud’s phenomenon:
Alpha-2A-adrenergic receptor for adrenaline, ADRA2A
- One was the alpha-2A-adrenergic receptor for adrenaline, ADRA2A, a classic stress receptor that causes the small blood vessels to contract.
- This makes sense when it’s cold or dangerous because the body has to supply the inside of the body with blood.
Transcription factor IRX1
- The second gene is the transcription factor IRX1, which may regulate the ability of blood vessels to dilate.
- If its production is increased, it may activate genes that prevent constricted vessels from relaxing as they would normally do.
- Together with the overactive adrenaline receptor, this may then lead to the vessels not supplying enough blood for a longer period, which leads to the observed white fingers and toes.
.jpg)
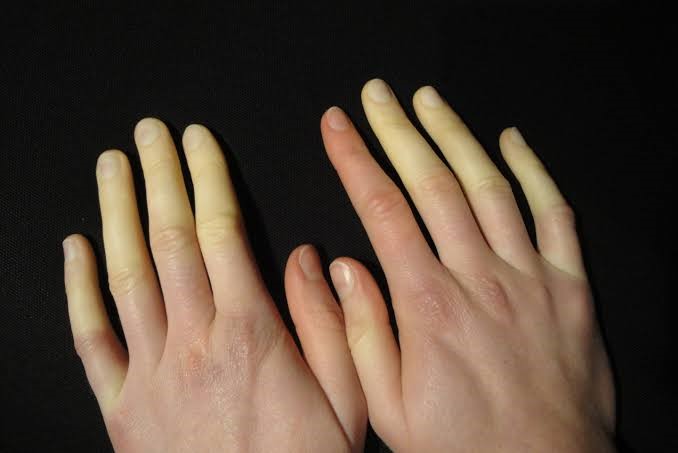
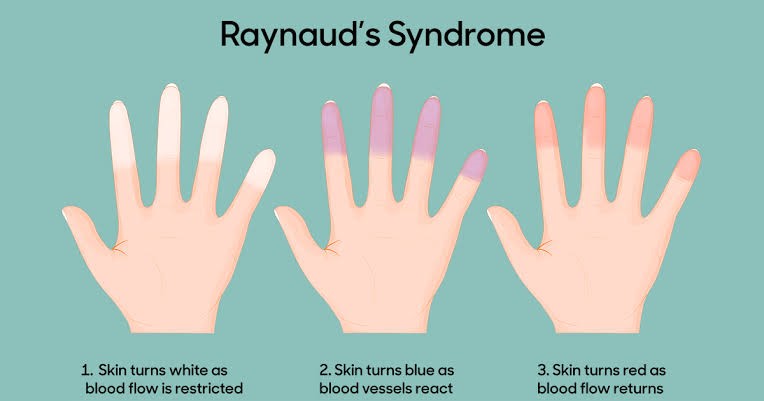
Raynaud’s phenomenon (RP)
- Raynaud’s phenomenon (RP) is a heritable blood circulation disorder.
- It’s a vasospastic disorder, which implies that small blood vessels near the skin’s surface spasm, limiting blood flow
Symptoms
- People with Raynaud’s syndrome frequently experience discomfort in their fingers and toes, as well as changes in skin colour, as a result of a lack of blood flow during attacks when they are cold or emotionally upset.
- In more extreme cases, it might result in severe pain or ulcers.
Prevalence
- Around 2-5 per cent of the population is affected by Raynaud’s.
- Raynaud’s is a painful, chronic condition that affects around one in ten people in the UK.
Issues with Raynaud’s phenomenon
- Despite it being a common condition, it’s under investigation and little is understood about the genetic cause of the condition.
- There are limited treatments available for RP.
- Doctors usually advise that the patient use ‘self-management’ strategies such as keeping warm and avoiding triggers of attacks.
- In severe cases medications can be prescribed, these are ‘repurposed drugs’, usually medicines to lower high blood pressure, which often cause severe side effects in patients.
Way ahead
- A better understanding of the underlying genetic mechanisms that cause RD is needed to develop safe and effective treatments.
- Research like this, which significantly advances our understanding of Raynaud’s and the role that genetics may play in causing it, is crucial.
- The next step is to confirm these important findings in more diverse population groups and validate the results through functional studies.
- If successful, these findings could help us unlock more new therapeutic avenues for Raynaud’s leading to better, more targeted and kinder treatments.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Consider the following statements about Raynaud’s phenomenon (RP)
- Raynaud’s phenomenon (RP) is a heritable blood circulation disorder.
- It’s a vasopastic disorder, which implies that small blood vessels near the skin’s surface spasm, limiting blood flow.
- Alpha-2A-adrenergic receptor for adrenaline, ADRA2A, gene is one of the factors leading to the disease.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- All are correct
Ans: D
|

https://www.aninews.in/news/health/study-finds-genetic-causes-of-raynauds-phenomenon20230804211801/