Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: freedomhouse.org
Context: Freedom House, a Washington DC-based non-profit organization, has released a new report titled 'Freedom on the Net 2023: The Repressive Power of Artificial Intelligence,' which highlights a concerning trend of declining global Internet freedom for the 13th consecutive year.
Details
- The report, the 13th edition of an annual study of human rights online, covers developments between June 2022 and May 2023, evaluating Internet freedom in 70 countries, accounting for 88% of the world's Internet users.
- According to the report, the environment for human rights online has deteriorated in 29 countries, while only 20 countries registered net gains in Internet freedom. One of the key concerns raised in the report is the increasing use of artificial intelligence by governments for censorship and the spread of disinformation.
- The report sheds light on the alarming ways in which governments and authoritarian actors are leveraging AI technologies to suppress internet freedom, manipulate information, and monitor citizens.
- This report reveals a crisis for human rights online, as AI tools enable governments to clamp down on dissent and control the flow of information more efficiently, swiftly, and inexpensively than ever before.
|
Key observations made in the Report
|
|
AI-Powered Censorship Tools
|
●Governments are increasingly relying on AI algorithms to automate the process of content censorship. These tools scan vast amounts of online data and identify content that violates government-defined guidelines. This content could include political dissent, criticism of the government, or discussions about sensitive social issues. Once identified, this content is swiftly blocked, restricting citizens' access to information and stifling freedom of expression.
|
|
Identification and Removal of Dissident Content
|
●AI algorithms are programmed to recognize keywords, phrases, or even sentiments that are critical of the government. When such content is detected on social media platforms or websites, AI-powered systems automatically remove or flag it for human review. This process allows authorities to suppress dissenting opinions, control narratives, and prevent the spread of information that challenges their authority.
|
|
Generation and Spread of Disinformation
|
●AI is employed to create and disseminate disinformation on a massive scale. These algorithms analyze social and political trends to craft false narratives, which are then strategically spread online. Disinformation campaigns can manipulate public opinion, influence elections, and create confusion among citizens. AI's ability to target specific demographics amplifies the impact of these false narratives, making it challenging for the public to discern fact from fiction.
|
|
Surveillance of Online Activity
|
●AI-driven surveillance systems monitor citizens' online activities, including social media posts, messages, and browsing history. These systems analyze patterns in online behaviour, allowing governments to identify individuals who may pose a threat to the established order. This pervasive surveillance creates a climate of fear, leading to self-censorship as individuals refrain from expressing their opinions freely online to avoid repercussions.
|
|
Legal Repercussions and Online Activities
|
●Individuals in a record 55 countries faced legal consequences for expressing themselves online, indicating a global trend of cracking down on online expression.
●The report notes an increase in countries where authorities impose severe penalties, including multi-year prison terms, for various online activities.
|
|
Elections and Digital Repression
|
●Elections serve as triggers for digital repression, with incumbent leaders using censorship and controlling information flow to influence election outcomes.
●Strategies such as blocking access to independent news sources are used to manipulate public opinion, impacting the fairness of elections.
|
|
About India
|
●The Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules require social media platforms to use AI-based moderation tools, leading to concerns about freedom of expression and criticism.
●The expanding censorship regime in India creates an uneven playing field, silencing criticism and independent reporting on the ruling party. This situation raises concerns about the fairness of democratic processes, especially in the context of the upcoming general elections in 2024.
●The report evaluates countries on several censorship methods, including internet connectivity restrictions; social media platform blocks, website blocks, VPN blocks, and forced removal of content.
○India is found to engage in most of these methods, except for VPN blocking, indicating a multifaceted approach to online censorship.
●India scored 50 out of 100, indicating a moderate level of digital freedom but highlighting areas of concern. Iceland (94) has the best climate for internet freedom.
|
|
Global Examples of AI-Powered Repression
|
●The Chinese government employs AI-powered facial recognition technology and internet monitoring systems to track citizens' activities. AI is used to censor online content deemed politically sensitive and identify dissidents, leading to their arrest and punishment.
●Russian authorities use AI algorithms to target individuals and organizations critical of the government. AI-driven tools identify content that opposes government policies, leading to the blocking of websites and social media platforms, and effectively silencing opposition voices.
●AI is used to monitor social media platforms for content that challenges the Saudi government. Dissident voices are swiftly identified and silenced through the removal of content or even arrest. AI-driven surveillance ensures tight control over online conversations.
●While democratic, the U.S. government employs AI for surveillance purposes. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of online data, including social media posts, to identify potential threats to national security. While the intention might be security-focused, this level of surveillance raises concerns about individual privacy and freedom of expression.
●Authorities shut down internet services, blocked popular messaging apps like WhatsApp and Instagram, and increased surveillance in response to anti-government protests.
|
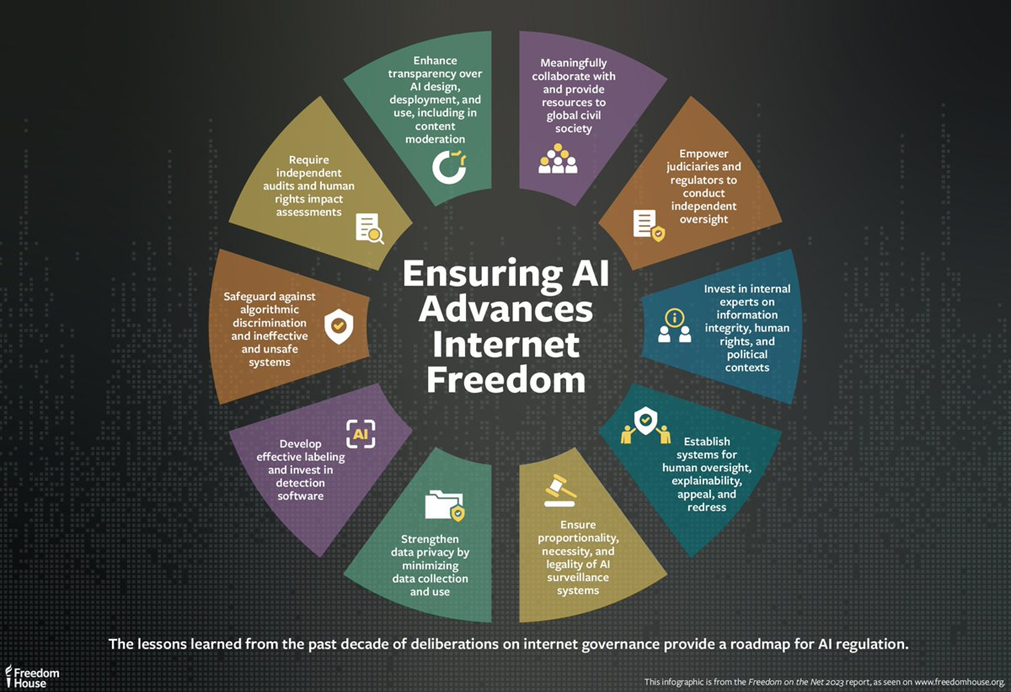
The report recommended some measures for Protecting Internet Freedom
- International Standards: Establishing international agreements and standards for the responsible use of AI is essential. These standards should encompass ethical guidelines that prioritize human rights, ensuring that AI technologies are not used to infringe upon freedom of speech or privacy.
- Open-Source AI Tools: Encouraging the development and use of open-source AI tools promotes transparency and accountability. Open-source solutions allow researchers, activists, and technologists to scrutinize algorithms, creating a collective defence against AI-driven repression.
- Public Education: Raising public awareness about the risks associated with AI-powered repression is crucial. Educated citizens are better equipped to identify disinformation, protect their privacy, and advocate for policies that safeguard internet freedom. Educational initiatives can empower individuals to navigate the digital landscape safely.
Picture Courtesy: freedomhouse.org
Repressive Power of Artificial Intelligence: A Case Study of India
About
- Artificial intelligence (AI) is a powerful technology that can enhance human capabilities, improve efficiency, and solve complex problems. However, AI can also be used for repressive purposes, such as censoring online speech, spreading disinformation, and manipulating public opinion.
- India has a vibrant and diverse online landscape, with more than 800 million internet users and hundreds of languages spoken. The internet has enabled Indians to access information, express their views, and participate in civic life. However, India also faces many challenges, such as communal violence, political polarization, misinformation, cyberattacks, and online harassment.
- These challenges have prompted the Indian government to adopt various measures to regulate the Internet, often at the expense of human rights and democratic norms.
- According to the Freedom on the Net 2023 report by Freedom House, India scored 50 out of 100 points on its internet freedom index, ranking it among the "partly free" countries. The report assesses countries on five censorship methods: internet connectivity restrictions, blocks on social media platforms, blocks on websites, blocks on VPNs, and forced removal of content. India engaged in all of them except one (VPN blocking).
Growing use of AI for censorship and disinformation purposes
Automated Content Removal
- The Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules 2021 mandate digital platforms to employ automated tools for content moderation. While the intention might be to curb illegal activities, the automated systems can lack nuance. This can result in the suppression of legitimate speech, artistic expression, and political dissent.
- Concerns arise regarding the potential bias in algorithms and the lack of human oversight, which could lead to the removal of content based on misunderstood context or controversial topics.
Internet Shutdowns
- Frequent internet shutdowns, especially in conflict zones like Jammu and Kashmir, disrupt normal life. Beyond inconveniences, these shutdowns hinder access to crucial services such as education, healthcare, and emergency communication. Moreover, they create an information vacuum, making it difficult for citizens to report and document human rights violations effectively.
- The lack of internet access impedes transparency and accountability, allowing potential abuses to go unreported and unchecked.
Website and Application Blocking
- The government's practice of blocking websites and applications, often without transparent procedures or judicial oversight, raises serious concerns about due process and freedom of expression.
- By restricting access to various online platforms, individuals are deprived of diverse sources of information. This limitation stifles open dialogue, a fundamental element of any democratic society, and limits citizens' right to express their opinions freely without fear of censorship.
Use of AI for Propaganda
- The use of AI-powered chatbots for political messaging, as observed during the 2023 general elections, introduces ethical and privacy concerns.
- Sending personalized messages blurs the line between genuine political engagement and manipulation. The collection of user data for targeted campaigning raises issues related to privacy and informed consent. Individuals may not be aware of how their data is being used, leading to questions about data protection and privacy rights.
Automated Facial Recognition
- The National Automated Facial Recognition System (NAFRS) presents significant privacy and human rights challenges.
- The mass collection of facial images from various sources, including CCTV cameras, social media platforms, and criminal records, raises concerns about the potential for misuse and unauthorized surveillance. Without clear regulations and safeguards, individuals' privacy rights are at risk, as their facial data could be exploited for purposes beyond the system's intended goals, such as tracking political dissidents or activists.

Impact of AI-enabled digital repression
Restriction of Free Expression and Dissent
- AI-enabled censorship creates a climate of fear where individuals refrain from expressing their opinions online. The fear of legal consequences or social backlash stifles open dialogue and dissenting voices. This chilling effect undermines the democratic principle of free speech, hindering the open exchange of ideas and diverse perspectives.
- Censorship limits access to diverse and independent sources of information. When certain voices are silenced, individuals are deprived of a comprehensive understanding of various issues. Informed decision-making, crucial for a functioning democracy, becomes challenging when citizens are unable to access a wide array of perspectives.
Undermining Trust and Creating Polarization
- AI-enabled disinformation erodes trust in online information sources and institutions. When false or misleading information circulates online, users become sceptical of the authenticity of news and facts. This scepticism can extend to legitimate sources, eroding trust in the media and public institutions.
- Disinformation campaigns create confusion among online users, making it difficult to discern fact from fiction. This confusion often leads to polarization, where individuals are divided into opposing camps, each adhering to their own set of beliefs. Such division weakens social cohesion and can lead to societal unrest.
Violation of Privacy and Autonomy
- AI-enabled surveillance, especially through technologies like facial recognition, intrudes upon individuals' privacy. The mass collection of personal data without adequate consent and safeguards exposes individuals to potential misuse or abuse by state or non-state actors. This violation of privacy rights raises ethical and legal questions about the surveillance practices employed by authorities.
- Constant surveillance curtails individuals' autonomy over their online activities. Knowing that their actions are being monitored, individuals may self-censor, refraining from engaging in certain discussions or activities online. This reduction in personal agency diminishes the free and open nature of the Internet, hindering the democratic ideal of individual freedom.
Steps taken to address the challenges posed by AI-enabled digital repression
Establishment of Institutions and Initiatives
- The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has set up committees to formulate a national strategy for AI. These committees work toward defining ethical guidelines and responsible use of AI technologies within the country.
- As a government think tank, NITI Aayog has published a discussion paper outlining India's national vision on AI. This paper likely outlines the country's strategic approach, potential applications, and ethical considerations related to AI.
- The National Association of Software and Services Companies (NASSCOM), an industry body, has launched the Responsible AI portal. This platform serves as a resource hub, offering guidance and materials on AI ethics and governance to businesses and developers, promoting responsible practices in the AI industry.
Participation in International Forums
- India's participation in the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI), a multi-stakeholder initiative, indicates the country's commitment to developing AI that is human-centric and trustworthy. By engaging with other nations, India contributes to shaping global norms and standards for ethical AI usage.
- India's membership in the UNESCO Ad Hoc Expert Group demonstrates its active involvement in drafting global recommendations on the ethical principles and values of AI. Being part of these international discussions ensures India's perspectives are represented in the formulation of global AI ethics standards.
Civil Society Actions and Judicial Interventions
- Entities like the Internet Freedom Foundation (IFF) and the Software Freedom Law Center (SFLC) have been active in challenging AI-enabled digital repression. They file petitions in courts and submit representations to authorities, raising concerns about issues like the IT Rules 2021, internet shutdowns, website blocking, and facial recognition systems.
- Courts in India have shown their support for internet freedom. For instance, the Supreme Court's ruling in 2020, declaring internet access as a fundamental right, reinforces the importance of ensuring unrestricted internet access to citizens, safeguarding their right to information and expression.
Challenges in ensuring that AI is used for enhancing rather than eroding internet freedom
Lack of Comprehensive Legal Framework
- Outdated Laws: Existing laws like the IT Act 2000 and the Personal Data Protection Bill 2019 were not specifically designed to handle the complexities of AI. The rapid advancement in AI technology often outpaces the legal framework, making it challenging to address emerging issues effectively.
- Transparency and Accountability: There is a lack of transparency and accountability mechanisms to oversee the development and deployment of AI. Clear regulations and oversight are essential to ensure that AI systems are not used to infringe upon citizens' rights, such as freedom of speech and privacy.
- Ethical and Responsible AI: Formulating guidelines for ethical and responsible AI usage is crucial. It involves defining the boundaries within which AI systems can operate, safeguarding against biases, and ensuring fairness and transparency in decision-making processes.
Lack of an Inclusive Ecosystem
- Shortage of Skilled Talent: India faces a shortage of skilled professionals in AI-related fields. The lack of experts hampers the development of innovative and ethical AI systems. Bridging the skill gap through education and training programs is essential.
- Limited Infrastructure: Adequate infrastructure, including high-performance computing resources, is vital for AI research and development. A lack of infrastructure inhibits the progress of AI initiatives and the testing of AI models, hindering innovation.
- Data Challenges: AI systems require vast amounts of data for training and validation. Limited access to diverse and high-quality datasets constrains the development of AI applications. Moreover, ensuring data privacy while facilitating data sharing for research purposes is a delicate balance that needs to be maintained.
- Diversity and Representation: There is a lack of diversity and representation, especially concerning marginalized communities, in the design and governance of AI systems. Diverse perspectives are essential to prevent biases in algorithms and ensure that AI technologies cater to the needs of all segments of society.
Geopolitical Pressures and Conflicts
- Global Competition: India faces intense global competition, particularly from countries like China and the United States, which are striving for leadership in AI technologies. Balancing India's strategic interests and values while engaging with these nations is challenging, as it involves navigating complex geopolitical dynamics.
- Geopolitical Tensions: The use or misuse of AI by state or non-state actors can lead to geopolitical tensions and conflicts. India needs to develop robust policies and strategies to protect its national interests while cooperating with the international community to establish ethical standards for AI usage.
Way forward to ensure that AI is used to advance internet freedom in the country
Enact a Comprehensive Legal Framework
- Develop a legal framework grounded in human rights principles, ensuring that AI applications respect fundamental rights such as freedom of speech, privacy, and non-discrimination.
- Clearly define AI-related terminologies and establish the objectives of AI regulations, outlining the goals of promoting innovation, ensuring public safety, and upholding democratic values.
- Clearly outline the roles and responsibilities of various stakeholders, including government, industry, and civil society. Implement safeguards against potential misuse, ensuring transparency and accountability in AI systems' development and deployment.
- Establish robust oversight mechanisms, such as regulatory bodies or ethical review boards, to monitor AI applications. These bodies should ensure compliance with ethical guidelines and intervene in cases of misuse.
- Ensure that the legal framework aligns with international norms, standards, and best practices on AI ethics and governance. Active participation in global discussions will help India stay updated with evolving standards.
Foster a Robust and Inclusive Ecosystem for Innovation
- Facilitate collaboration among government, industry, academia, civil society, media, and users. Engage in open dialogues to address concerns, share knowledge, and work collectively towards ethical and innovative AI solutions.
- Allocate adequate resources, both financial and infrastructural, for research and development in AI. Invest in educational programs to bridge the skill gap, ensuring a steady supply of skilled professionals in AI-related fields.
- Provide incentives for companies and researchers involved in ethical AI development. Encourage startups and established companies to invest in AI technologies that align with democratic values and respect user freedoms.
- Establish platforms for collaboration and knowledge-sharing. Develop AI research hubs, innovation centres, and platforms that encourage interdisciplinary research and cooperation among stakeholders.
Pursue a Proactive Role in Shaping the Global AI Agenda
- Capitalize on India's democratic credentials, demographic dividend, digital potential, and cultural diversity. Showcase India's unique strengths in AI research, development, and application to influence global discussions.
- Actively engage with other countries, particularly those from the Global South, to foster cooperation and solidarity on AI-related issues. Share knowledge, best practices, and experiences to collectively address challenges.
- Demonstrate ethical leadership by adhering to the highest standards of AI ethics. Uphold transparency, accountability, and fairness in AI systems. Encourage other nations to follow suit by setting an example through ethical practices.
.jpg)
Conclusion
- AI is a double-edged sword that can be used for good or evil. India has a unique opportunity and responsibility to harness the power of AI to enhance internet freedom and democracy. However, India also faces significant risks and challenges from the misuse or abuse of AI for repressive purposes. India needs to adopt a holistic and balanced approach that ensures that AI is developed and deployed in a manner that respects human rights, promotes social good, and preserves public trust.
Must Read Articles:
World Press Freedom Index 2023: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/world-press-freedom-index-2023
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. How does the growing power of Artificial Intelligence influence our society, economy, and individual lives, and what strategies should be in place to harness this power for the benefit of humanity while addressing potential risks?
|










