



Experts from India and Bangladesh are collaborating to assess climate risks and build resilience in the Meghna river basin, which supports over 50 million people, including indigenous communities. The basin faces threats from climate change, such as irregular rainfall, rising temperatures, and industrial pollution. With no existing treaty covering the Meghna river, stakeholders aim to improve data sharing and promote sustainable water management through joint research and dialogue. This effort seeks to protect ecosystems and secure livelihoods dependent on the river.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: Down To Earth
A three-day conference will bring together experts and stakeholders from India and Bangladesh to evaluate climate risks and explore ways to improve resilience in the Meghna river basin, a shared water system crucial to over 50 million people, including indigenous communities like the Khasi, Garo, and Jaintia.
Picture Courtesy: cwejournal.org
|
Level |
Measures / Initiatives |
Details |
Source |
|
National Govt |
National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) |
Framework with missions on water, solar energy, sustainable agriculture, and more to enhance climate resilience |
MoEFCC |
|
National Water Mission |
Focuses on water conservation, minimizing wastage, and ensuring equitable water distribution |
MoEFCC |
|
|
Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABHY) |
Groundwater management program promoting community participation |
MoWR |
|
|
National Adaptation Fund for Climate Change (NAFCC) |
Provides financial support to projects for climate adaptation at local levels |
MoEFCC |
|
|
Climate Resilient Agriculture Programs |
Promote climate-smart farming techniques, watershed management, and crop diversification |
ICAR |
|
|
State Initiatives |
Measures / Initiatives |
Details |
Source |
|
Kerala |
Resilient Kerala Program |
$150 million World Bank loan to enhance resilience against floods and climate risks |
World Bank |
|
Thrithala Water Budgeting |
Legislative constituency initiative for rainwater harvesting and artificial recharge |
|
|
|
Tamil Nadu |
Green Tamil Nadu Mission (GTM) |
Palmyra tree restoration to improve groundwater recharge and soil conservation |
Times of India |
|
Waterbody Restoration |
Restoration of 100 water bodies under PMKSY, focusing on desilting and encroachment removal |
Times of India |
|
|
Manali-Ennore Region Revitalization |
Ecological restoration of degraded coastal region through mangrove planting and community infrastructure |
Times of India |
|
|
Maharashtra |
Vaitarna Basin Groundwater Recharge |
Amazon & ICRISAT project for rainwater harvesting ponds and soil erosion control |
Indian Express |
|
Samvardhan Water Project |
Watershed management and climate-resilient agriculture in Vidarbha region |
Asia Initiatives |
|
|
Godavari Initiative |
Multi-stakeholder platform promoting sustainable water management in Godavari Basin |
Godavari Initiative |
Source: Down to Earth
|
Practice Question Q. Discuss the multidimensional impacts of climate change on river basins in India, highlighting the challenges and government measures taken to build resilience. Suggest a way forward to ensure sustainable river basin management.” (250 words) |
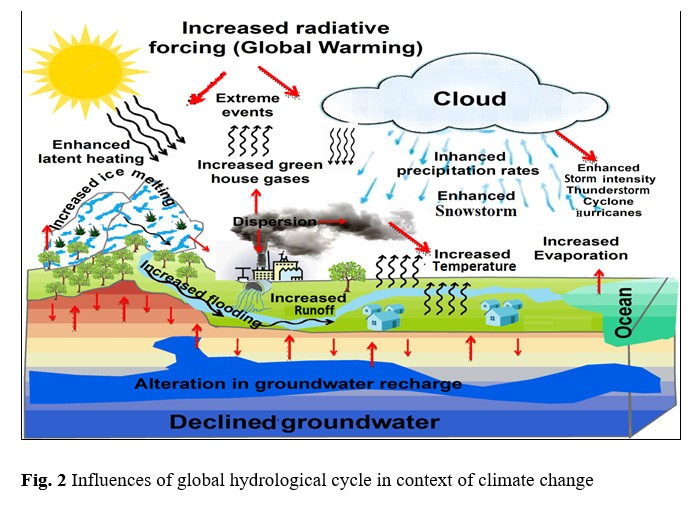
Climate change leads to altered rainfall patterns, increased frequency of floods and droughts, rising temperatures, reduced water availability, and changes in river flow affecting agriculture, fisheries, and livelihoods.
Rivers like the Ganges, Brahmaputra, Meghna, and their tributaries are highly vulnerable due to their large population dependence and susceptibility to glacial melt and erratic monsoons.
Challenges include unpredictable water flows, pollution from industrial waste, loss of biodiversity, lack of coordinated data sharing, and inadequate infrastructure for water conservation.




© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved