Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
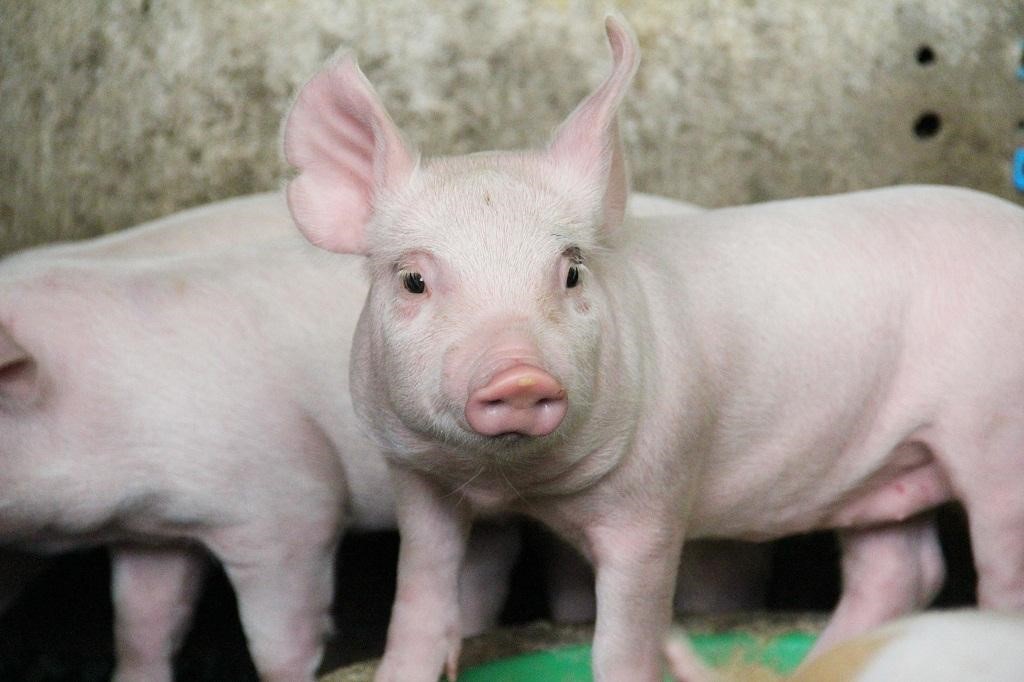
Context: African swine fever, a highly contagious virus, has hit 49 countries since 2021.
About African Swine Fever (ASF)
- African Swine Fever (ASF), is a highly contagious hemorrhagic viral infection.
- It afflicts domestic and wild pigs and boars.
- It has a nearly 100 per cent mortality rate.
- The virus spreads through soft ticks and quickly engulfs the entire pig population.
- The livestock disease was first reported in Kenya in 1921.
Treatment and cure
- There is no cure or vaccine to contain the African swine fever virus.
- The only way to contain it is to cull the infected and in-contact pigs and bury them in lime-treated deep trenches.
Findings of a report on ASF by the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH)
- The fever has spread to 49 countries since January 2021.
- ASF has resulted in around 1.5 million animal losses since 2021, affecting more than 0.95 million pigs and more than 28,000 wild boars.
- The highest losses of domestic pigs were reported from Europe (one million), followed by Asia (0.37 million and Africa (24,143).
- The losses could be much more than these figures as according to the report, the figures refer to losses in the establishments affected by the outbreaks and do not include the animals culled in areas around the outbreak to control the disease.
About World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH)
- It is an intergovernmental organization established in 1924.
- It aims to disseminate information on animal diseases and improve animal health globally.

ASF and India
- India managed to avert the virus for a century.
- The first case was only reported in 2020 in Assam, after its advent in China in 2018 which decimated porcine populations across Asia.
- Disease even hit the bio-secure environment of the Assam government’s pig-breeding farm and the ICAR-National Research Centre on Pig, both in Guwahati. This resulted in the death of three pigs and the culling of approximately 292 in the last two weeks.
- After the first ASF outbreaks, cases were also reported from other north-eastern states of Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim.
- Following this, the disease spread to Bihar, Kerala, Punjab, Haryana, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Tripura, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh and Delhi.
- The disease is still prevalent in India, with the most recent cases reported in May and June 2023 from Meghalaya and Mizoram, respectively.
Way ahead
- This spread confirms the global threat of the disease. There is a need to implement biosecurity measures.
- An early reporting and response system for preventing the spread of disease at an early stage should be prevented.
- There is a need for maintaining a high level of disease awareness among all actors involved in the value chain.
- WOAH recommended veterinary services remain vigilant.
- There is a need to implement science-based international standards and guidelines in their national disease prevention and control programmes.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q) The recent incident of African Swine Fever outbreaks confirms the global threat of the disease. In this regard highlight the need for implementing biosecurity measures and early reporting and response systems for preventing future epidemics.
|
https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/agriculture/african-swine-fever-highly-contagious-virus-hit-49-countries-since-2021-91295