






|
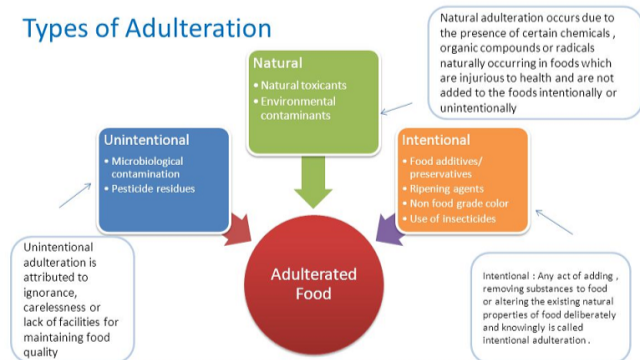
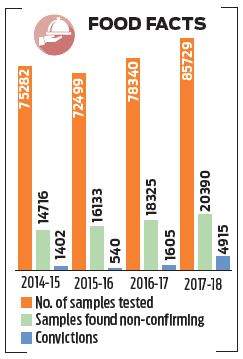
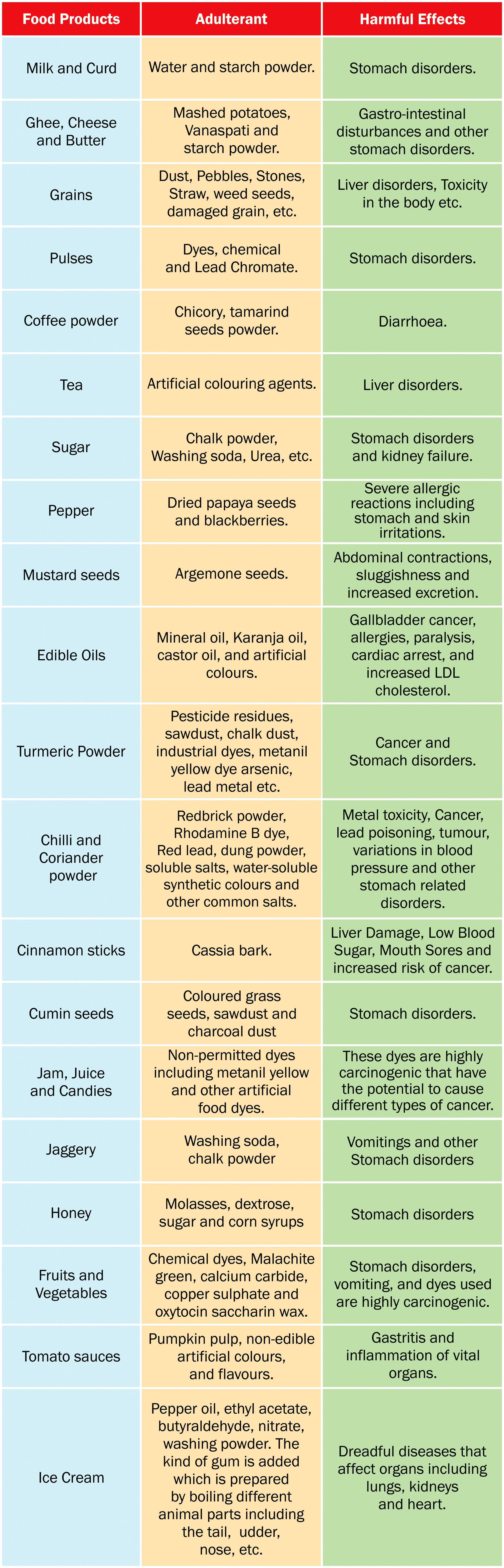
“The lure of riches and general apathy towards mankind has led to adulterants being added to food from the simple stones in rice to the more harmful brick and boric powder…"
It is important to note that Food Adulteration is a part of a broader issue – i.e Food Fraud!


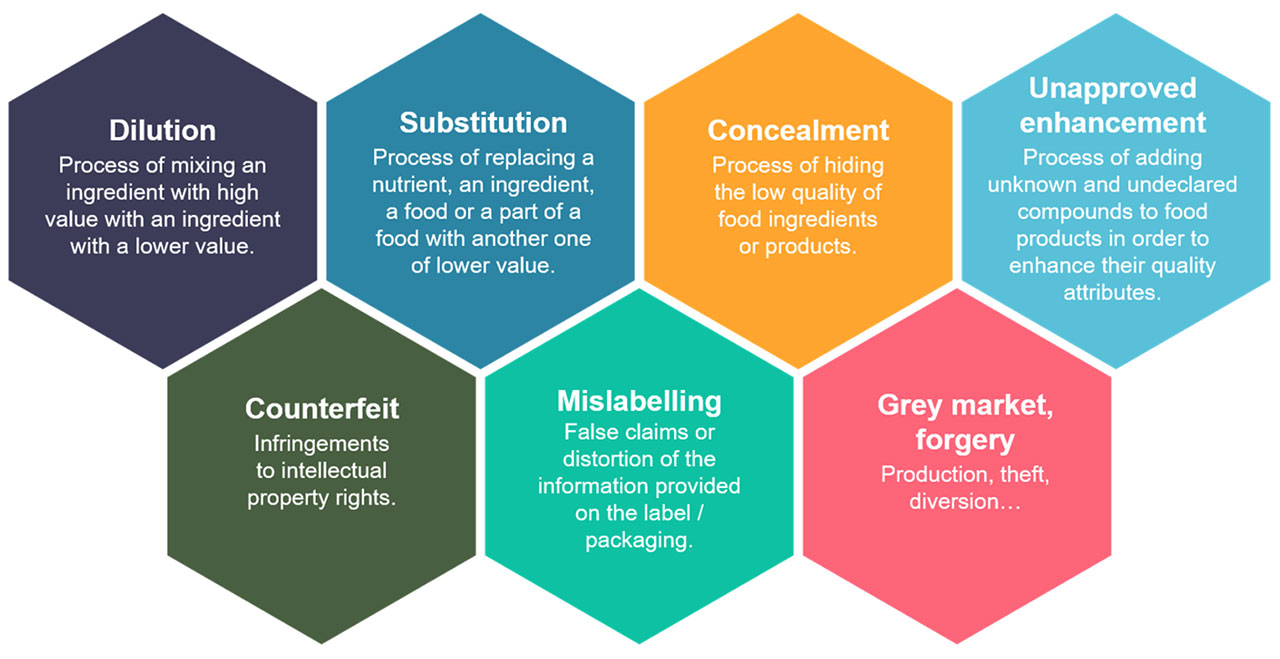

|

Development of stricter monitoring programs to screen all food products for safety is the only way to secure food supply and address the growing concern over food adulteration.

© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved