



Two recent shipping accidents off Kerala involved MV Wan Hai 503 catching fire on June 9, 2025, and MSC ELSA 3 sinking on May 25, 2025. A bill of lading is a contract for cargo transport. The IMO regulates global shipping, and SOLAS sets safety standards for merchant ships.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: THE HINDU
Context:
Who is Responsible When Ships Sink?
MV Wan Hai 503 => Singapore-flagged container vessel caught fire about 88 nautical miles off Kerala's coast. It was carrying over 2,000 tonnes of fuel and hundreds of containers, some with hazardous materials, sparking fears of a major ecological disaster.
MSC ELSA 3: Liberian-flagged container ship sank off the coast of Kochi. It was carrying hundreds of containers, including hazardous substances like calcium carbide, leading to pollution from plastic pellets (nurdles) and oil slicks along the Kerala coast.
No single country can regulate international shipping alone. This requires a coordinated global effort.
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) => It is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for the safety and security of shipping and the prevention of marine pollution by ships.
Directorate General (DG) of Shipping, India => This is the primary body in India responsible for implementing and enforcing maritime laws and conventions. It operates under the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways and handles all executive matters related to merchant shipping.
"Flags of Convenience" (FOC) => Ships are often registered in countries different from where their owners are based.
|
The International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) is the most important international treaty concerning the safety of merchant ships. The first version of SOLAS was adopted in 1914 in response to the sinking of the Titanic in 1912. It has been updated and amended many times since. |
When a ship sinks, the liability for lost cargo and environmental damage primarily falls on the ship owner.
Liability for Cargo
A Bill of Lading is a legal document in shipping. It serves three main functions:
The ship owner issues the bill of lading to the exporter. In case the cargo is lost or damaged, the ship owner is contractually obligated to compensate whoever legally holds the bill of lading at that time (usually the importer after payment).
Ship owners are protected by:
Protection and Indemnity (P&I) Clubs are mutual insurance associations that provide cover for massive, open-ended risks.
International conventions often place a cap on the ship owner's financial liability for cargo loss. However, there is no limit on claims for environmental damage, which operates on the "polluter pays" principle. This could apply to the hazardous materials lost from the MSC ELSA 3 and the potential fallout from the MV Wan Hai 503.
India is a signatory to many key IMO conventions. However, it has not yet ratified the 2010 Hazardous and Noxious Substances (HNS) Convention.
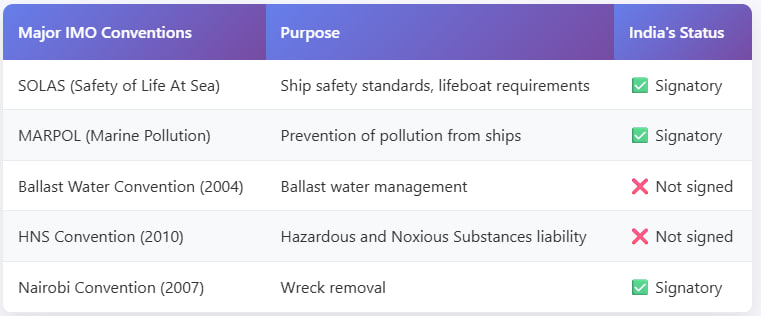
The HNS Convention establishes a dedicated liability and compensation system specifically for incidents involving hazardous substances, like the chemicals on the MSC ELSA 3. Without ratifying it, India must rely on its domestic merchant shipping laws, which may not be as comprehensive for securing adequate compensation in such complex cases.
Must Read Articles:
India holds on to High Seas Treaty
Source:
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. In the context of oil spill remediation, which of the following statements accurately describe the process of bioremediation?
How many of the above statements are correct? A) Only one B) Only two C) Only three D) All four Answer: B Explanation: Statement 1 is incorrect: Bioremediation can involve the use of naturally occurring microorganisms already present in the environment. While genetically engineered microorganisms (GEMs) can be developed and used to enhance the degradation of pollutants, bioremediation is not limited to them. Statement 2 is correct: The growth of naturally occurring hydrocarbon-degrading microbes can be limited by the availability of nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus. By adding these nutrients to a contaminated site, a process known as biostimulation, the growth and activity of these beneficial microorganisms can be enhanced. Statement 3 is correct: Phytoremediation is a type of bioremediation that utilizes plants and the microorganisms associated with their root systems (rhizosphere) to clean up contaminants. Plants can help degrade, extract, or stabilize pollutants, including those from crude oil spills. The microbes in the soil around the plant roots play a significant role in breaking down the hydrocarbons. Statement 4 is incorrect: The effectiveness and speed of bioremediation are dependent on various factors such as the type of oil, environmental conditions (like temperature and oxygen levels), and the specific microorganisms involved. While it is considered a more environmentally friendly and often less expensive option, it can be a slow process. Other methods like mechanical removal (using booms and skimmers) or in-situ burning might be faster and more effective in certain situations. |



© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved