Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
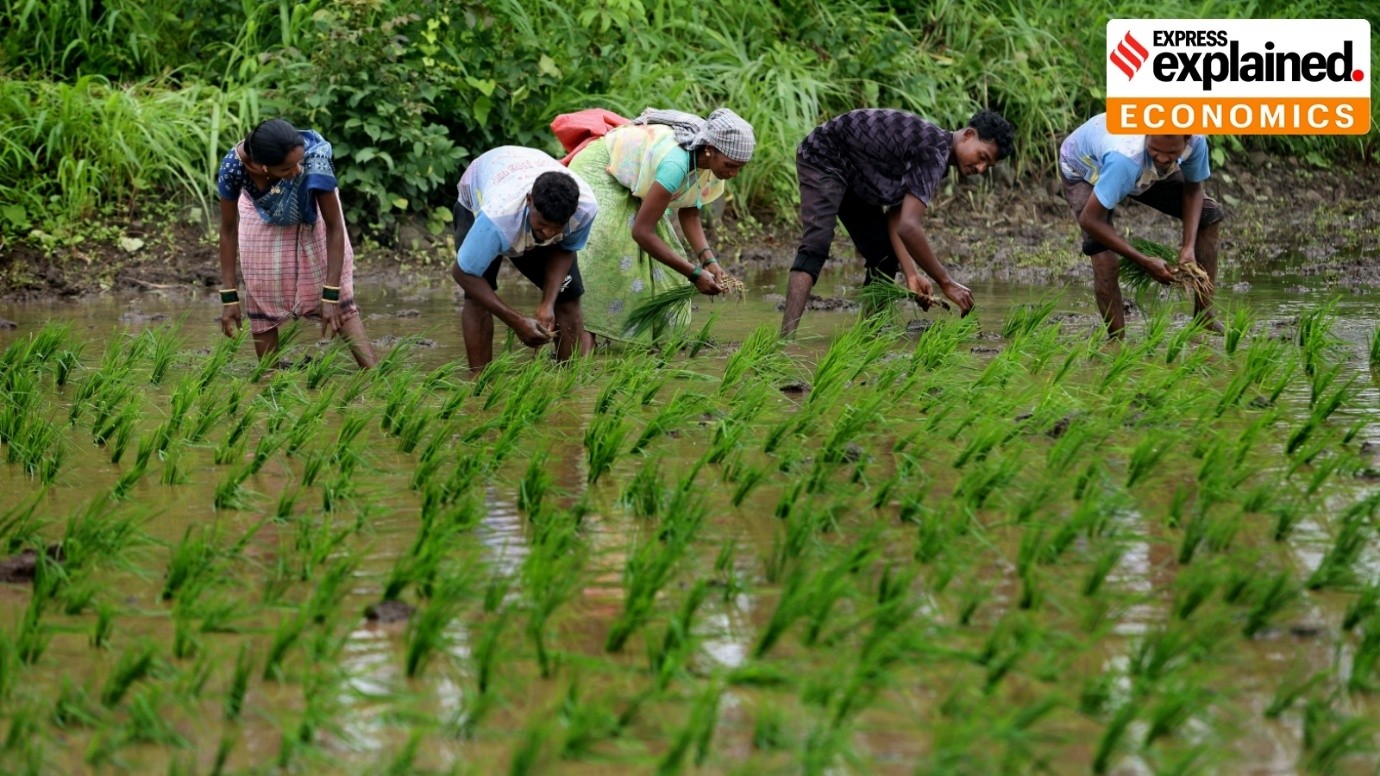
- Odisha is promoting climate-resilient agriculture through rice fallow initiative.
Rice Fallow Initiative
- The Rice Fallow Initiative in Odisha represents a pivotal step towards fostering climate-resilient agricultural practices in the region.
- By actively encouraging the cultivation of short-duration pulse and oilseed crops in rice fallow lands, the initiative aims to optimize land utilization, enhance farmers’ income, and champion regenerative agriculture principles.
Utilizing Residual Moisture:
- One of the core strategies of the initiative involves capitalizing on the residual moisture present in the soil post-rice harvest.
- This moisture, although often overlooked, proves to be adequate for the cultivation of short-duration pulse and oilseed crops.
- By efficiently utilizing these resources, farmers can intensify crop production sustainably while simultaneously boosting land productivity.
Addressing Agricultural Challenges:
- The Rice Fallow Initiative also addresses longstanding agricultural challenges prevalent in eastern India, particularly in Odisha.
- Rice fallow lands, which traditionally remained uncultivated after rice harvest, are transformed into productive assets through the introduction of tailored technologies and crop varieties suited to the landscape.
- This shift not only enhances farm income but also contributes significantly to food and nutritional security in the region.
Scope in Odisha:
- Given Odisha's substantial cultivable area, which exceeds 6.18 million hectares, and its reliance on rice cultivation to meet food demands, the potential impact of the Rice Fallow Initiative is profound.
- With rice crops typically covering around 60% of the total sown area during the Kharif season, the initiative holds promise for diversifying agricultural production and improving resilience against climate variability.

Challenges in Rabi Season:
- However, challenges persist, particularly during the Rabi season when limited irrigation facilities constrain crop production.
- Traditional agricultural practices like the Paira cropping system, once prevalent in coastal areas, have dwindled due to changing climatic patterns.
- This underscores the importance of initiatives like the Rice Fallow Initiative in revitalizing agricultural landscapes and ensuring sustainable crop production.
Potential of Rice Fallow Land:
- The sheer magnitude of rice fallow land in Odisha, estimated at approximately 1.6 million hectares, presents a significant opportunity for agricultural transformation.
- By harnessing just a fraction of this land—about 1 million hectares—for cultivating short-duration pulse and oilseed crops during the Rabi season, Odisha can substantially increase crop production and enhance food security.
Promoting Rice Fallow Management:
- Central to the success of the Rice Fallow Initiative is the promotion of effective rice fallow management practices.
- These practices not only improve soil health and climate resilience but also contribute to enhanced crop coverage, reduced soil degradation, and increased soil nutrient levels.
- The government of Odisha is committed to scaling up these efforts in the coming years to maximize the initiative's impact.
Implementation and Success:
- The successful implementation of the initiative during the 2022-23 and 2023-24 Rabi seasons is a testament to its efficacy.
- By covering substantial land areas across all 30 districts of the state, the initiative has demonstrated its potential to achieve objectives such as optimal utilization of residual soil moisture, increased cropping intensity, and enhanced production of pulses and oilseeds.
Objectives of the Scheme:
- The overarching objectives of the scheme include restoring soil health, fostering better market linkages, and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
- By targeting crops such as green gram, black gram, field pea, Bengal gram, grass pea, lentil, mustard, and sesamum, the initiative aims to diversify crop production and enhance resilience against environmental stressors.
Support Mechanisms:
- To support farmers in adopting regenerative agricultural practices, the initiative provides access to eco-friendly agri-inputs such as bio-fertilizers, bio-pesticides, and integrated pest management techniques.
- Additionally, balanced nutrient management and soil acidity amelioration strategies are being employed to improve crop yields and ecosystem health.
Addressing Soil Acidity:
- An integral component of the initiative is addressing soil acidity, which poses a significant hurdle to improving the productivity of non-paddy crops.
- Through initiatives like "Acid Soil Management," dolomitic limestone is provided to farmers for the amelioration of acid soils, thereby enhancing soil fertility and crop productivity.
National Impact:
- Beyond its localized impact in Odisha, the Rice Fallow Initiative sets a precedent for sustainable crop management practices nationwide.
- By integrating climate resilience and nutrition sensitivity into agricultural programs, Odisha is not only leading the way in promoting regenerative agriculture but also contributing to broader efforts aimed at ensuring food security and environmental sustainability across the country.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Evaluate the impact of Odisha's Rice Fallow Initiative on enhancing climate-resilient agriculture. Discuss its objectives, implementation strategies, and outcomes, with a focus on addressing agricultural challenges during the Rabi season. Assess the potential national implications of such initiatives for sustainable crop management practices in India.
|