Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
The development of new niche base station solutions by the IIITB COMET Foundation (COMET), Bengaluru, represents a significant stride towards realizing the government's vision of affordable connectivity for all.
Details
- The aim is to develop high-speed and reliable connectivity solutions at a viable cost for unconnected and remote areas, aligning with the government's vision of ensuring connectivity for all.
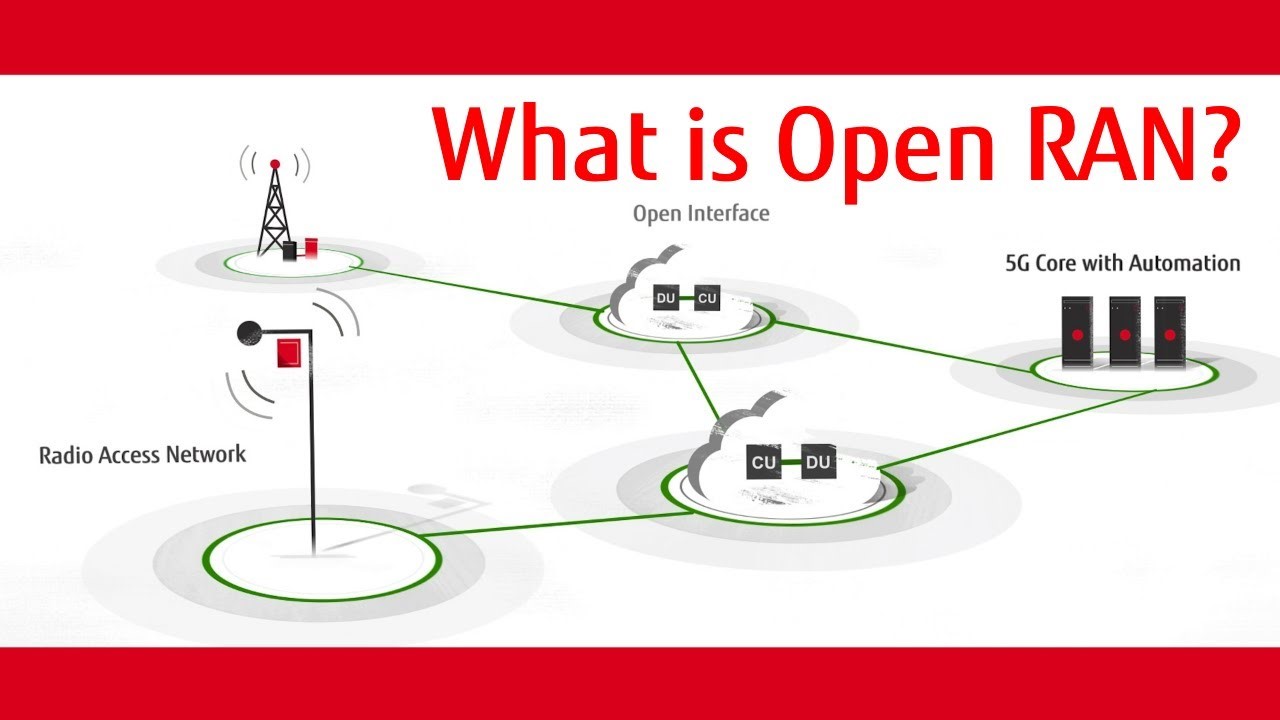
- The base station solutions are designed for Open Radio Access Network (ORAN), a critical component of next-generation telecommunications infrastructure.
- ORAN solutions disaggregate software and hardware components, making it easier, efficient, and economically viable to provide internet access in remote areas.
Features and Benefits
- Cost-Effectiveness: By breaking down Radio Access Network (RAN) functions and removing vendor lock-in, Open RAN solutions help reduce network costs and complexity, making connectivity more affordable.
- Interoperability: Open RAN facilitates smooth interoperation between cellular network equipment provided by different vendors, promoting competition and innovation.
- Spectral and Energy Efficiency: The ORAN base station solutions developed by COMET focus on creating spectral and energy-efficient wireless communications technology for 5G and 5G-Advanced radio networks.
- Capacity Enhancement: The introduction of revolutionary ORAN technology, such as harnessing multiple antennas on cell towers, promises to enhance cell coverage and boost capacity by up to three-fold compared to existing 4G networks.
.jpg)
About ORAN
- Open RAN refers to a disaggregated approach to building radio access networks (RANs) that allows for interoperability between hardware and software components from different vendors.
- It aims to break down the traditional monolithic RAN architecture, enabling network operators to mix and match components from various suppliers.
Components:
- RAN Hardware: This includes baseband units (BBUs), remote radio units (RRUs), antennas, and other physical equipment used to transmit and receive wireless signals.
- RAN Software: Software-defined components responsible for controlling and managing the RAN hardware, including radio resource management (RRM), beamforming, and spectrum allocation.
- Open Interfaces: Standardized interfaces that allow different hardware and software components to communicate and interoperate, facilitating vendor-neutral deployments.
Benefits:
- Vendor Neutrality: Open RAN enables network operators to select best-of-breed components from multiple vendors, promoting competition and innovation.
- Interoperability: Standardized interfaces ensure compatibility between different components, reducing vendor lock-in and allowing for more flexible network deployments.
- Cost Reduction: By leveraging commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) hardware and open-source software, Open RAN can potentially lower deployment and operational costs compared to proprietary solutions.
- Faster Innovation: With an open ecosystem, developers can more easily introduce new features, services, and optimizations, accelerating the pace of innovation in RAN technology.
Challenges:
- Performance and Optimization: Ensuring that disaggregated components work seamlessly together and deliver the required performance levels can be challenging, particularly for latency-sensitive applications like ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC).
- Integration Complexity: Integrating components from multiple vendors and managing interoperability issues requires robust testing and validation processes.
- Security Concerns: Open RAN introduces new security considerations, as the disaggregation of hardware and software may increase the attack surface and complexity of securing the network.
- Standardization: Developing and maintaining open interfaces and standards is essential for the success of Open RAN but requires collaboration among industry stakeholders and standards bodies.
Significance:
- Diversification of Supply Chain: Open RAN aims to reduce reliance on a small number of traditional vendors, promoting a more diverse and competitive ecosystem of RAN suppliers.
- Flexibility and Innovation: By enabling interoperability and encouraging competition, Open RAN can drive innovation and offer network operators greater flexibility in designing and optimizing their networks.
- Global Connectivity: Open RAN has the potential to democratize access to wireless technology by lowering barriers to entry for new vendors and fostering the deployment of mobile networks in underserved areas.
- 5G Evolution: As 5G networks continue to evolve and expand, Open RAN provides a framework for deploying and scaling next-generation RAN infrastructure in a cost-effective and efficient manner.

Conclusion
The development of new niche base station solutions by COMET represents a significant milestone in advancing telecommunications infrastructure in India. By focusing on affordability, interoperability, and efficiency, these solutions contribute to bridging the digital divide and empowering communities with access to connectivity.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Open RAN represents a paradigm shift in the design and deployment of wireless networks, offering the promise of increased flexibility, interoperability, and innovation. Elaborate. (15 marks)
|












