Description
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: blog.researchandranking.com
Context: Traditional advice suggests buying undervalued assets during market downturns, emphasizing intrinsic value, while momentum investing involves buying assets with upward price trends, focusing on continued momentum rather than intrinsic value.
Details
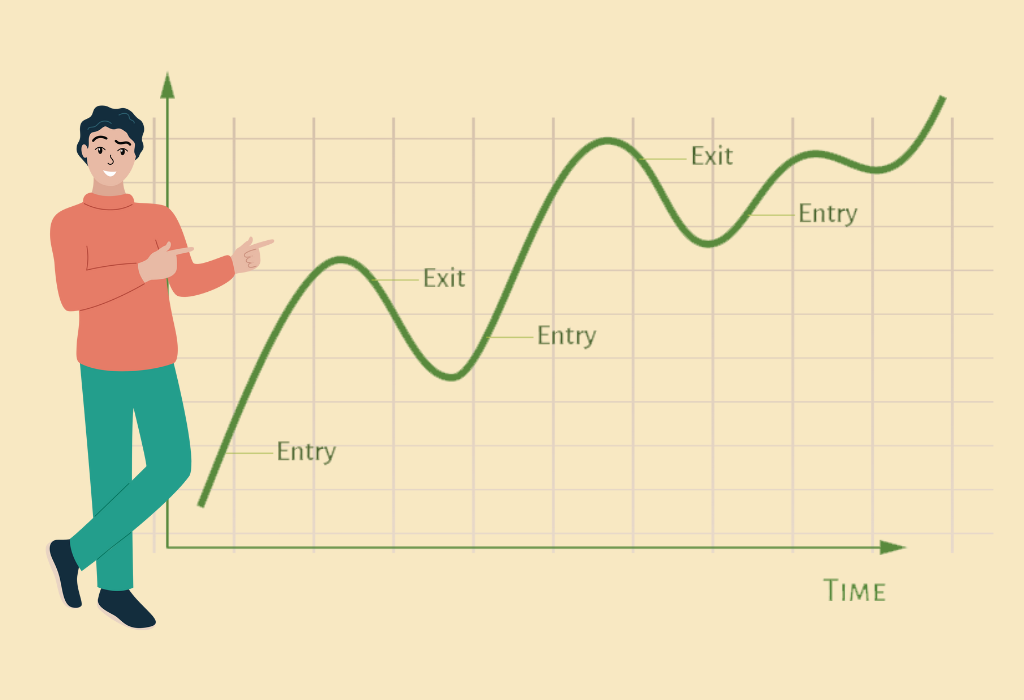
- Momentum investing is a strategy where investors focus on buying assets that have shown a consistent upward trend in their prices and selling assets that have shown a consistent downward trend. This strategy is based on the belief that trends in asset prices tend to persist over time, allowing investors to capitalize on the momentum and make profitable trades.
Key concepts and aspects of momentum investing
Buy High, Sell Higher Philosophy
- Traditional investment advice often emphasizes buying assets when they are undervalued, especially during times of financial crisis. This is based on the "buy low, sell high" principle.
- Momentum investing, on the other hand, adopts a "buy high, sell higher" approach. Investors identify assets with rising prices, expecting the momentum to continue, allowing them to sell at even higher prices in the future.
Trend Recognition
- Momentum investors believe that discernible trends exist in asset prices, and these trends tend to persist. Identifying and participating in these trends early on is crucial for making significant profits.
Limited Fundamental Analysis
- Unlike traditional value investors who conduct in-depth analyses of a company's fundamentals, momentum investors often rely solely on the observable trend in the asset's price.
- Critics argue that this lack of fundamental analysis may lead to unsustainable price movements, as investors may be driven by the trend rather than the intrinsic value of the asset.

Combining Value and Momentum Investing
- Some investors combine value investing with momentum investing. This involves considering both the intrinsic value of an asset and its current trend.
- The goal is to avoid locking money in undervalued assets for extended periods and benefit from the existing trend toward intrinsic value.
Passive Investing and Momentum
- Momentum investors argue that even passive investing strategies, such as investing in index funds, are inherently based on momentum.
- Index funds, like the S&P 500 or Dow Jones, comprise companies with high market capitalization, often driven by consistent stock price growth rather than fundamental factors.
Methods of Gauging Momentum
- Simple momentum strategies involve buying assets with the highest percentage gains over a specified period and selling those with the steepest percentage losses.
- More sophisticated approaches may involve analyzing price charts, comparing an asset's performance to benchmark indices, or assessing the strength of the trend.
Sideways Movement and Cash Holding
- Not all assets exhibit clear trends; some may move sideways. During such periods, momentum investors may choose to stay out of the market and hold cash until a clear trend emerges.
.jpg)
Conclusion
- Momentum investing relies on the idea that trends persist, and by identifying and riding these trends, investors can generate significant returns. However, critics argue that the strategy may lead to inflated asset prices divorced from their intrinsic value, potentially resulting in losses for late-joining investors when prices are correct.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. What is the core philosophy of momentum investing?
A. Buy assets at their intrinsic value.
B. Follow rising price trends for gains.
C. Invest in undervalued assets during crises.
D. Hold cash during market uncertainties.
Answer: B
Explanation:
Momentum investing involves buying assets with rising prices, expecting the upward trend to continue for profitable gains.
|











