Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context: There were two documents signed between India and Japan - Renewal of MOC (Memorandum of Cooperation) in the Japanese language, essentially focussing on higher level language learning and second agreement was Exchange of notes on JICA loan for 300 bn$ on Mumbai-Ahmedabad high-speed railway project.
Details:
Highlights of the visit:
- 2023 has been announced as the India-Japan year of tourism.
- Japanese PM formally invited Indian PM to G7 Hiroshima Summit which was accepted.
- Both reaffirmed commitment to a peaceful, stable, and prosperous Indo-Pacific with the latter calling India an indispensable partner
.jpeg)
Free and open Indo-Pacific (FOIP) policy:
- Japanese Prime Minister unveiled his plan for a "free and open Indo-Pacific" with a focus on India's increasingly significant role in the region.
- Japan announced $75 billion to bolster Japan’s free and open Indo-Pacific (FOIP) policy. Japan would mobilise a total of more than $75 billion in public and private funds in the Indo-Pacific region by 2030 in infrastructure “and grow together with other countries.
- The policy will be based on four pillars, including
- principles for peace and rules for prosperity,
- addressing challenges in an Indo-Pacific way,
- multi-layered connectivity, and
- extending efforts for security and safe use of the sea to the air.
- Japan referred to the Ukraine conflict seven times as it condemned Russia’s actions in Ukraine saying Moscow’s aggression had “obliged” the world to face the most fundamental challenge of defending peace.
- They also discussed in detail defence and economic cooperation.
- Japan will promote the Bay of Bengal-north-east India value chain concept in cooperation with India and Bangladesh for the development of the entire region.
JICA Loan:
- Earlier in 2022, JICA signed a loan agreement with India to provide ODA loan of 100,000 million Japanese Yen as Tranche 3 on the 'Project for the Construction of Mumbai-Ahmedabad High-Speed Rail (MAHSR).'
- The objective of the project is to develop a high-frequency mass transportation system by constructing the High-Speed Rail between Mumbai and Ahmedabad, using Japan's Shinkansen technology (Bullet Train).

Background of relations:
History:
- Exchange between Japan and India is said to have started in the 6th century when Buddhism was introduced to Japan.
- Indian culture filtered through Buddhism greatly influenced Japanese culture and this is the source of the sense of affinity between Japanese and Indian society.
- Japan and India signed a peace treaty and established diplomatic relations on April 28, 1952.
- After the visit of Japanese Prime Minister Nobusuke Kishi to India in 1957, Japan began lending yen to India in 1958, the first yen loan issued by the Japanese government.
- Prime Minister Yoshiro Mori's visit to India in August 2000 gave impetus to strengthening Japan-India relations. Mr Mori and Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee decided to create a "global partnership between Japan and India".
Post-2014:
- In 2014, the Prime Minister made his first bilateral visit outside India to close neighboring Japan.
- During the visit, India-Japan relations developed into a special strategic global partnership.
- The Prime Minister referred to India-Japan relations as one of the most natural partnerships in the region.
- A special India-Japan strategic global partnership based on the shared values of democracy, freedom and the rule of law is important for the promotion of peace, prosperity and stability in the Indo-Pacific region.
- India and Japan have both focus on the larger vision of act East.
Cooperation in Security Fields:
- The Joint Declaration on Security Cooperation between Japan and India was issued in 2008.
- There are also various frameworks of security and defense dialogue between Japan and India including Foreign and Defense Ministerial Meeting (“2+2” meeting), annual Defense Ministerial Dialogue and Coast Guard-to-Coast Guard dialogue.
- In September 2022, the second ”2+2” meeting was held in Tokyo.
- Agreement Concerning Reciprocal Provision of Supplies and Services between the Self-Defense Forces of Japan and the Indian Armed Forces (so-called “Acquisition and Cross-Servicing Agreement” or ACSA) was signed in 2020.

Economic Relations:
- India is Japan's 18th largest trading partner, Japan was India's 13th largest trading partner in 2021.
- Also, direct investment from Japan to India increased and Japan became the 5th largest investor in India in 2021.
- Japanese private sector interest in India is on the rise and now, by 2021, around 1,439 Japanese companies have branches in India.
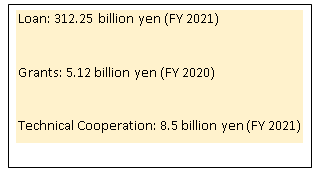
- India has received Japan's largest ODA loan in recent decades. For example: Delhi Metro.
- Japan continues to focus on the synergy between ''Act East'' policy and ''Partnership for Quality Infrastructure'' thereby enhancing connectivity with North east
Culture:
- Under the theme "Resurgent Japan, Vibrant India: New Perspectives, New Exchanges", various cultural events are organized in Japan and India to promote mutual understanding between the two countries.
- In 2022, Japan will celebrate anniversaries with seven countries in West Asia, including India.
- Japan has designated 2022 as "Japan-Southwest Asia Exchange Year" in order to take relations with West Asian countries to a new level.
Number of Residents: Number of Indian nationals residing in Japan: 40,752 (as of June, 2022)

|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q) India-Japan relations have truly developed into a special strategic global partnership. Examine. (150 words)
|

https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/japans-75-billion-boost-for-free-open-indo-pacific/articleshow/98833193.cms?from=mdr












