Description
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.mei.edu/publications/enhancing-india-oman-economic-engagement-four-promising-initiatives
Context: A delegation from the National Archives of India (NAI) visited the National Records and Archives Authority (NRAA) of Oman to explore potential areas of collaboration in the field of archival management.
Key Highlights
As a gesture of goodwill, India provided the NRAA with:
- A list of 70 select documents pertaining to Oman is available in the NAI (covering 1793-1953 and various topics).
- 523 pages of document copies covering significant events like the change of the Omani flag (1868), succession of Sayyid Faisal bin Turki (1888), Sultan of Muscat and Oman visit to the Viceroy of India (1937), and the Treaty of Friendship, Commerce and Navigation (1953) in English, Hindi, and Arabic.
- Facsimile prints of three important treaties (1798, 1800, 1865).
Outcomes
- Both parties agreed on the need to formalize cooperation between NAI and NRAA.
- A draft Executive Programme of Cooperation (EPC) was finalized for approval by relevant authorities.
EPC Activities (proposed)
- Joint Exhibition and Conference: Organizing an exhibition showcasing selected historical materials from both archives alongside a conference highlighting the historical connections between India and Oman.
- Digital Document Exchange: Establishing a framework for exchanging digital copies of documents that hold mutual interest to enrich both collections.
- Expert Exchange Program: Facilitating an exchange program for experts in digitization and preservation, allowing them to share knowledge and best practices.
- Joint Publication: Collaborating on a publication based on curated archival materials from both archives.

India-Oman Relations
Historical Connections
- Ancient Trade Links: Maritime trade and cultural exchange have existed for over 5,000 years, evident through archaeological findings and historical records.
- Formal Ties: Diplomatic relations were established in 1955, marking the beginning of official cooperation.
- Strategic Partnership: Upgraded to a "Strategic Partnership" in 2008, signifying further strengthening of ties across various sectors.
Political Cooperation
- Frequent High-Level Interactions: Regular visits by heads of state, government officials, and ministers foster strong political understanding and collaboration.
- Regional and International Collaboration: Both nations collaborate on diverse issues within organizations like the United Nations, Non-Aligned Movement, and G20, promoting shared interests and perspectives.
- Oman as India's Gulf Bridge: Oman plays a crucial role as an interlocutor for India within the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), Arab League, and IORA, facilitating smoother engagement in these regions.
Economic Interdependence
- Trade Dynamics: India is Oman's second-largest non-oil export market and fourth-largest overall trade partner (as of 2023).
- Mutually Beneficial Trade Flow: After China, India is Oman's second-biggest destination for crude oil exports. In return, India exports various goods like tea, coffee, spices, dairy products, textiles, machinery, and electrical equipment to Oman.
- Significant Indian Investments: Indian companies have made substantial investments in Oman's oil and gas, IT, and infrastructure sectors, contributing to their development and economic diversification.
Defence and Security Collaboration
- Pioneering Partnership: Oman holds the distinction of being the first Gulf nation to establish formal defence relations with India.
- Joint Military Exercises: Regular exercises like "Eastern Bridge," "Al Najah," and "Naseem Al Bahr" strengthen military cooperation and interoperability.
- Strategic Berthing Rights: India enjoys berthing rights in Omani ports, which are strategically valuable for anti-piracy operations in the Gulf of Aden.
- Shared Security Agenda: Both nations collaborate on combating terrorism, maritime security concerns, and cyber security threats, contributing to regional stability.

Cultural Connections
- Flourishing Indian Diaspora: Approximately 624,000 individuals of Indian origin resided in Oman as of 2021, forming a significant and well-integrated expatriate community.
- Generational Ties: Many Indian families have been in Oman for generations, contributing to the cultural tapestry and fostering closer human interactions.
- Education and Healthcare Links: Oman attracts Indian students seeking higher education opportunities while increasing numbers of Omani patients utilize India's advanced healthcare facilities.
- Cultural Exchange Platforms: Regular cultural events, exchange programs, and collaborations in art, music, and film further enrich the understanding and appreciation of each other's cultural heritage.
Future Prospects
- Economic Diversification: Potential for enhanced cooperation in renewable energy, tourism, and healthcare sectors, fostering mutual economic growth and diversification.
- People-to-People Bridges: Continued endeavours to encourage cultural exchange programs, student mobility, and knowledge-sharing initiatives to enrich people-to-people connections.
- Strategic Partnership Evolution: Continuous efforts to deepen collaboration in the spheres of defence, security, and emerging challenges like cyber security, ensuring regional stability and collective security.
- Global Cooperation Platforms: Collaboration on global issues of shared interest within international organizations to promote peace, development, and a rules-based international order.
|
OMAN
|
|
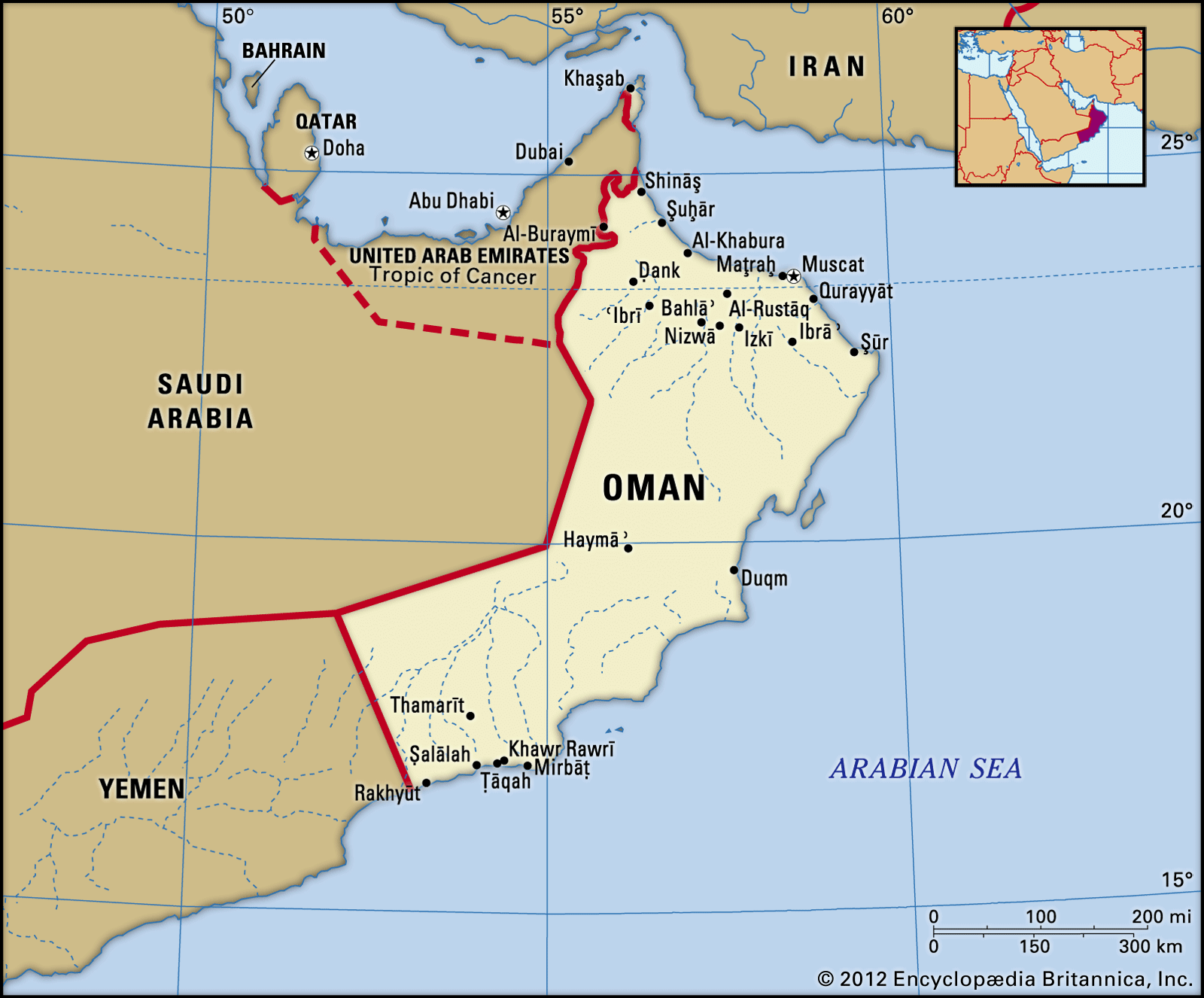
Bordering Countries
|
United Arab Emirates
Saudi Arabia
Yemen
|
|
Water Bodies
|
Arabian Sea
Gulf of Oman
|
|
Economy
|
Dominant Sector: Oil and Gas (accounts for a significant portion of GDP)
Growing Sectors: Tourism, Logistics, Fisheries
Challenges: Diversification away from oil dependence
|
|
Political System
|
Type: Hereditary Monarchy
Limited political participation: The Sultan holds significant executive power.
|
|
Physical Features
|
Terrain: Mostly mountainous desert plateau with coastal plains.
Hajar Mountains: Run along the northern and eastern coasts, with Jabal Shams being the highest peak.
Rub' al Khali desert: Covers a large portion of the south, known as the "Empty Quarter."
Dahliyah Sands Wadis: Seasonal river beds that become temporary waterways during heavy rains.
Oases: Scattered fertile areas with natural springs or underground water sources.
|
|
Environment
|
Climate: Arid with hot summers (average highs exceeding 40°C) and mild winters (average lows around 15°C).
Rainfall: Scarce and sporadic, concentrated in the winter months.
Biodiversity: Diverse, with over 550 bird species, 120 mammal species, and unique flora adapted to the arid climate.
Environmental challenges: Desertification, water scarcity, habitat loss due to development.
|
Must Read Articles:
INDIA OMAN RELATIONS: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/india-oman-relations-5
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Which country does not share a land border with Oman?
A) Saudi Arabia
B) Yemen
C) Iran
D) Qatar
Answer: D
Explanation:
Oman is situated in the southeastern corner of the Arabian Peninsula, bordered by Saudi Arabia to the west, Yemen to the southwest, and the Strait of Hormuz to the north. It does not share a land border with Qatar, which is located across the Persian Gulf.
|












