 Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Cabinet approves signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between India and Oman on cooperation in the field of Information Technology.
India Oman Relations
Historical Relations:
- The maritime trade routes connecting the Sumerian and Harappan civilizations underscore the deep historical ties between India and Oman.
- These ancient links, particularly through Gujarat and the Malabar Coast, have left a lasting cultural imprint on both nations.
Political Relations:
- Political engagement has evolved into a strategic partnership, positioning Oman as a key ally for India.
- The collaboration extends to regional forums, including the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), Arab League, and the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), showcasing a shared commitment to regional stability.
Oman’s Friendly Relation:
- Oman's unique stance as one of the few Arab countries maintaining close ties with India during and after the Cold War is a testament to the strength of the bilateral relationship.
- This enduring friendship has transcended geopolitical shifts in the Arab world.
G20 Summit:
- The invitation to Oman as a guest country during India's G20 Presidency in 2023 reflects the exceptional nature of the diplomatic tie It symbolizes the recognition of Oman's significance in India's global partnerships.
Diplomatic Relations:
- Established in 1955, the diplomatic relationship between India and Oman has matured into a strategic partnership since 2008. Built on mutual trust and shared interests, the diplomatic ties have fostered cooperation across various sectors.
Economic Relations:
- India's position as one of Oman's top trading partners underscores the economic collaboration.
- Beyond being the second-largest market for Oman's crude oil, the economic relations encompass diverse sectors, making both nations integral to each other's economic growth.
Crude Oil Trade:
- India stands as the second-largest market for Oman's crude oil.
- This position is exceeded only by China in Oman's global crude oil export destinations.
Non-Oil Exports:
- In the realm of non-oil exports, India maintains its position as the second-largest market for Oman, following Saudi Arabia. This dynamic reflects the diversification of trade ties beyond the energy sector.
Main Items of India’s Export to Oman:
India exports a diverse range of products to Oman, with key items including:
- Mineral fuels, mineral oils, and products of their distillation.
- Inorganic chemicals, organic or inorganic compounds of precious metals.
- Iron and steel.
- Ships, boats, and floating structures.
Main Items of India’s Import from Oman:
Conversely, India imports various commodities from Oman, with a focus on:
- Mineral fuels, mineral oils, and products of their distillation.
- Inorganic chemicals, organic or inorganic compounds of precious metals.
- Fertilizers.
- Iron and steel.
- Ships, boats, and floating structures.
Oman-India Joint Investment Fund (OIJIF):
- The creation of OIJIF in 2010 as a joint venture showcases a commitment to bilateral investments.
- This Special Purpose Vehicle, equally owned by the State Bank of India and Oman's State General Reserve Fund, facilitates strategic investments in India.
Rupay Debit Card:
- The launch of the Rupay debit card in Oman is a tangible expression of India's initiative to promote digital public infrastructure globally.
- It not only enhances financial connectivity but also signifies the technological footprint of India in the international arena.
Defence Cooperation:
- Oman stands out as India's closest defence partner in the Gulf region. Joint exercises across maritime, military, and air domains, including Naseem al-Bahr, Al Najah IV, and Eastern Bridge VI, illustrate the depth of defence collaboration
Operation Sankalp:
- The Indian Navy's Operation Sankalp during the Persian Gulf crisis in 2019 demonstrated India's commitment to ensuring the safety of its flagged ships off the coast of Oman. It highlights the collaborative efforts in maritime security
Cultural Relations:
- The deep socio-cultural bond between India and Oman is evident in various initiatives, such as yoga events and the Festival of India. Example: ‘Oman yoga yatra’ and ‘Yoga for Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam’ was launched.
- These activities not only celebrate cultural richness but also foster a better understanding between the people of both nations.
Indian Community in Oman:
- The organized Indian community in Oman, represented by social clubs and linguistic wings, serves as a cultural bridge.
- These groups contribute to preserving cultural heritage and fulfilling the social needs of the expatriate Indian population.
Pravasi Bharatiya Samman Awards:
- The recognition through the Pravasi Bharatiya Samman Awards highlights the significant contributions of the Indian diaspora in Oman.
- This acknowledgment strengthens the bonds between the two nations, recognizing the role of individuals in enhancing bilateral relations.

Significance of Oman in India's foreign policy framework
The significance of Oman in India's foreign policy framework can be understood through various strategic, economic, and diplomatic dimensions:
Strategic Importance:
- Maritime Control: Oman controls the southeastern entrance to the Strait of Hormuz, a critical chokepoint for global oil shipments. This strategic position enhances India's maritime security and trade interests in the region.
Energy Security:
- Oil and Gas Cooperation: Oman is a crucial partner in India's quest for energy security. It is a significant supplier of crude oil, and bilateral agreements and investments in the energy sector contribute to India's diverse energy sources.
Diplomatic Collaboration:
- Regional Forums: Oman serves as an important interlocutor for India at regional forums such as the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), Arab League, and Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA). This diplomatic collaboration strengthens India's presence and influence in the Middle East.
Historical and Cultural Ties:
- Trade and Cultural Links: The historical trade routes and cultural exchanges between India and Oman foster a deep socio-cultural bond. This shared history provides a foundation for diplomatic and economic cooperation.
Defense and Security Cooperation:
- Strategic Partnership: Oman is recognized as India's closest defense partner in the Gulf region. Joint military exercises and defense collaboration contribute to regional security and stability.
Economic Collaboration:
- Trade Relations: Oman is among India's top trading partners, and the economic collaboration extends beyond crude oil to non-oil sectors. Diversified economic ties contribute to mutual growth and development.
Counter-Terrorism Cooperation:
- Shared Security Concerns: Both nations share concerns related to regional security and counter-terrorism efforts. Collaboration in intelligence sharing and joint initiatives contributes to the broader goal of maintaining stability in the region.
Multilateral Engagement:
- G20 Participation: Oman's inclusion as a guest country during India's G20 Presidency reflects the recognition of its importance in India's global engagement strategy.
In summary, Oman occupies a strategic position in India's foreign policy, contributing to energy security, economic growth, and diplomatic influence in the Middle East. The historical ties and multifaceted collaboration between the two nations underscore Oman's significance in shaping India's geopolitical and economic interests.
Oman
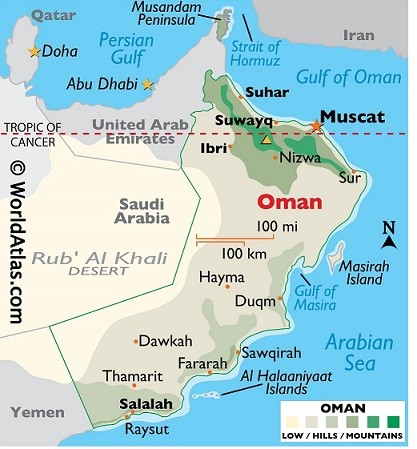
- Location: Southeastern Arabian Peninsula, bordered by UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Yemen.
- Capital: Muscat
- Topography: Al Hajar Mountains in the north, desert plains, Rub' al Khali in the central and southern regions.
- Climate: Desert climate with a monsoon-influenced region in the south (Dhofar).
- Hydrography: Seasonal rivers (Wadis), extensive coastline along the Arabian Sea and Gulf of Oman.
- Natural Resources: Abundant oil and gas reserves, minerals like copper and chromite.
- Strategic Importance: Controls the entrance to the Strait of Hormuz, a vital maritime passage.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Evaluate the strategic dimensions and economic implications of India-Oman relations, considering historical ties, energy cooperation, and diplomatic engagements. Analyze the significance of Oman in India's foreign policy framework.
|





 Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.



