




Disclaimer: Copyright infringement is not intended.
Context:
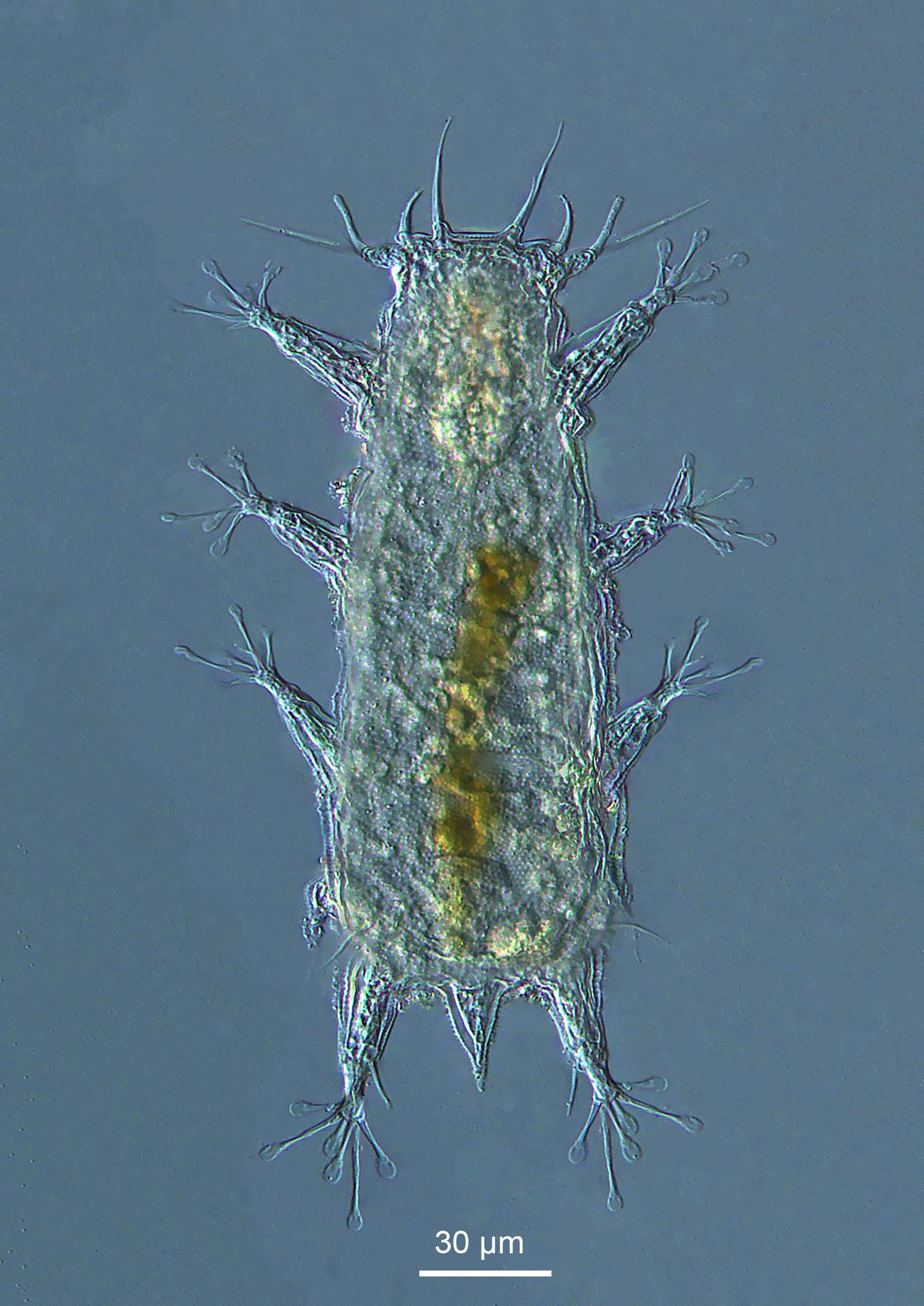
Batillipes chandrayaani
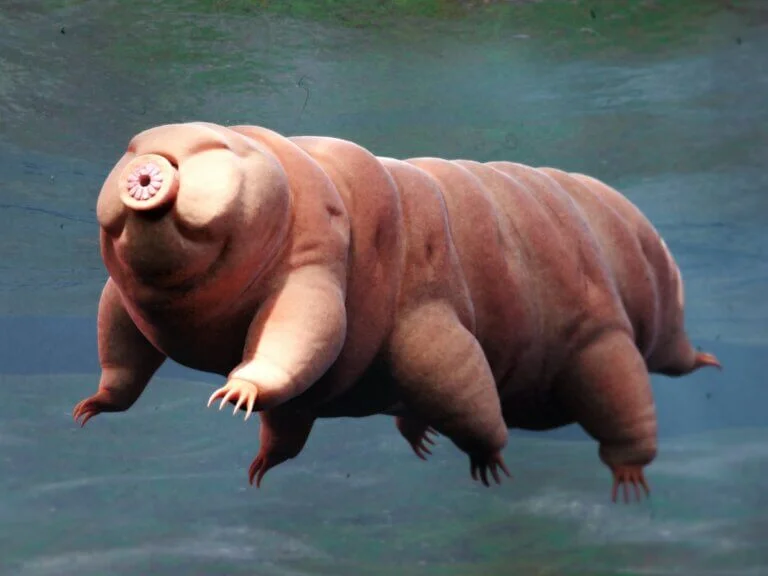
Tardigrades:
Details about Tardigrades:

Source:
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Consider the following statements about the characteristics of tardigrades: 1) They primarily inhabit terrestrial environments and are rarely found in aquatic ecosystems. 2) They possess a complex digestive system, including multiple stomach chambers for efficient food digestion. 3) They undergo a complex life cycle with seven distinct stages, including multiple larval phases. 4) Tardigrades exhibit remarkable resilience and can survive extreme environmental conditions, including exposure to vacuum and high levels of toxins. How many of the above statements are correct? A. Only one B.Only two C.All three D.None Correct Answer: A) Explanation: Statement 1 is incorrect: Tardigrades can withstand a wide range of extreme environmental conditions, including high and low temperatures, high pressures, radiation, desiccation (extreme dehydration), and exposure to vacuum. These adaptations enable tardigrades to survive in diverse habitats, ranging from polar regions to deserts and deep sea trenches. Statement 2 is incorrect: One of the most remarkable features of tardigrades is their ability to enter a state of cryptobiosis in response to unfavorable environmental conditions. During cryptobiosis, tardigrades undergo extreme dehydration and metabolic shutdown, effectively suspending their biological processes. This allows them to survive in a desiccated state until conditions become favorable again, at which point they can rehydrate and resume normal activity. Statement 3 is incorrect: Tolerance to Toxins: Tardigrades have been found to exhibit remarkable tolerance to various toxins and pollutants, including heavy metals and chemicals. They can detoxify harmful substances and survive exposure to high levels of toxins that would be lethal to most other organisms. Statement 4 is incorrect: Tardigrades have attracted significant attention from scientists due to their unique biology and extreme resilience. They are studied for their potential applications in fields such as astrobiology, biotechnology, and medicine. Their ability to survive extreme conditions and recover from cryptobiosis has implications for understanding the mechanisms of stress tolerance and adaptation in living organisms. |





© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved