Description
GS PAPER III: Indian Economy and issues relating to Planning, Mobilization of Resources, Growth, Development and Employment.
Context: The RBI clarification came after State Bank of India and HDFC Bank cautioned their customers against dealing in virtual currencies such as Bitcoin citing the April 2018 order of the RBI.
What did the RBI say ?
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI) said banks and other regulated entities cannot cite its April 2018 order on virtual currencies (VCs) as it has been set aside by the Supreme Court of India in 2020.
Does it clarify the policy position for cryptocurrency holders?
- RBI is developing its own virtual currency, is expected to give some relief to customers who have invested in cryptocurrencies.
- As many Indians have invested in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, the RBI move will be a big respite for them and their money – estimated to be around Rs 10,000 crore — won’t be blocked.
What are banks expected to do now?
- Banks, as well as other entities addressed above, may continue to carry out customer due diligence processes in line with regulations governing standards for Know Your Customer (KYC), Anti-Money Laundering (AML), Combating of Financing of Terrorism (CFT) and obligations of regulated entities under Prevention of Money Laundering Act, (PMLA), 2002 in addition to ensuring compliance with relevant provisions under Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) for overseas remittances.
- In other words, banks can’t take action against investors in virtual currencies following the court and RBI directives.
What’s the RBI’s position?
- The RBI’s 2018 position was more restrictive.
- It has been decided that, with immediate effect, entities regulated by the Reserve Bank shall not deal in VCs or provide services for facilitating any person or entity in dealing with or settling VCs.
- Such services include maintaining accounts, registering, trading, settling, clearing, giving loans against virtual tokens, accepting them as collateral, opening accounts of exchanges dealing with them and transfer / receipt of money in accounts relating to purchase or sale of VCs.
- The RBI had said regulated entities which already provide such services should exit the relationship within three months from the date of the circular.
- However, the RBI which is against other virtual cryptocurrencies has warned people against such currencies several times in the past.
- RBI has indicated that it is ready to launch its own digital currency.
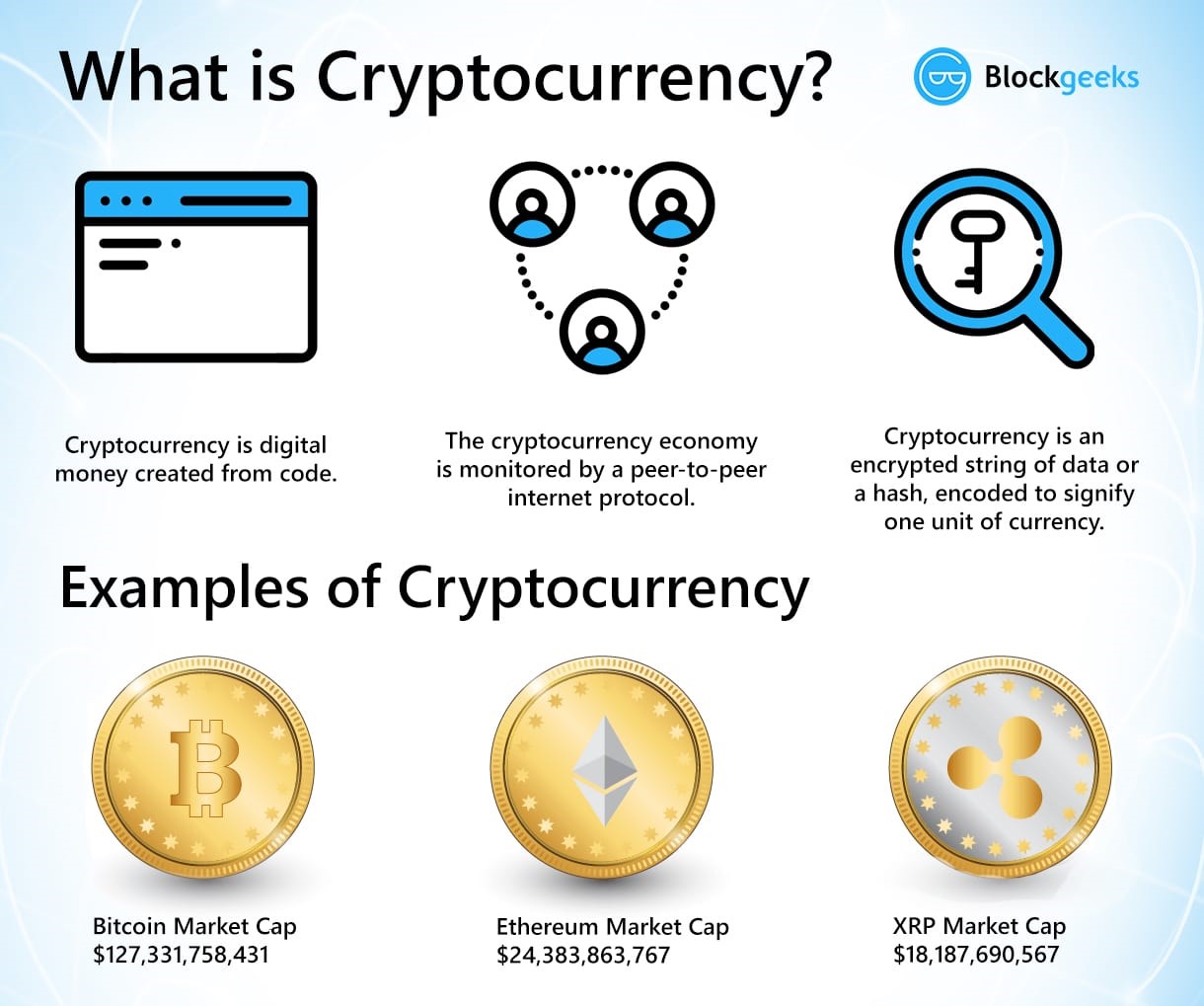
What is Cryptocurrency?
- A cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency that is meant to be a medium of exchange.
- Cryptography is a method of using encryption and decryption to secure communication in the presence of third parties with ill intent.
- It is quite similar to real-world currency, except it does not have any physical embodiment, and it uses cryptography to work.
- Because cryptocurrencies operate independently and in a decentralized manner, without a bank or a central authority, new units can be added only after certain conditions are met.
- For example, with Bitcoin, only after a block has been added to the blockchain will the miner be rewarded with bitcoins, and this is the only way new bitcoins can be generated. The limit for bitcoins is 21 million; after this, no more bitcoins will be produced.

https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-what-does-rbis-latest-circular-on-cryptocurrencies-mean-7339651/