Description
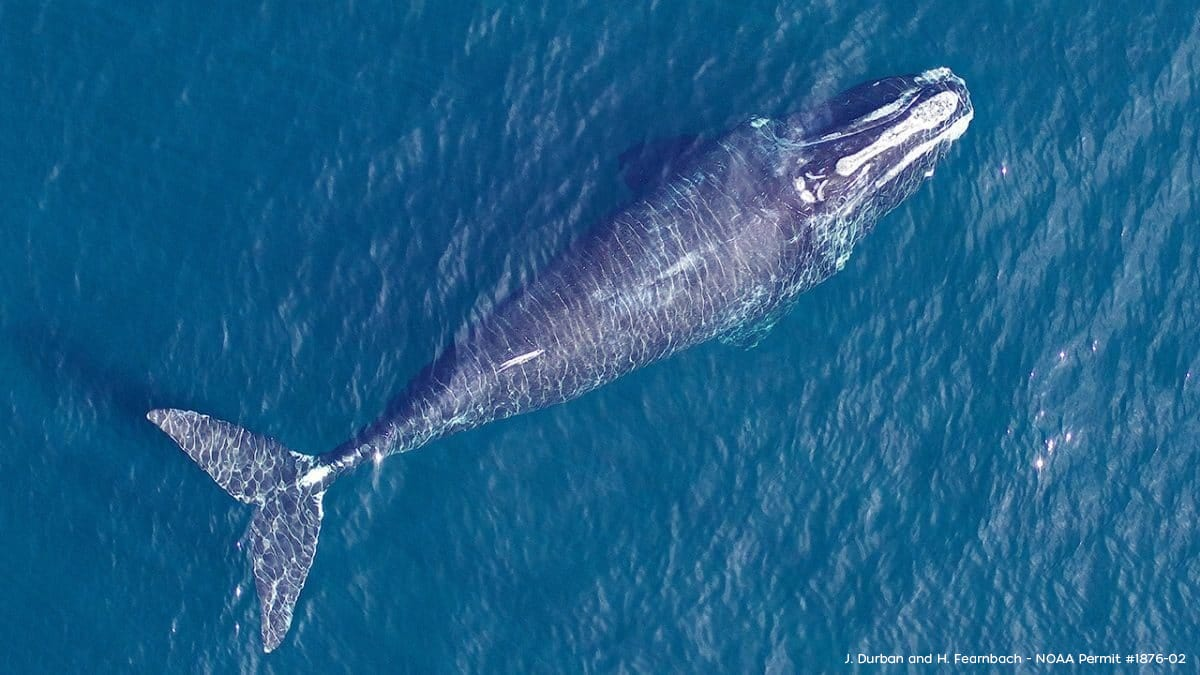

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.whoi.edu/know-your-ocean/ocean-topics/ocean-life/marine-mammals/right-whales/
Context: Scientists reveal the consequences of declining body size in critically endangered right whales, leading to a decrease in calving probability and overall health.
Key Highlights
Reduced Body Size and Calving Probability
- The study indicates that North Atlantic right whales are getting smaller, particularly in terms of body length.
- Smaller females are shown to have fewer calves, with a significant decrease in the probability of giving birth as size diminishes. This trend is concerning for the already precarious population of North Atlantic right whales.
Link to Health Decline
- The researchers suggest that the declining trend in calving probability is associated with the decreasing body size of the whales, adding to existing evidence of the declining health of the population.
- This implies that the overall health of the whales is at risk, potentially impacting their ability to reproduce and survive.

Importance of Body Size for Reproduction
- The study emphasizes the role of body size in reproduction, with the length of the whale being a crucial factor influencing the likelihood of having calves.
- The accumulation of energy reserves, specifically lipids, is mentioned as a critical aspect affected by the smaller size, potentially impacting the ability to successfully breed.
Population Threat and Extinction Risk
- North Atlantic right whales are already the most endangered among the right whale species, with just 356 individuals believed to be alive.
- The decline in calving rates increases the risk of extinction for this already vulnerable population.
Climate Change and Size Reduction
- Stressors such as climate change are suggested as possible reasons behind the decreasing size of North Atlantic right whales since 1981.
- The exact mechanisms behind the size reduction are unclear, but it is speculated to be linked to reduced nutrient availability, a phenomenon observed in various terrestrial and marine species in response to climate change.
Human-Induced Threats
- The study emphasizes the urgent need for effective protection, highlighting the vulnerability of North Atlantic right whales to human threats.
- Human-induced threats include boat strikes and entanglement in fishing gear, both of which have resulted in the death of whales, including juveniles and newborn calves.

Conclusion
- The findings of the study underscore the complex interplay between environmental factors, body size, and reproductive success in North Atlantic right whales, raising urgent concerns about the future of this critically endangered species. The call for stronger protections and conservation efforts is crucial to mitigate human-induced threats and address the challenges faced by these whales.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. What is the conservation status of North Atlantic right whales?
A) Least concern
B) Vulnerable
C) Critically endangered
D) Extinct
Answer: C
Explanation:
North Atlantic right whales are classified as critically endangered by the IUCN (International Union for the Conservation of Nature) due to their extremely low population numbers and ongoing threats.
|