Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Context
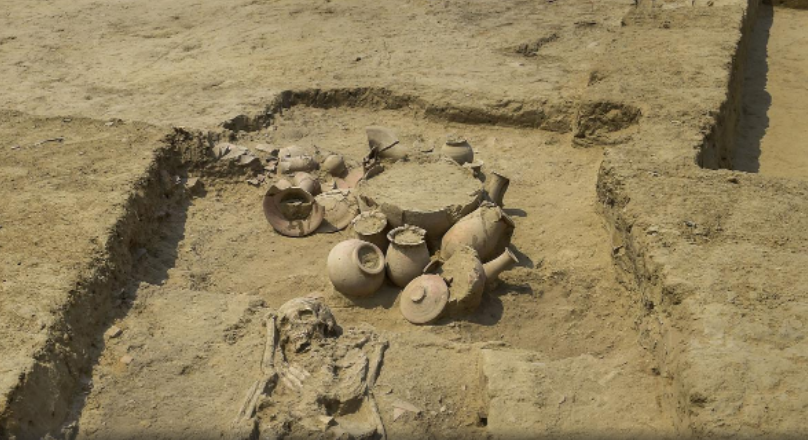
- DNA samples collected from two human skeletons unearthed at a necropolis of a Harappan-era city site in Haryana have been sent for scientific examination, the outcome of which might tell about the ancestry and food habits of people who lived in the Rakhigarhi region thousands of years ago.
- The skeletons of two women were found a couple of months ago at mound number 7 (named RGR 7 by the Archaeological Survey of India or (ASI), believed to be nearly 5,000 years old. Pots and other artefacts were also found buried next to them in a pit, part of the funerary rituals back in the Harappan Civilisation era.
About Harappan Civilisation
- Indus Valley Civilization is also known as the Harappan Civilization because Harappa was the first site to be excavated in 1921 under the supervision of Daya Ram Sahni.
- The known extent of IVC is up to Suktagendor in Baluchistan in the west; Alamgirpur (UP) in the east; Daimabad (Maharashtra) in the South; and Manda (Jammu & Kashmir) in the north.
- Indus Valley Civilization is the home to the largest of the four of its contemporary urban civilizations namely Mesopotamian or Sumerian Civilization, Egyptian Civilization, and Chinese Civilization.
- While IVC is on the banks of Indus, Egyptian Civilization flourished on the banks of the river Nile, Mesopotamian Civilization flourished on the banks of Tigris or Euphrates River and Chinese Civilization flourished on the banks of Hwang Ho River.
- Since it belongs to the Bronze/Chalcolithic age, it is also known as the Bronze Age Civilization.
- In the 1920s, the excavations were carried out in the Indus Valley regions, where ruins of the old cities were found. The first city to be unearthed was Harappa.
- In 1924, John Marshall, the then Director-General of the Department of Archaeology announced the discovery of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Features of Harappan Civilisation
- Urbanization & Town Planning
- Town planning is the most important and distinguishing feature of the Harappan Civilization. Hence, it was called an urban civilization.
- Towns were divided into parts namely citadel and lower town. Citadels were occupied by members of the ruling class and the lower town was inhabited by the common people.
- Another important feature of IVC is the drainage system. Drains were built of burnt bricks and covered by stone lids.
- Chanhudaro was the only town without a citadel.
- Agriculture & Economy
- They grew wheat and barley on a large scale. Other crops that they grew included pulses, cereals, cotton, dates, melons, pea, sesamum, and mustard.
- No clear evidence of rice has been found.
- Harappan people were mostly peasants and thus the Harappan civilization was an agro-commercial civilization.
- Harappans were the earliest people to grow cotton.
- Their most important artistic work is sealed. Seals are made of steatite and they are square.
- The most depicted animal is the bull.
- Bangle making and shell ornament making were also practised.
- Land and sea trade was in vogue in Indus Valley Civilization.
- A dockyard has been found at Lothal which is the longest building of the Harappan Civilization.
- Religion of Harappans
- Pashupati seal has been found in Mohenjodaro in which a Yogi has been depicted.
- The Yogi on the seal is surrounded by buffalo, tiger, elephant, rhinoceros, and deer.
- Signs of phallic worship have been found.
- Harappans worshipped the mother Goddess. It is evident from the terracotta figurine recovered from Harappa.
- A building called Great Bath has been found at Mohenjodaro. It was meant for ritual bathing.
- No evidence of temples has been found in this civilization.
- Amulets were found in large numbers
- Script of Harappans
- The Harappans knew the art of writing.
- More than 4000 specimens of scripts were found in excavations.
- The script, however, is not alphabetical but pictographic and it has not been deciphered yet.
Important Sites of Harappan Civilisation
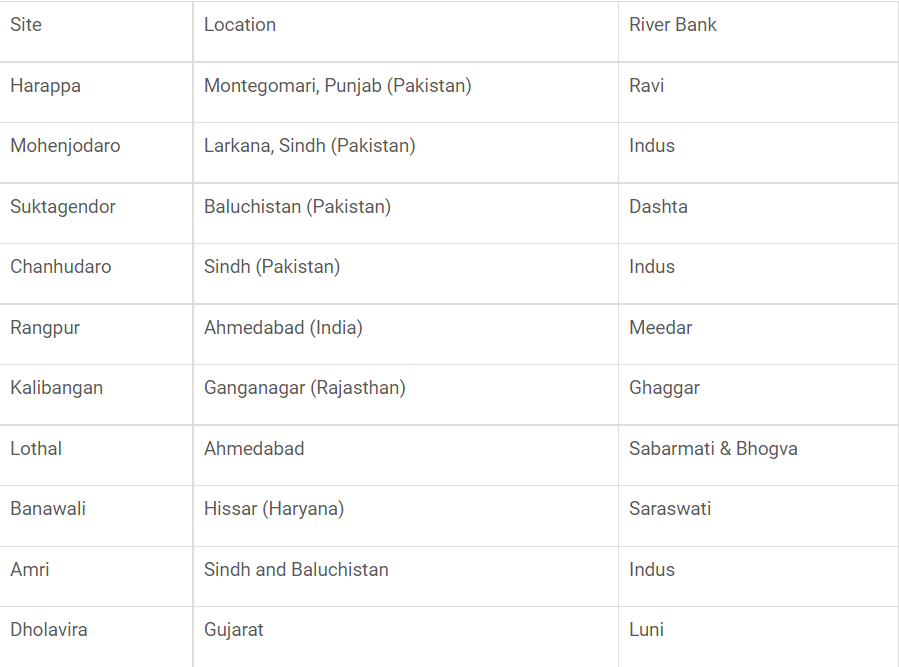
Copyright infringement not intended
https://epaper.thehindu.com/Home/ShareArticle?OrgId=GR29PT9KC.1&imageview=0

















