
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- As part of a maritime security initiative in the Red Sea named Operation Prosperity Guardian, the United States military opened fire on Yemen’s Houthi rebels.
Houthi conflict
- The Houthi conflict, also known as the Yemeni Civil War, involves various factions competing for control in Yemen, with the Houthi rebel movement playing a central role. Here are key points about the Houthi conflict:
Background:
Houthi Rebellion:
- The conflict originated with the Houthi movement, formally known as Ansar Allah, which emerged in the early 2000s in northern Yemen. The group is named after its founder, Hussein Badreddin al-Houthi.
Zaidi Shia Influence:
- The Houthi movement is rooted in the Zaidi Shia sect, a minority in Yemen. It has historical grievances related to political and economic marginalization.
Escalation and Chronology:
Saada Wars (2004-2010):
- The conflict began with clashes between Houthi rebels and the Yemeni government, leading to multiple Saada Wars in the Saada Governorate.
Arab Spring (2011):
- The Arab Spring protests in Yemen provided an opportunity for various groups, including the Houthis, to escalate their activities against the government.
Houthi Takeover (2014-2015):
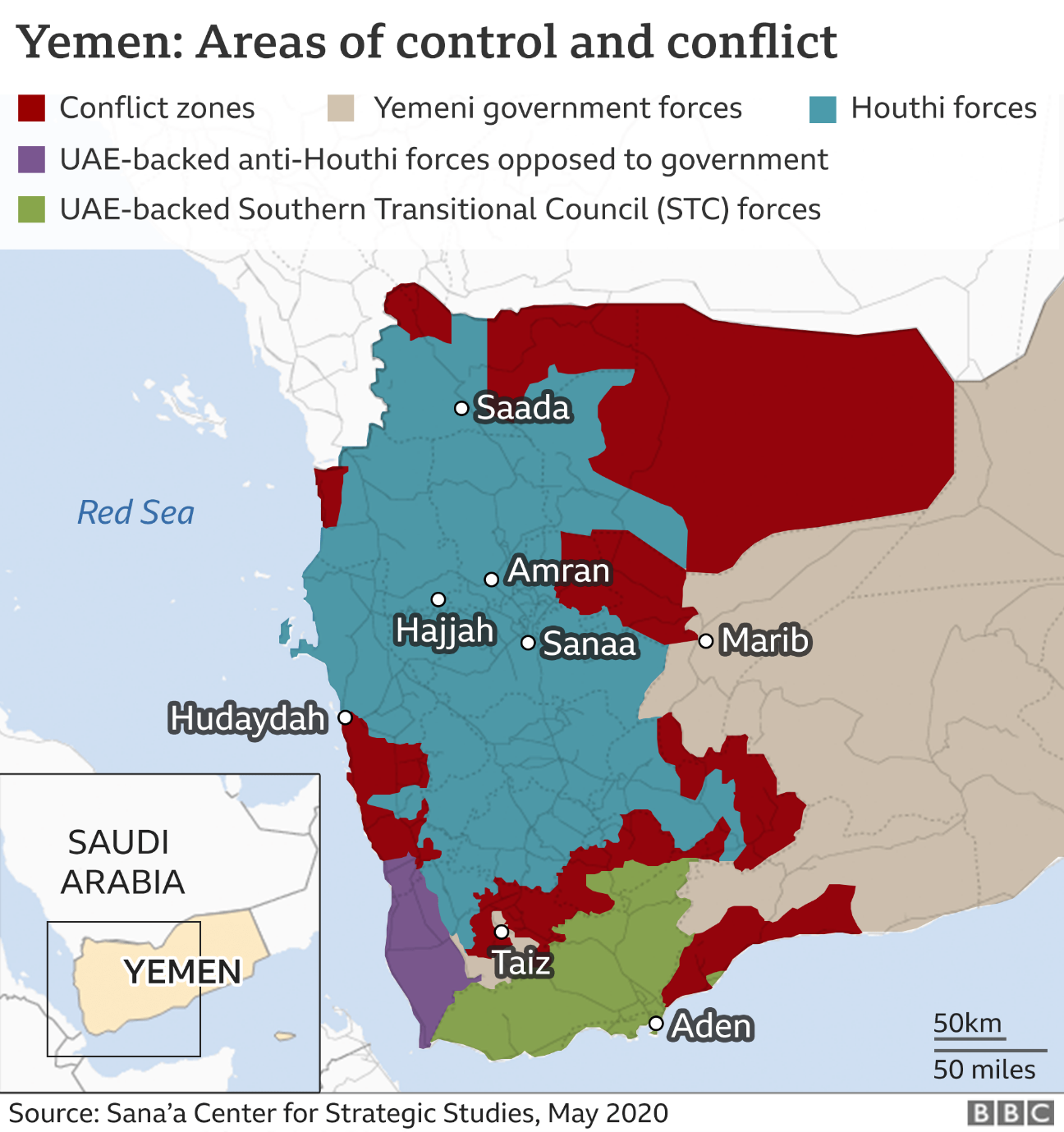
- The Houthis, capitalizing on popular discontent, seized control of the Yemeni capital, Sana'a, in 2014, leading to the ousting of President Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi.
Saudi-led Intervention (2015-present):
- A coalition led by Saudi Arabia, with support from the UAE and others, intervened in 2015 to restore the Yemeni government and counter Houthi influence.
Key Actors:
Houthi Movement (Ansar Allah):
- The Houthi rebels, with allegiance to the Zaidi Shia sect, have been central to the conflict. They control significant parts of northern Yemen, including the capital, Sana'a.
Yemeni Government Forces:
- Forces loyal to the internationally recognized government of President Hadi have received support from the Saudi-led coalition.
Southern Separatists:
- The Southern Transitional Council (STC), seeking an independent South Yemen, has at times aligned with and at times opposed both the government and the Houthis.
Humanitarian Crisis:
Humanitarian Impact:
- The conflict has resulted in a severe humanitarian crisis, with millions facing food insecurity, displacement, and inadequate access to healthcare.
Cholera Outbreak:
- Yemen has faced one of the world's worst cholera outbreaks, exacerbated by damaged infrastructure and limited access to clean water.
International Involvement:
Saudi-led Coalition:
- The Saudi-led coalition, supported by the United States and other Western allies, has conducted airstrikes against Houthi targets.
Iranian Involvement:
- Iran has been accused of providing support to the Houthi rebels, including weapons and training, although the extent of this support is a subject of international debate.
Peace Efforts:
UN-led Negotiations:
- Various attempts by the United Nations to broker a political solution, including peace talks in Sweden, have faced challenges in reaching a sustainable agreement.
Ceasefires and Fragile Truces:
- Periodic ceasefires and truces have been declared, but they often break down due to ongoing hostilities.
Remarks
- The Houthi conflict remains a complex and protracted crisis with significant regional and international implications. Efforts toward a lasting solution involve addressing the root causes of the conflict, fostering inclusive dialogue, and addressing the urgent humanitarian needs of the Yemeni population.

Implications of the Yemen-Houthi conflict for the Red Sea region
The Yemen-Houthi conflict has significant implications for the Red Sea region, affecting maritime security, trade routes, and the geopolitical landscape. Here are key impacts on the Red Sea:
Maritime Security:
Shipping Routes Disruption:
The conflict has raised concerns about the safety of shipping routes in the Red Sea. Houthi-controlled areas in Yemen are strategically located along the Bab el-Mandeb Strait, a crucial maritime chokepoint.
Houthi Naval Threat:
Houthi rebels have targeted shipping in the Red Sea through attacks on vessels, including both commercial and military ships. These actions raise concerns about the security of maritime traffic in the region.
Geopolitical Tensions:
Saudi Arabia and Iran Rivalry:
- The Houthi rebels, aligned with Iran, have contributed to the ongoing regional rivalry between Iran and Saudi Arabia. This rivalry extends to the Red Sea, impacting the geopolitical dynamics of the region.
Regional Alliances:
- The involvement of regional actors, such as Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates (UAE), in the conflict has implications for their influence along the Red Sea coastline, affecting regional alliances and security arrangements.
Economic Impact:
Disruption of Trade:
- The conflict has the potential to disrupt trade and economic activities along the Red Sea, impacting countries that rely on the seaway for commerce.
Oil and Gas Transit:
- The Red Sea is a critical transit route for oil and gas shipments. Any disruption caused by the conflict could impact the global energy market and increase transportation costs.
Humanitarian Concerns:
Refugee Flows:
- The conflict has led to a humanitarian crisis in Yemen, prompting displacement and refugee flows. Neighboring countries along the Red Sea may bear the socio-economic consequences of hosting refugees and managing the spillover effects.
Environmental Impact:
Potential for Maritime Pollution:
- Ongoing conflict raises concerns about the potential for maritime accidents, leading to oil spills or other forms of pollution in the Red Sea. This could have severe environmental consequences for the region.
Counterterrorism Efforts:
Security Challenges:
- The conflict contributes to security challenges in the Red Sea region, potentially facilitating the activities of non-state actors and terrorist groups.
International Counterterrorism Cooperation:
- The instability caused by the conflict prompts international efforts to address terrorism-related concerns in the Red Sea, fostering collaboration among countries to enhance maritime security.
In conclusion, the Yemen-Houthi conflict has broad implications for the Red Sea region, impacting maritime security, trade, geopolitics, and the overall stability of the area. The international community has a vested interest in finding diplomatic solutions to mitigate the negative consequences and promote stability in the Red Sea.

Way Forward
A comprehensive and effective way forward to address the implications of the Yemen-Houthi conflict on the Red Sea region involves a multi-faceted approach, considering diplomatic, humanitarian, and security measures. Here are some key suggestions:
- Diplomatic Resolution:
- International Mediation: Encourage and support international mediation efforts, involving key stakeholders and regional powers, to facilitate diplomatic negotiations and peace talks between the conflicting parties.
- UN-led Initiatives: Strengthen the role of the United Nations in facilitating negotiations and peace-building processes. The UN can play a crucial role in bringing together conflicting parties, promoting dialogue, and overseeing ceasefires.
- Humanitarian Assistance:
- Humanitarian Aid Access: Advocate for unhindered access to humanitarian aid in conflict-affected areas. Ensure that relief organizations can reach those in need, particularly in Yemen, to address the severe humanitarian crisis.
- Refugee Support: Provide support to countries in the Red Sea region hosting refugees from Yemen. Enhance international collaboration to share the burden and address the socio-economic challenges associated with refugee flows.
- Maritime Security Enhancement:
- International Naval Patrols: Collaborate on international naval patrols in the Red Sea to ensure the security of maritime routes. This can help deter piracy and protect commercial vessels navigating through critical chokepoints.
- Regional Security Cooperation: Encourage regional security cooperation mechanisms to address common security threats. This may involve sharing intelligence, joint naval exercises, and coordinated efforts to counter illicit activities.
- Economic Development Initiatives:
- Investment in Infrastructure: Promote economic development initiatives in the Red Sea region to enhance infrastructure, trade capabilities, and economic diversification, contributing to long-term stability.
- Regional Trade Agreements: Facilitate regional trade agreements to boost economic integration and cooperation among Red Sea countries. This can contribute to economic resilience and reduce dependency on a single route or market.
- Environmental Protection Measures:
- Environmental Cooperation: Establish regional cooperation mechanisms to address potential environmental hazards arising from the conflict. Collaborate on preventive measures and response strategies to mitigate environmental risks.
- International Assistance: Seek international assistance and expertise to address and mitigate the environmental impact of the conflict, particularly in preventing and responding to potential maritime accidents.
- Capacity Building and Conflict Prevention:
- Local Capacity Building: Invest in local capacity building initiatives to enhance the ability of Red Sea countries to manage and prevent conflicts. This includes building institutional capacities for conflict resolution and crisis management.
- Early Warning Systems: Establish or strengthen early warning systems to identify and address potential sources of tension before they escalate. Proactive conflict prevention measures can contribute to maintaining regional stability.
- Public Diplomacy and Awareness:
- Public Engagement: Promote public diplomacy and awareness campaigns to foster understanding among the populations of Red Sea countries. Encourage people-to-people exchanges, cultural initiatives, and dialogue to build trust and mitigate tensions.
- International Collaboration:
- Multilateral Engagement: Encourage continued multilateral engagement through organizations like the Arab League, African Union, and other regional forums. Engage with the international community to garner support for regional stability initiatives.
Closing Remarks
- Implementing these suggestions requires a concerted effort from the international community, including regional actors, global organizations, and key stakeholders. The goal is to foster sustainable peace, enhance security, and promote economic development in the Red Sea region.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. What are the key implications of the Yemen-Houthi conflict on the Red Sea region, particularly in terms of maritime security, geopolitical tensions, economic impact, and humanitarian concerns? Discuss the potential consequences for shipping routes, regional alliances, trade disruption, refugee flows, and the overall stability of the Red Sea, considering both immediate challenges and long-term consequences.
|










