Description
Copyright infringement not intended
Context: In a written response submitted to the Rajya Sabha, the minister of women and child development provided information on the many measures the Indian government is taking to promote proper nutrition.
Details
- In the Rajya Sabha, the minister of women and child development said that the government of India has taken the issue of malnutrition with great importance and is working hard to achieve positive nutritional outcomes.
- The Minister also provided information on various actions taken periodically to update, enhance, and strengthen the infrastructure of anganwadis across the country.
.jpeg)
Highlights of the Minister of women and child development statement in the Rajya Sabha
- Global Hunger Index (GHI): According to the minister, the Global Hunger Index (GHI) is a misleading indicator of "hunger," it does not accurately represent India's situation. It is unsuitable and not indicative of the widespread hunger in a nation; thus, it shouldn't be taken seriously.
- Only one of its four indicators “undernourishment” has a direct connection to hunger. The other indicators "stunting and wasting" are the results of complicated interactions between several different other factors, including sanitation, genetics, environment, and how food is used. There is also no evidence that hunger contributes to the fourth indicator "child mortality".
- The GHI index is inaccurate because it is based on a survey with a relatively limited sample size and ignores the numerous steps made by the Indian government to guarantee food security in the nation.
- Nutrition indicators improved: The Minister stated that the latest 5th National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5), which collects data on nutritional indicators every few years, has shown improvements in the nutritional indicators for children under 5 years old since NFHS-4 (2015-16).
- Stunting has decreased from 38.4% to 35.5%, wasting from 21.0% to 19.3%, and the prevalence of underweight has decreased from 35.8% to 32.1%.
- Mission Poshan 2.0: Mission Poshan 2.0 aims to address the issues of malnutrition in children, adolescent girls, pregnant women, and lactating mothers through a strategic shift in nutrition content and delivery as well as by building a converging eco-system to create and promote behaviours that foster health, wellness, and immunity.
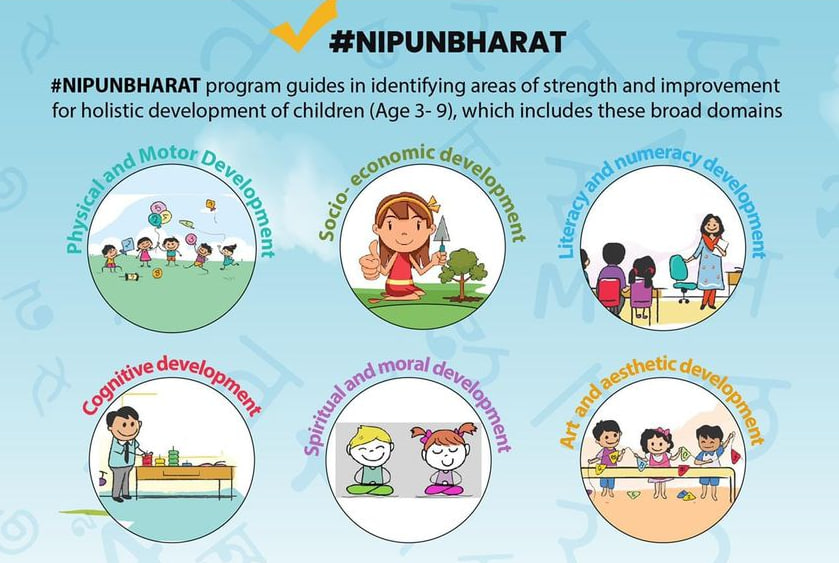
- NIPUN Bharat: The government has launched a national mission called "National Initiative for Proficiency in Reading with Understanding and Numeracy (NIPUN Bharat)" through the Department of School Education & Literacy to make sure that by the end of Grade 3, every child in the nation has acquired the fundamentals of literacy and numeracy.
About Nipun Bharat Scheme
- The Ministry of Education launched the National Mission on Foundational Literacy and Numeracy called National Initiative for Proficiency in Reading with Understanding and Numeracy (NIPUN Bharat) in July 2021.
- NIPUN Bharat Mission has been launched under the aegis of the centrally sponsored scheme of Samagra Shiksha.
- The Department of School Education and Literacy, Ministry of Education (MoE) will be the implementing agency at the national level and will be headed by a Mission Director.
- The Ministry of Education has launched NIPUN Bharat, for ensuring that every child in the country necessarily attains foundational literacy and numeracy (FLN) by the end of Grade 3, by 2026-27.
- The mission will focus on children of the age group of 3 to 9 years including preschool to Grade 3.
- The children who are in Classes 4 and 5 and have not attained the foundational skills will be provided individual teacher guidance and support, peer support and age-appropriate and supplementary graded learning materials to acquire the necessary competencies.

Objectives of NIPUN Bharat
- It will stress giving children access to and keeping them in school during their early years, strengthening teacher capacity, creating high-quality, diversified student and teacher resources/learning materials, and monitoring each child's progress in achieving learning outcomes.
- All public, government-aided, and private schools must fulfil the mission's aims and objectives by 2026–27.
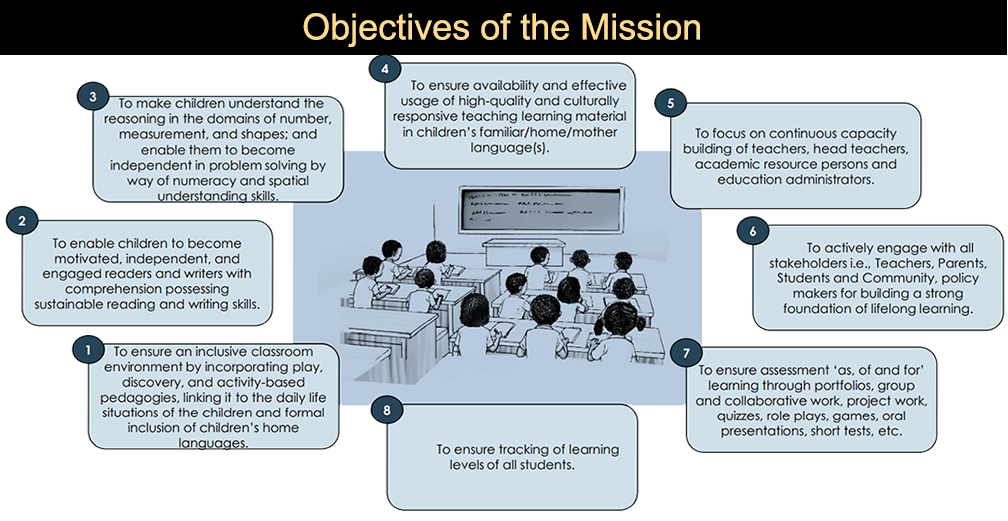
- To create an inclusive learning environment in the classroom by integrating play, discovery, and activity-based pedagogies, connecting them to the children's daily lives, and formally embracing their native languages.
- To help kids develop a passion for reading, independence, and engagement in their writing, as well as comprehension and long-lasting reading and writing abilities.
- To make children understand the reasoning in the domains of numbers, measurement and shapes; and enable them to become independent in problem-solving by way of numeracy and spatial understanding skills.
- To ensure availability and effective usage of high-quality and culturally responsive teaching learning material in children’s familiar/home/mother language(s).
- To focus on continuous capacity building of teachers, head teachers, academic resource persons and education administrators.
- To actively engage with all stakeholders i.e., Teachers, Parents, Students and Community, and policymakers for building a strong foundation of lifelong learning.
- To ensure assessment ‘as, of and for’ learning through portfolios, group and collaborative work, project work, quizzes, role plays, games, oral presentations, short tests, etc.
- To ensure tracking of learning levels of all students.
Foundational literacy: The pre-existing knowledge of the language helps in building literacy skills in languages. The key components in Foundational Language and Literacy are:
- Oral Language: Development Includes improved listening comprehension; oral vocabulary and extended conversation skills. The experiences in oral language are important for developing skills in reading and writing.
- Decoding: This involves deciphering written words based on understanding the relationship between symbols and their sounds.
- Reading Fluency: Refers to the ability to read a text with accuracy, speed (automaticity), expression (prosody), and comprehension that allows children to make meaning from the text. Many children recognize akharas, but read them laboriously, one by one.
- Reading Comprehension: Involves constructing meaning from a text and thinking critically about it. This domain covers the competencies of understanding texts and retrieving information from them, as well as interpreting texts.
- Writing: This domain includes the competencies of writing akharas and words as well as writing for expression.

Foundational Numeracy: Foundational Numeracy means the ability to reason and to apply simple numerical concepts in daily life problem-solving. The major aspects and components of early mathematics are;
- Pre-number concepts: Count and understand the number system.
- Numbers and operations on numbers: Learn conventions needed for mastery of Mathematical techniques such as the use of a base ten system to represent numbers.
- Shapes and Spatial Understanding: Perform simple computations in her/his own way up to three-digit numbers and apply these to their day-to-life activities in different contexts.
- Measurement: Understand and use standard algorithms to perform operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division on numbers up to three digits.
- Data Handling: Identify and extend simple patterns starting from repeating shapes to patterns in numbers, and interpret simple data/information in his/her daily life activities.
Way Forward
- Foundational skills help keep kids in school, which lowers dropout rates and improves the rate of transition from primary to upper primary and secondary levels.
- Education will be of higher quality if it is activity-based and is conducted in a supportive environment.
- Teachers will become more empowered and have more autonomy in their pedagogy selection with intensive capacity building.
- Children achieve a higher learning curve, which may have favourable effects on achievements in later life and career.
- Since every kid attends the early grades, focusing on them will also help the socioeconomically disadvantaged group, ensuring that they have access to a quality education that is egalitarian and inclusive.
- A Holistic Progress Card will reflect the child's holistic growth by concentrating on a variety of interrelated and dependent developmental areas, such as physical and motor development, socio-emotional development, literacy and numeracy development, cognitive development, life skills, etc.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Consider the following Statement about the NIPUN Bharat Mission;
1. It was launched by the Finance Minister during the Union Budget 2023-24.
2. It has been launched under the aegis of the central sector scheme of Samagra Shiksha.
3. It focuses on children of the age group of 3 to 9 years including preschool to Grade 3.
Which of the following Statement is/are incorrect?
(A) 1 and 2 only
(B) 2 and 3 only
(C) 1 and 3 only
(D) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The Ministry of Education launched the National Mission on Foundational Literacy and Numeracy called National Initiative for Proficiency in Reading with Understanding and Numeracy (NIPUN Bharat) in July 2021.
Statement 2 is incorrect: NIPUN Bharat Mission has been launched under the aegis of the centrally sponsored scheme of Samagra Shiksha.
Statement 3 is correct: The mission will focus on children of the age group of 3 to 9 years including preschool to Grade 3.
Q. The Success of the National Education Policy 2020 depends on the success of NIPUN Bharat. Discuss
|

https://newsonair.com/2023/03/16/parliament-session-nipun-bharat-nep-bringing-big-changes-anganwadis-being-revamped/












