Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: www.downtoearth.org.in
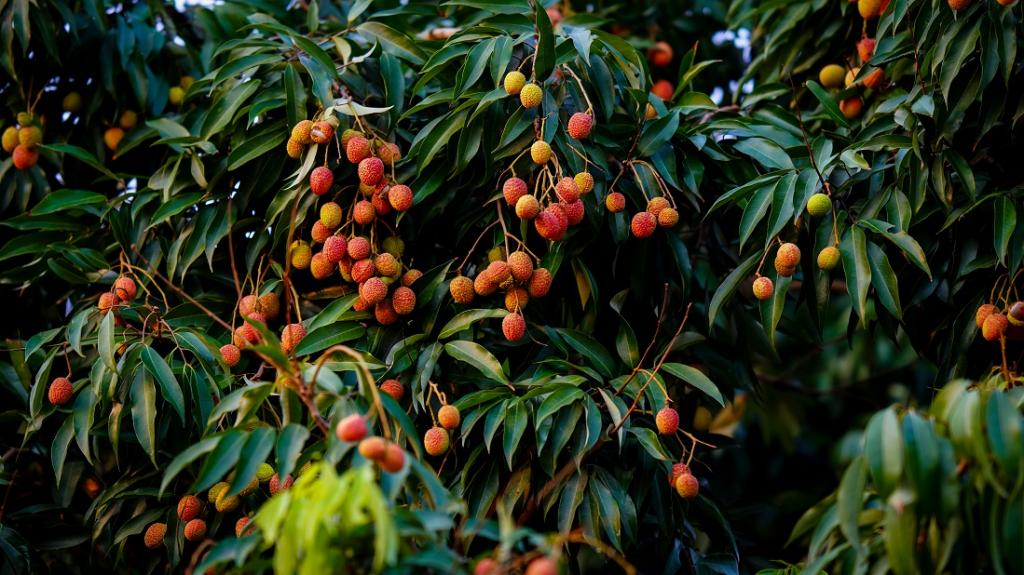
Context: The National Research Centre on Litchi (NRCL) in Muzaffarpur significantly contributed to the expansion of litchi cultivation across 19 Indian states by providing technical support, plants, and training to farmers.
Key Highlights
- Expansion of Litchi Cultivation: Litchi cultivation, initially concentrated in specific regions like Bihar, has now spread to 19 states across India. This expansion is attributed to the NRCL's initiatives in providing resources and knowledge to farmers.
- NRCL's Role: The NRCL plays a pivotal role by nurturing thousands of litchi saplings in its nursery annually and distributing them to farmers in different states. This includes popular varieties like Shahi litchi, China, Gandki Lalima, Gandki Sampada, and Gandki Yogita.
- Scientific Basis: The decision to expand litchi cultivation was grounded in scientific studies that identified suitable soil and climate conditions for successful cultivation in various states.
- Challenges and Considerations: Litchi is a sensitive fruit, highly responsive to temperature, rainfall, humidity, and soil conditions. Variations in these factors have affected litchi crops in recent years, impacting fruit quality.
- Transition to Commercial Production: While there's a substantial expansion in litchi cultivation, transitioning this growth into full-scale commercial production will take time. Saplings planted in orchards typically require several years before they begin bearing fruit.
- Geographical Distribution: Traditionally grown in the Himalayan foothills in states like Uttarakhand, Bihar, West Bengal, and Jharkhand, litchi cultivation in Bihar alone accounts for nearly 40% of India's total production. Other states, like West Bengal and Jharkhand, also contribute significantly.
- New Regions and Challenges: While litchi was previously cultivated in limited areas for non-commercial purposes in states like Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, and Assam, recent initiatives have introduced cultivation in Karnataka and Kerala. However, challenges such as seasonal differences in harvesting in regions like Karnataka compared to the traditional summer harvest in North India exist.
This expansion signifies a positive trend toward diversifying crop cultivation across India, potentially impacting the overall agricultural landscape and contributing to the fruit's availability in various regions.

|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. What are the emerging trends and challenges facing horticulture in India, and how are advancements in technology impacting the sector's growth and sustainability?
|