Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement is not intended.
Context:
- The just transition approach is gaining popularity in recent times.
The concept of ‘just transition’:
- It encompasses a socio-economic framework that aims to navigate the shift away from plastic-dependent industries towards more sustainable alternatives while ensuring equity and inclusivity.
- This approach prioritizes addressing social and economic impacts associated with transitioning, such as job losses and economic disruptions, by providing support to affected workers and communities.
- It particularly focuses on marginalized or vulnerable groups, including informal waste workers, ensuring they are not disproportionately affected by industry shifts and promoting social justice through inclusive decision-making processes and resource access.
Just transition initiatives
- Just transition initiatives involve retraining and upskilling programs to enable workers to pursue employment in emerging green sectors like renewable energy, recycling, and sustainable packaging.
- Parties committed to just transition initiatives aim to promote fair, equitable, and inclusive transitions for affected populations, with a special focus on women and vulnerable groups.
- This includes establishing national coordinating bodies to engage with stakeholders, improving income and livelihood opportunities through workforce training and social programmes tailored to community needs, and incentivizing skill development across the plastic value chain.
- These investments in alternative industries not only create new job opportunities but also contribute to economic development.
- The framework also emphasizes global cooperation and solidarity, recognizing that transitioning away from plastic pollution requires collective action and support among countries and regions.
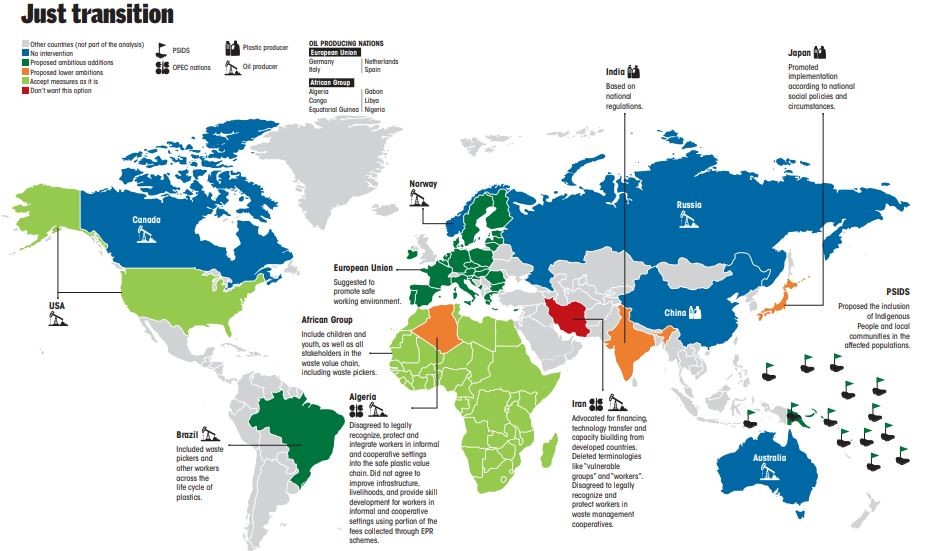
Stand of different countries on the same
- The European Union (EU), Pacific Small Island Developing States (PSIDS) and Brazil have proposed higher ambition for just transition provisions.
- The EU has proposed the promotion of safe working environments.
- Brazil has proposed including waste pickers and other workers across the life cycle of plastics.
- PSIDS countries have proposed the inclusion of indigenous people and local communities.
- The United States and African groups have supported most of the existing provisions. They have expressed support for children, youth, and stakeholders, including waste pickers.
- Algeria did not align with the African group and disagreed on legally recognizing, protecting, and integrating workers from informal and cooperative settings into the safe plastic value chain.
- India and Japan agreed to just transition provisions but strictly based on national regulations to promote implementation.
- Iran advocated for financing, technology transfer, and capacity building from developed countries. It also deleted terminologies like ‘vulnerable groups’ and ‘workers’. It disagreed on legally recognizing and protecting workers in waste management cooperatives.
What benefits does a just transition offer for tackling climate change?
There are many ways in which a just transition can help as countries address the impacts of climate change and green their economies.
- Building Public Support: If governments can demonstrate the socio-economic benefits afforded by a green transition – including economic benefits and new green jobs – they can build a broad base of public support for higher climate ambition as citizens will be more likely to get behind the associated policies and investments.
- Creating Quality Jobs: Green transitions can generate jobs with good wages, safety protections, and health benefits, benefiting workers and communities.
- Fostering Resilience: Involving stakeholders in planning can reduce conflict and fears, making the shift away from harmful practices smoother.
- Driving Local Solutions: Considering local impacts helps find the best climate solutions for each area, maximizing benefits.
- Urgency and Focus: A just transition keeps leaders focused on rapid decarbonization while ensuring fairness and inclusivity in the process.
Way ahead to ensure just transition
- Developed countries should create mitigation strategies that help developing countries participate in clean tech economy value chains without imposing barriers.
- Encourage technology co-development systems recognizing developing country markets' contribution and allowing shared ownership of intellectual property.
- Ensure international agreements support developing countries' industrial policies for economic development.
- Advocate for lower cost of capital for sustainable infrastructure investment in developing countries and promote private sector involvement while ensuring universal access to essential services.
- Ensure multilateral development banks' engagement in climate action doesn't divert resources from productive capacity development and Sustainable Development Goals.
- Support capacity building to regulate environmental and social actions of non-state entities for participation in regulated markets and international investment.
- Call for immediate capitalization of loss and damage finance facility and Increase financing for resilience-building and reducing inequalities, especially for climate-vulnerable and marginalized communities.
- Establish effective international mechanisms for payments for ecosystem services.

Conclusion:
- Focus on informal and cooperative workers ensures legal recognition, protection and improved working conditions. These efforts align with broader environmental goals and international efforts to address plastic pollution while fostering social justice and human rights.
Source: https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/waste/global-plastic-profiles-where-do-countries-stand-on-a-just-transition-for-the-plastic-industry--95711
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q) Examine the challenges and opportunities associated with implementing a 'just transition' approach in developing countries to address climate change. (250 words)
|












