




Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://ipvsoc.org/hpv-day/
Context: International HPV Awareness Day, observed annually on March 4th, aims to raise awareness about the Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and its role in causing various cancers, particularly cervical cancer.
|
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) |
|
|
About |
Details |
|
Virus Type |
DNA virus |
|
HPV Types |
Over 100 were identified, with more than 40 affecting the genitals, mouth, and throat. |
|
Transmission |
Skin-to-skin contact: Can also spread through other forms of intimate skin-to-skin contact. Transmission even without symptoms: An infected person can transmit HPV even if they have no visible signs. |
|
Risk Factors |
Multiple sexual partners: The more sexual partners have, the greater the chance of exposure. Weakened immune system: HIV/AIDS or other conditions can make more susceptible to HPV infection and complications. Early age of first intercourse: Younger age at first sexual contact increases risk. Smoking: Increases risk of HPV-related cancers. |
|
Symptoms |
Often no symptoms. Symptoms vary depending on the type of cancer. |
|
Diagnosis |
Pap smear: Routine cervical cancer screening test that can detect precancerous cells. HPV DNA test: Detects the presence of specific HPV strains. |
|
Treatment |
No cure for HPV itself, but treatments exist for warts and precancerous lesions: ●Genital warts: Topical medications, cryotherapy, laser surgery. ●Precancerous lesions: Cryotherapy, laser surgery, loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP). ●Treatment for HPV-related cancers: Varies depending on the type and stage of cancer. May involve surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination. |
|
Prevention |
HPV vaccination: Gardasil 9 is the most common vaccine, protecting against 9 HPV strains. Recommended for both males and females at ages 11 or 12; can be given up to age 46. Safe sex practices: Consistent condom use can reduce (but not eliminate) HPV transmission. Limiting sexual partners. |
|
International HPV Awareness Day |
|
|
About |
Description |
|
Date |
March 4th (Annually) |
|
Theme for 2024 |
“Learn. Prevent. Screen.” |
|
Purpose |
Raise awareness about Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and its link to various cancers. |
|
Key Points |
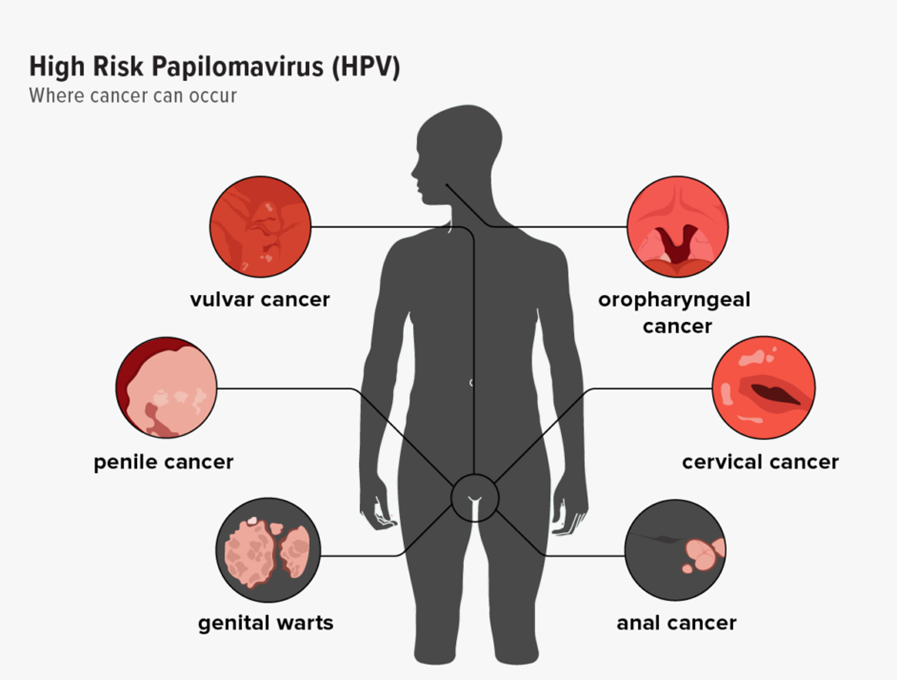
●HPV is a very common virus transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, including sexual contact. ●Certain types of HPV can lead to cervical cancer, vulvar cancer, vaginal cancer, anal cancer, and some head and neck cancers. ●HPV vaccination is a safe and effective way to prevent HPV infection and related cancers (recommended for girls and boys starting at age 11 or 12). Regular cervical cancer screening is crucial for early detection and treatment of precancerous lesions. |
|
Challenges |
●Limited public and healthcare professional knowledge about HPV and its connection to cancers. ●Misconceptions and myths surrounding HPV and the vaccine can create vaccine hesitancy. |
|
Importance of Awareness |
●Empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health (vaccination and screening). ●Promotes HPV vaccination as a primary prevention strategy. ●Encourages regular cervical cancer screening for early detection. ●Combats misinformation and vaccine hesitancy. |
|
Organizations Leading the Initiative |
●International Papillomavirus Society (IPVS) ●World Health Organization (WHO) ●Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) |
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Which of the following are the characteristics of cancer cells? 1. Uncontrolled growth and division 2. Ability to invade healthy tissues 3. Increased blood supply to the tumour 4. Production of useful substances for the body Select the correct code: A) Only one B) Only two C) Only three D) All four Answer: C Explanation: Cancer cells are defined by their uncontrolled growth and ability to invade healthy tissues. They often create new blood vessels to support their growth, but they do not produce beneficial substances for the body. 1. Uncontrolled growth and division: This is a key characteristic of cancer cells. Unlike normal cells that have a controlled growth cycle and stop dividing when there are enough, cancer cells continue to divide uncontrollably, forming tumours. 2. Ability to invade healthy tissues: This characteristic allows cancer cells to spread to other parts of the body. They can break through the normal boundaries of tissues and enter the bloodstream or lymphatic system, reaching distant organs and forming secondary tumours (metastasis). 3. Increased blood supply to the tumour: As tumors grow, they need more oxygen and nutrients to survive. Cancer cells can signal the body to create new blood vessels (angiogenesis) to supply the tumour with these essentials, promoting further growth. 4. Production of useful substances for the body: This is not a characteristic of cancer cells. In fact, cancer cells often malfunction and don't perform the specialized functions that normal cells do for the body. They might even release harmful substances that disrupt normal bodily processes. Therefore, only options 1, 2, and 3 represent true characteristics of cancer cells. They exhibit uncontrolled growth, invade healthy tissues, and promote their own blood supply, contributing to their harmful effects on the body. |






© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved