Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The technology powering hybrid electric vehicles explained in “The Hindu”.
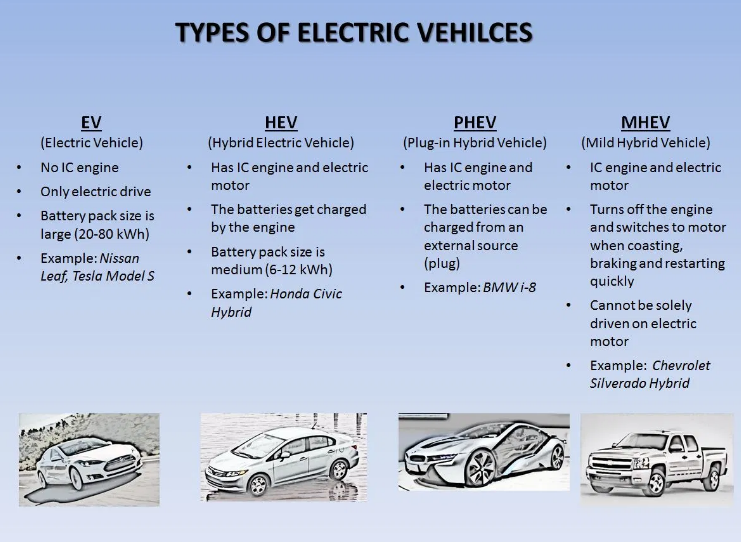
Electric Vehicles:
- Electric vehicle uses electricity from extravehicular sources, or it can be powered by a battery (sometimes charged by solar panels).
- Electric vehicles are vehicles that are either partially or fully powered on electricity.
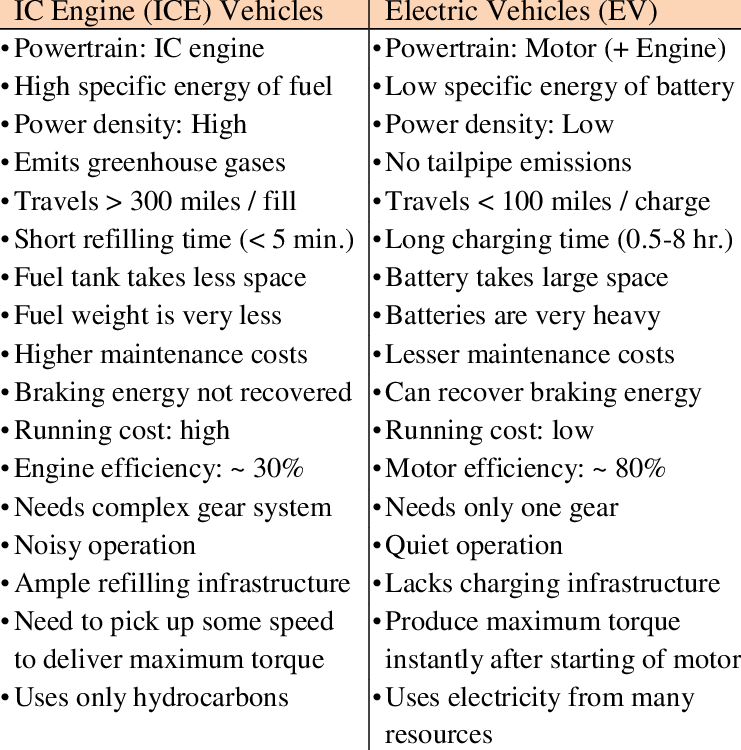
- Electric vehicles have low running costsas they have less moving parts for maintenance and also are very environmentally friendly as they use little or no fossil fuels(petrol or diesel).
- Electric Vehicles are easy and cheaper to maintain because of their simple structure and operations.
- Another benefit that an EV can deliver is the silent functioning capability.
- Switching to Electric Vehicles willimprove the overall energy securitysituation as the country imports over 80% of its total crude oil requirements, and also save valuable foreign reserves. This will help India in achieving the goal of ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat”.
- Increasing demand for EVs is also expected to boost the local EV manufacturing industry,this will support the “Make in India” programme.
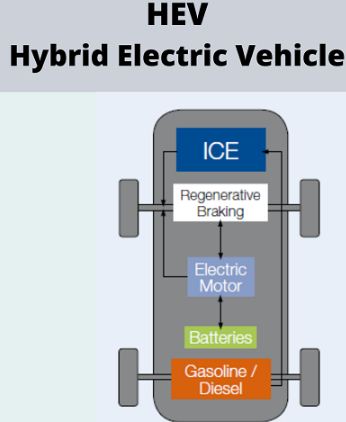
What is a hybrid electric vehicle?
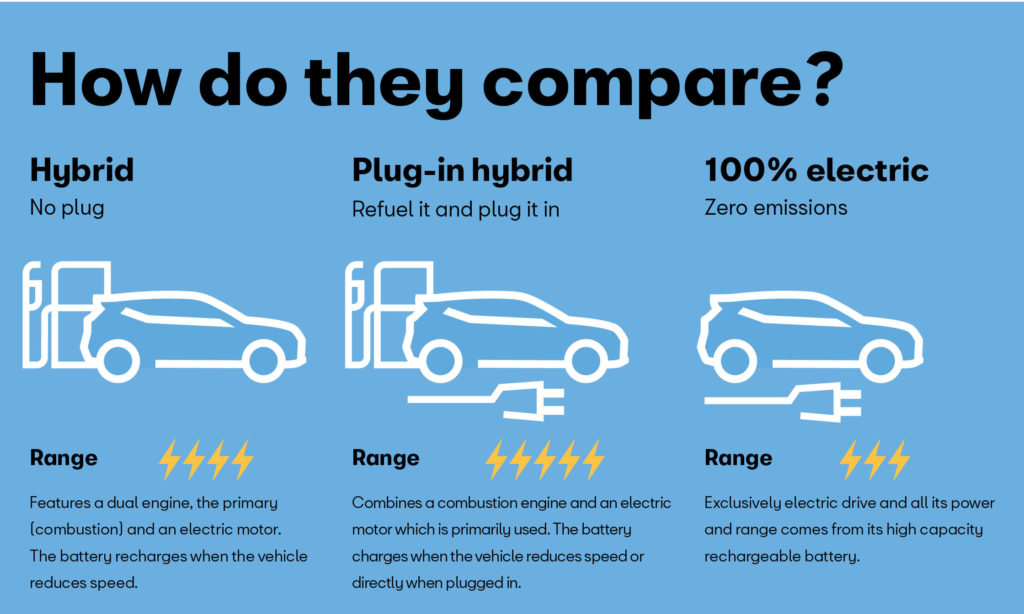
- A hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) uses an ICE (a petrol/diesel engine) and one or more electric motors to run. It is powered by the electric motor alone, which uses energy stored in batteries, by the ICE, or both.
- The powertrain of the HEV is more complex than a regular ICE-powered car as it has EV components and a conventional ICE. That means a typical HEV will have a low-voltage auxiliary battery, a traction battery pack to store electricity for the electric motor, an electric generator, an AC/DC converter, a power electronics controller, a thermal system to maintain working temperature, an ICE, a fuel tank, a fuel filler, a transmission and an exhaust system.
How do HEV powertrains work?
- HEV powertrains are designed to power cars in a series, parallel or series-parallel (power split) methods. A series HEV uses only the electric motor to drive the wheels, while the ICE powers the generator, which in turn recharges the battery. A parallel HEV, based on the driving condition, uses the best power source to power the vehicle. It will alternate between the electric motor and the ICE to keep the car moving.
- A series-parallel HEV offers a combination of both models and allows splitting power, wherein power is routed from the ICE alone or from the battery to the electric motor to drive the vehicle. Moreover, in all three designs, the battery is charged through regenerative braking technology.
How does regenerative braking work?
- A regenerative braking system (RBS) used in automotive applications has several advantages like better braking efficiency in stop-and-go traffic which enhances fuel economy and also helps in reducing carbon emissions. Besides, RBS also helps in energy optimisation resulting in minimum energy wastage.
What are the different types of HEVs?
- The HEVs can be categorised into micro, mild and full hybrid vehicles, based on the degree of hybridisation.
Full HEV
- A full HEV will have a larger battery and a more powerful electric motor compared with a mild HEV. As a result, a full HEV can power the vehicle for longer distances using just electric mode, whereas a mild HEV cannot drive using only the electric motor and uses the battery at traffic lights or in stop-and-go traffic to support the ICE. Micro hybrids do not offer electric torque assistance as they lack an electric motor, but they have an idle stop-start system and energy management functions. Full HEVs offer better fuel economy compared with the other two types of HEVs but they also cost more than them.
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs)
- Plug-in hybrids are typically powered by gasoline and a large battery. The battery can be charged with power from your house, and some models can also be charged using public charging stations, often called “SuperChargers”.
- Although the plug-in hybrid behaves like an electric car when fully charged, the gasoline engine remains dormant. If the battery is low, it will bring the engine to life and allow the vehicle’s normal gasoline hybrid to operate.
- To conserve fuel, regenerative braking can also be used. Not all PHEVs can be called hybrids. If one can plug it in and fill it up, it’s a plug-in hybrid.
- PHEVs generally use the electric motor until the battery is almost drained, and then automatically switch to the ICE. PHEVs accounted for about 23% of 1.95 million global EV shipments in the first quarter of 2022.
What are the main advantages of using hybrid technology?
- Most vehicles with hybrid technology offer better fuel efficiency, more power, and minimum emissions.
- The design of hybrid vehicles for reduced engine size and car weight as compared to ICE vehicles, translates into increased mileage to favour the demand for these vehicles.
- Moreover, with the increase in total power and torque, HEVs can deliver instant torque and provide high torque even at low speeds.
What are some challenges of hybrid technology?
- In a price-sensitive market like India, one of the major challenges for HEVs is the high vehicle cost. Battery, a vital component of an HEV, increases the cost of the vehicle, making it pricier than vehicles powered only by an ICE. The RBS also adds to the higher cost of an HEV.
Hybrid vs. plug-in hybrid — pros & cons
Hybrid car pros & cons
Pros
- You can fill up at any gas station quickly
- The most affordable electrified vehicle
- Plugging in is not a problem
- Apartment dwellers are able to live in peace.
- Can you only have one car?
Cons
- Plug-in hybrids have a higher gas-saving potential but not as many.
- The hybrid’s gasoline engine is weak and lacks power.
- No rated electric range
Plug-in hybrid pros & cons
Pros
- Can be used during your weekday commute as an electric car
- It will continue running even when it runs out power.
- A gasoline engine can be used to make road trips
- Can you only have one car?
- Tax incentives, both federal and state, may help offset higher costs
Cons
- It is more expensive than regular hybrids
- The range of an electric vehicle is insufficient to eliminate gasoline completely.
- It will need be plugged in regularly to make sense. You may not need 240-volt equipment.
- The powertrain can take up space, and may compromise functionality.

Hybrid vs. electric — pros & cons
Hybrid vehicle pros & cons
Pros
- It is not necessary to charge
- Gas propulsion makes it possible to travel anywhere without worrying about range anxiety
- Can you only have one car?
- It’s affordable to purchase
Cons
- It isn’t as efficient as an electric car.
- It is necessary to change your oil and maintain your engine.
- Lacks an EV’s drive-away smoothness, silence
- Compared to this, initial acceleration is very weak
There are pros and cons to electric vehicles
Pros
- Zero tailpipe emissions
- You can accelerate smoothly and quietly without shifting
- The only thing that needs to be maintained is the tire and wipers.
- Cost per mile for electricity is lower than gasoline
- There is no need to stop for gas.
Cons
- Range anxiety is a problem because it takes time to recharge.
- It will need to be plugged in and may also require a 240-volt homestation.
- Renters struggle to charge rent
- Long trips require fast charging stations.
- Higher prices to purchase
Read: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/types-of-electric-vehicle-batteries
https://epaper.thehindu.com/Home/ShareArticle?OrgId=G5QA3KCA6.1&imageview=0
1.png)














