Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
As fighting displaces thousands of people in North and South Kivu, concerns grow about the spread of disease due to overcrowded, unsanitary living conditions.
Details
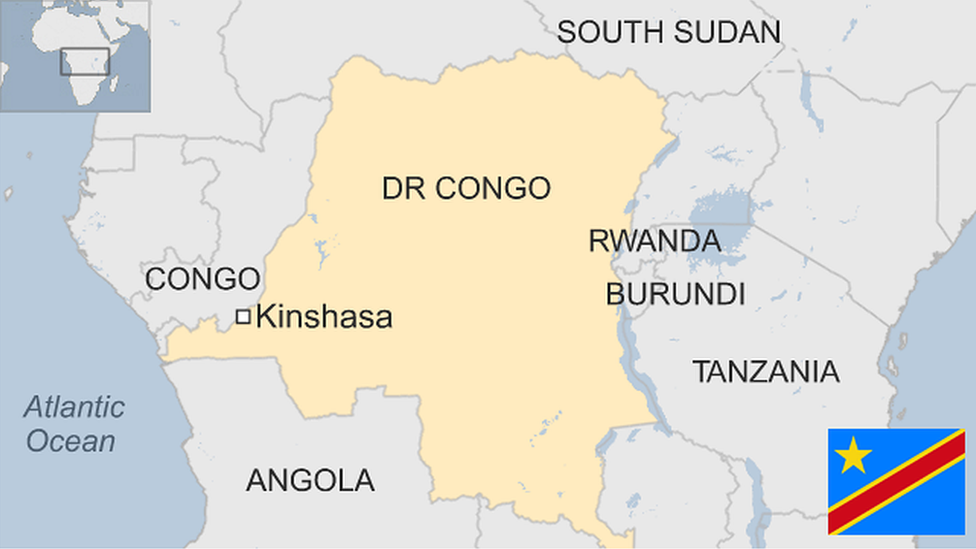
DR Congo
- Capital: Kinshasa
- Area: 2,345,409 sq km
- Population: 108.4 million
- Languages: French, Kituba, Lingala, Swahili, Tshiluba
- Life expectancy: 59 years (men) 62 years (women)
- Coastline: 37 km, territorial sea: 12 nm
- Exclusive economic zone: since 2011 the DRC has a Common Interest Zone agreement with Angola for the mutual development of off-shore resources

Detail
- The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), is located in central sub-Saharan Africa, within the Congo Basin.
- The DRC’s territory straddles the Equator, with one-third of its land area to the north and two-thirds to the south.
- It is the second largest country in Africa, with a total land area of 2,345,408 km2.
- Border: The DRC shares borders with the Republic of Congo to the northwest, the Central African Republic to the north, South Sudan to the northeast, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania (Lake Tanganyika) to the east, Zambia to the southeast and Angola to the west.
- Climate : The DRC has a largely equatorial climate; however, this varies across the country’s extensive land area. Generally, the country is hot and humid in the north and west, an area located within a significant portion of the Congo River Basin. The southern, central and eastern areas are generally cooler and drier.
- Biodiversity: The DRC is home to an exceptionally high degree of diversity biomes, ecosystems, and habitats, notably dry rainforests (Muhulu), open woodland forests (Miombo), savannahs, as well as cloud and gallery forests.
- A large network of protected areas, safeguarding this diversity, covers approximately 8% of the national territory.
- The majority of the land area of the DRC is within the world’s second largest area of tropical rainforest, which is documented to store 8% of global forest carbon stocks.
- It is also characterized by mountain terraces, plateaus, savannahs, grasslands and mountains.
- Natural resource: The DRC has over 80 million hectares of arable land and over 1,100 listed minerals and precious metals. The country has a significant natural resource base of timber, energy, minerals and gemstones.
Population distribution:
- Urban clusters are spread throughout the country, particularly in the northeast along the boarder with Uganda, Rwanda, and Burundi; the largest city is the capital, Kinshasha, located in the west along the Congo River; the south is least densely populated.
Natural hazards:
- Periodic droughts in the south; Congo River floods (seasonal); active volcanoes in the east along the Great Rift Valley
Volcanism
- Nyiragongo (3,470 m), which erupted in 2002 and is experiencing ongoing activity, poses a major threat to the city of Goma, home to a quarter million people; the volcano produces unusually fast-moving lava, known to travel up to 100 km /hr.
- Nyiragongo has been deemed a Decade Volcano by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth’s Interior, worthy of study due to its explosive history and close proximity to human populations; its neighbor, Nyamuragira, which erupted in 2010, is Africa’s most active volcano; Visoke is the only other historically active volcano
.jpg)
Recent Issue
- A resurgence of violence between armed groups in eastern Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) has displaced more than 1.6 million people over the last two years, in a region already devastated by 30 years of conflict.
- For two years, the armed group M23 (March 23 Movement) has been fighting the Congolese army and its allies in North Kivu province, and the violence began to intensify in late January. Now, the fighting has reached the border with South Kivu province.
- This new escalation of the conflict has once again caused entire communities to flee. Armed clashes forced over 70,000 people to flee to South Kivu and 200,000 people to Goma, where more than half a million displaced people had already settled over the past two years.
- The current situation has raised major health concerns. First, the influx of newly displaced people arriving in Goma is exacerbating the critical health situation and urgent needs in camps and increases the risk of epidemics, especially cholera.
|
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Which one of the following is a part of the Congo Basin?
- Cameroon
- Nigeria
- South Sudan
- Uganda
Answer A
|










