Description
Copyright infringement not intended
In News:
- For the violation of standards mandated by the Union Government for the sale of toys, the Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) has issued notices to e-commerce entities; Amazon, Flipkart, Snapdeal, etc.
- The Authority has asked for a response from the e-commerce entities within 7 days, if they fail to submit their response within the period then necessary action may be initiated against them under the provisions of the Consumer Protection Act, 2019.
- The Authority has also written to the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) to take immediate necessary action in the matter.
- The Authority has expanded the country-wide campaign to prevent the sale of goods that violate Quality Control Orders (QCOs) published by the Central Government.
- The list includes consumer durables such as electric immersion water heaters, electric iron, domestic gas stove, microwave oven, sewing machines, etc.
- The Authority has written to all District Collectors across India to investigate unfair trade practices and violations of consumer rights concerning the manufacture or sale of such goods and submit an Action Taken Report.
- Under Section 2(10) of the Consumer Protection Act, 2019, "defect" means any fault, imperfection or shortcoming in the quality, quantity, potency, purity or standard which is required to be maintained by or under any law.
- The Consumer Protection (E-commerce) Rules, 2020 specify that no e-commerce entity should adopt any unfair trade practice.
.jpeg)
Consumer Protection Act, 2019:
- The Act defined a consumer as a person who buys any goods or avails of service for final use.
- It does not include a person who buys a good for resale or a good or service for commercial purposes.
- It covers transactions through all modes including offline, and online.
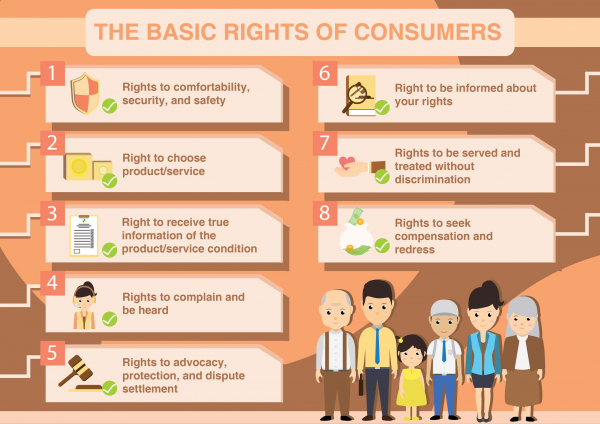
- The Act clearly defined 6 Rights of consumers:
- Right to be protected against the marketing of goods and services which are hazardous to life and property.
- Right to be informed about the quality, quantity, potency, purity, standard and price of goods or services.
- Right to Choice among a variety of goods or services at competitive prices.
- Right to be heard
- Right to seek Redressal against unfair or restrictive trade practices.
- Right to Consumer Awareness
- Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) promotes, protects and enforces the rights of consumers.
- CCPA is a regulatory authority set up under Section 10(1) of the Consumer Protection Act, 2019.
- It functions under the guidelines of The Minister of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution
- It regulates matters linked to the violation of consumer rights, unfair trade practices, and misleading advertisements.
- The CCPA has an investigation wing; they may conduct an inquiry or investigation into the case of violations of rules.
- Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) functions;
- Inquiring into violations of consumer rights, investigating and taking appropriate action.
- It could pass orders to recall goods or withdraw hazardous services, and refund the price paid.
- It Issues directions to the concerned trader/ manufacturer/ endorser/ advertiser/ publisher to either discontinue a false or misleading advertisement.
- It imposes penalties on a manufacturer or an endorser of up to Rs 10 lakh and imprisonment for up to two years for a false or misleading advertisement. In case of a subsequent offense, the fine may extend to Rs 50 lakh and imprisonment of up to five years.
- It Issues safety notices to consumers against unsafe goods and services.
- Consumer Disputes Redressal Commissions (CDRCs) at the District, State, and national levels.
- Appeals from the State CDRC will be heard by the National CDRC.
- The final appeal to the Supreme Court.
- The District CDRC will entertain complaints where the value of goods and services does not exceed Rs 1 crore.
- The State CDRC will entertain complaints when the value is more than Rs 1 crore but does not exceed Rs 10 crore.
- Complaints with a value of goods and services over Rs 10 crore will be entertained by the National CDRC.

Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS):
- It is the National Standards Body under the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution.
- It is a statutory body established under the Bureau of Indian Standards Act, 2016.
- BIS has more than 500 scientific officers working as Certification Officers.
- BIS was formerly known as the Indian Standards Institution (ISI).
- ISI was set up in 1946.
- The ISI was registered under the Societies Registration Act, of 1860.
- Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) headquarters are in New Delhi, with regional offices in Kolkata, Chennai, Mumbai, Chandigarh and Delhi.

https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1890737











