Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Thailand replaced its Ambassador to the WTO following India's protest over her comments on India's Public Stockholding (PSH) program.
READ ABOUT WTO’s AGRICULTURAL SUBSIDIES: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/wto-agrcultural-subsidies
|
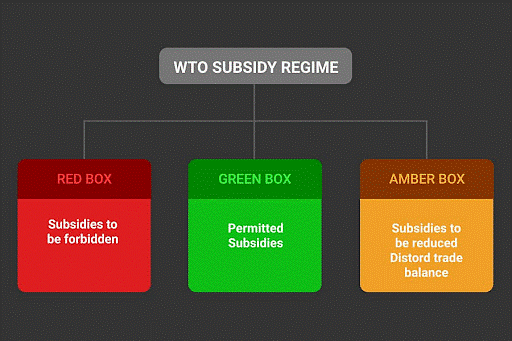
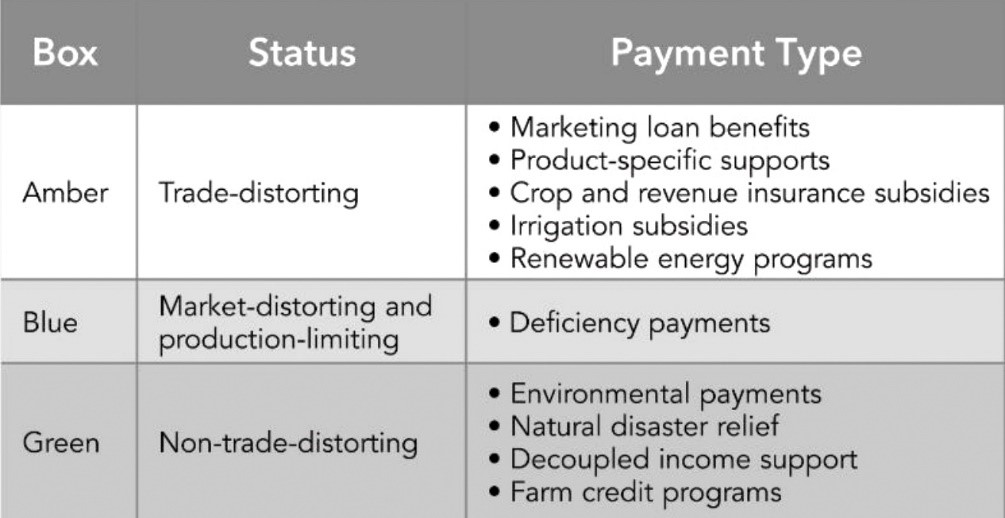
WTO’s AGRICULTURAL SUBSIDIES
- The WTO regulates agricultural subsidies to ensure fair competition in global trade.
- Subsidies that distort trade are subject to limits set by the WTO to prevent unfair advantages for certain countries or producers.
Types of Agricultural Subsidies:
- Domestic Support:
- Direct payments to farmers.
- Price support measures such as Minimum Support Prices (MSP).
- Input subsidies for fertilizers, seeds, etc.
- Export Subsidies:
- Payments to producers to encourage exports, leading to lower global prices.
- Market Access Subsidies:
- Subsidies that lower the cost of importing agricultural products, affecting global market prices.
WTO Agreement on Agriculture (AoA):
- The AoA sets limits on the total value of domestic support measures (de minimis) that countries can provide.
- Developed countries have a lower de minimis limit (5% of the total value of agricultural production) compared to developing countries (10%).

|
Recent issue:
- Thailand replaced its Ambassador to the WTO following India's protest over her comments on India's Public Stockholding (PSH) program.
- Thai Ambassador Pimchanok Vonkorpon Pitfield criticized India's rice procurement program, stating that it is aimed at capturing the export market rather than benefiting the public.
India-Thailand Relations at WTO:
- India, the second largest rice exporter, imposed temporary restrictions on rice exports to control domestic prices.
- Tensions between India and Thailand led Indian negotiators to refuse participation in some WTO deliberations where the Thai representative was present.
Concerns Raised by Thailand:
- Thailand, a member of the Cairns Group, has questioned India's PSH program at WTO, arguing that it distorts global food prices and hurts the food security of other countries.
- The Cairns Group has been lobbying for agricultural trade liberalization and seeks to get India to reduce the scope of its Minimum Support Price (MSP) scheme.
India's Subsidy Issue:
- India breached the de minimis limit in rice subsidies, angering other exporters like Thailand, who are losing market share to India.
- India has questioned the way subsidies are calculated at the WTO, seeking a change in calculations that currently overestimate the subsidy.

Efforts for a Permanent Solution:
- India and a group of developing nations are seeking a permanent solution for public stockholding for food grains at the WTO, as the interim peace clause is considered onerous.
Farmer Protests and Demands:
- Indian farmers have protested against WTO policies, demanding legal guarantees for MSP, debt waiver, and implementation of Swaminathan Commission recommendations.
- Experts caution that leaving the WTO agreement could restrict India and other developing nations from disciplining subsidies by developed countries.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. What is the primary purpose of the WTO's Green Box subsidy category?
A) To allow subsidies that cause minimal distortion to trade without limits.
B) To prohibit subsidies that significantly distort trade.
C) To regulate subsidies that are subject to reduction commitments.
D) To monitor subsidies that may distort trade and require limits.
|











