AIR Discussions (September 3rd Week)
AIR SPOTLIGHT: PRODUCTION LINKED INCENTIVES IN KEY SECTORS
CONTEXT:
- The Centre approved a production-linked incentive scheme for the automobile and drone industries with a budgetary outlay of ₹26,058 crore.
- This tranche is part of the overall plan for 13 sectors highlighted during the Budget announcements for 2021-22, with a total outlay of ₹1.97 lakh crore
FEATURES OF THE SCHEME APPROVED:
PLI Scheme for Auto Industry:
- The PLI scheme for the auto sector will incentivize high value Advanced Automotive Technology vehicles and products.
- It envisages overcoming the cost disabilities to the industry for the manufacture of Advanced Automotive Technology products in India.
- The incentive structure will encourage industry to make fresh investments for indigenous global supply chain of Advanced Automotive Technology products.
- It is expected to bring in fresh investments to the tune of ₹42,500 crore, and lead to an incremental production of over ₹2.3 lakh crore.
- It is also estimated that it will create employment opportunities of over 7.5 lakh jobs.
- Two components of the scheme:
- Champion OEM Incentive Scheme: It is a ‘sales value linked’ scheme, applicable on Battery Electric Vehicles and Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles of all segments.
- Component Champion Incentive Scheme: It is a ‘sales value linked’ scheme.
PLI Scheme for Drone Industry:
- This scheme addresses the strategic, tactical and operational uses of drone technology.
- It is expected to help build capacity in this sector and make it the key driver of India’s growth strategy.
- It will lead to investments worth ₹ 5,000 Crore, increase in eligible sales of ₹ 1500 crore and create additional employment of about 10,000 jobs.
- The total outlay for the scheme is INR 120 crore spread over three financial years.
- The incentive for a manufacturer of drones and drone components shall be as high as 20% of the value addition made by the manufacturer.
- The minimum value addition norm is at 40% of net sales instead of 50%, another exceptional treatment given to the drone industry.
BACKGROUND:
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman had announced an outlay of Rs 1.97 lakh crore for the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for 13 identified sectors in her 2021-22 budget speech.
- The scheme, which aimed to boost domestic manufacturing under the government’s Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative, was introduced in March last year and is expected to result in a minimum production worth more than $500 billion in five years.
What is the Production-Linked Incentive scheme and why it is needed?
- Scheme provides incentives to companies for enhancing their domestic manufacturing apart from focusing on reducing import bills and improving the cost competitiveness of local goods.
- PLI scheme offers incentives on incremental sales for products manufactured in India.
- The first three PLI schemes were approved in March last year followed by 10 new schemes which were notified in November.
- The scheme for respective sectors has to be implemented by the concerned ministries and departments.
- Savings, if any, from one PLI scheme of an approved sector can be utilised to fund the scheme for another approved sector.
- Eligibility criteria for businesses under the PLI scheme vary based on the sector approved under the scheme
Which sectors are currently supported under the scheme?
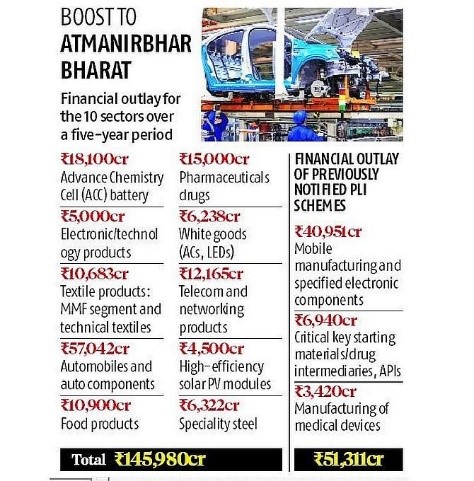
Key features of the PLI scheme:
- The scheme is outcome-based, which means that incentives will be disbursed only after production has taken place.
- The calculation of incentives is based on incremental production at a high rate of growth.
- The scheme focuses on size and scale by selecting those players who can deliver on volumes.
- The selection of sectors covering cutting-edge technology, sectors for integration with global value chains, job-creating sectors and sectors closely linked to the rural economy, is highly calibrated.
- Also, the design of the earlier PLI scheme for electronics is such that it is compatible with World Trade Organization commitments as the quantum of support is not directly linked to exports or value-addition.
ADVANTAGES OF PLI SCHEMES:
- The PLI Scheme augments the present achievements of India. For example, Indian Textile Industry is one of the largest in the world. India is the second-largest producer of steel. Introducing the PLI Scheme in these sectors will further expand these sectors.
- India is expected to have a USD 1 trillion digital economy by 2025. The projects like Smart City Mission and Digital India require huge investments. PLI Scheme will provide low-cost indigenous products.
- Government cannot make sustained investments in capital-intensive sectors. Because they have a longer gestation period.
- PLI Scheme based on incremental output is more effective than the other grant-based input subsidy schemes like Mega Food Parks, etc.
- By increasing manufacturing in labour intensive sectors, India can reduce the unemployment ratio and also create skilled manpower.
- The scheme aims to develop local industries.
- It also facilitates innovation and research, development and up-gradation of technology of Indian firms.
CHALLENGES:
- The scheme contains a financial cap on incentives. This makes an over-performing company not to reap the benefits of its over achievements.
- In India for the majority of the PLI Scheme focussed sectors the effective cost of manufacturing is higher than the competitors. So, the investors will prefer other countries despite the PLI scheme.
- Scheme will benefit the international player more than the Domestic firms.
- Domestic firms may also face competition from cheap imports.
- India so far not focussed on adequate R&D development and Raw machinery.
- Challenge of WTO: Chinese Taipei contested the raise in tariffs under the Phased Manufacturing Programme.
WAY FORWARD:
- The government has to encourage the Foreign firms under the PLI policy to co-locate(placement of several entities in a single location) with their established industrial ecosystems.
- Government must also focus on the service industry
- India also needs to consider reducing its factor costs of power and logistics.
- Encouraging states to be competitive and not indulge in trade-restrictive practices like Job reservation for locals, etc.
- Further, Implementing structural reforms such as Land reforms etc.
- India needs to improve human capital to meet the demands of the sunrise industries.
- India should act fast to attract outgoing investment from China.
NEWS IN BRIEF: PRELIMS SPECIAL
Engineers’ Day
- India celebrates September 15 as Engineers’ Day to mark the birth anniversary of M Visvesvaraya.
- Also called Sir MV after he was knighted by the British, he was a civil engineer and statesman.
- A Bharat Ratna awardee (1955), Visvesvaraya is best known for designing one of India’s first flood protection systems, in Hyderabad, and setting up one of the first engineering institutes in the country, the Government Engineering College, now called University Visvesvaraya College of Engineering, Bengaluru.
- One of his major contributions was the Krishnarajasagara (KRS) reservoir on the Kaveri river.
- Visvesvaraya’s other inventions included designing the block system of irrigation and the introduction of automatic sluice gates on dams.
- Engineers’ Day is also observed in Sri Lanka and Tanzania in his honour.
https://newsonair.com/2021/09/15/engineers-day-celebrating-indias-engineering-capabilities/
‘Shoonya’ Campaign
- NITI Aayog, RMI, and RMI India Launch ‘Shoonya’ Campaign.
- It is an initiative to promote zero-pollution delivery vehicles by working with consumers and industry.
- The campaign aims to accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in the urban deliveries segment and create consumer awareness about the benefits of zero-pollution delivery.
SCO Peaceful Mission 2021
- Indian Military Contingent participates in the 6th Edition of Exercise SCO Peaceful Mission 2021 at Orenburg, Russia.
- Joint Counter Terrorism Exercise PEACEFUL MISSION is a Multilateral Exercise, which is conducted biennially as part of military diplomacy between SCO member states.
- The aim of the exercise is to foster close relations between SCO member states and to enhance abilities of the military leaders to command multi-national military contingents.
Global Ozone Day
- India observed the 27th Global Ozone Day on 16 September.
- World Ozone Day is celebrated on 16th September each year to commemorate the signing of the Montreal Protocol.
- The Government of India (Ozone Cell, MoEF&CC) started observing this Day in 1995.
- The theme of World Ozone Day 2021 was “Montreal Protocol – Keeping us, our food and vaccines cool”.
https://newsonair.com/2021/09/16/world-ozone-day-2021-keeping-us-our-food-vaccines-cool/
Report on Reforms in Urban Planning Capacity in India
- NITI Aayog Launches Report on Reforms in Urban Planning Capacity in India.
- India is home to 11% of the total global urban population. By 2027, India will surpass China as the most populous country in the world. Unplanned urbanization, however, exerts great strain on our cities.
- Recommendations made:
- Central Sector Scheme ‘500 Healthy Cities Programme’, for a period of 5 years, wherein priority cities and towns would be selected jointly by the states and local bodies.
- All the cities and towns under the proposed ‘Healthy Cities Programme’ should strengthen development control regulations based on scientific evidence to maximize the efficiency of urban land (or planning area). The report recommends a sub-scheme ‘Preparation/Revision of Development Control Regulations’ for this purpose.
- States/UTs may need to expedite the filling up of vacant positions of town planners, and additionally sanction 8268 town planners’ posts as lateral entry positions
- Ensuring Qualified Professionals for Undertaking Urban Planning
- Constitution of a high-powered committee to re-engineer the present urban-planning governance structure.
- Revision of Town and Country Planning Acts
- ‘Citizen Outreach Campaign’ for demystifying urban planning.
- Steps for Enhancing the Role of Private Sector
- Steps for Strengthening Urban Planning Education System
- Constitution of a ‘National Council of Town and Country Planners’ as a statutory body of the Government of India. Also, a ‘National Digital Platform of Town and Country Planners’ is suggested to be created within the National Urban Innovation Stack of MoHUA.
https://newsonair.com/2021/09/19/niti-aayog-report-for-reforms-in-urban-planning-capacity-in-india/
G33
- Union Minister for Commerce & Industry addresses the G-33 Virtual Informal Ministerial Meeting.
- The G-33 Virtual Informal Ministerial Meeting organized by Indonesia was held to discuss the Agricultural Priority Issues of G33 and the Way Forward for the Twelfth Ministerial Conference (MC-12) scheduled to be held in November-December 2021.
- The G33 (or the Friends of Special Products in agriculture) is a coalition of developing countries, established prior to the 2003 Cancun ministerial conference, that have coordinated during the Doha Round of World Trade Organization negotiations, specifically in regard to agriculture.
- India is a member of this group, as also are China and Pakistan, among others. There are currently 47 members in the G33.
International Coastal Clean Up Day
- The 36th International Coastal Cleanup Day was celebrated consecutively for the tenth year by Eastern Naval Command (ENC).
- Every year, on the third Saturday of September, the International Coastal Clean-up Community encourages people around the world to remove trash and debris from beaches, waterways and other water bodies.



1.png)
