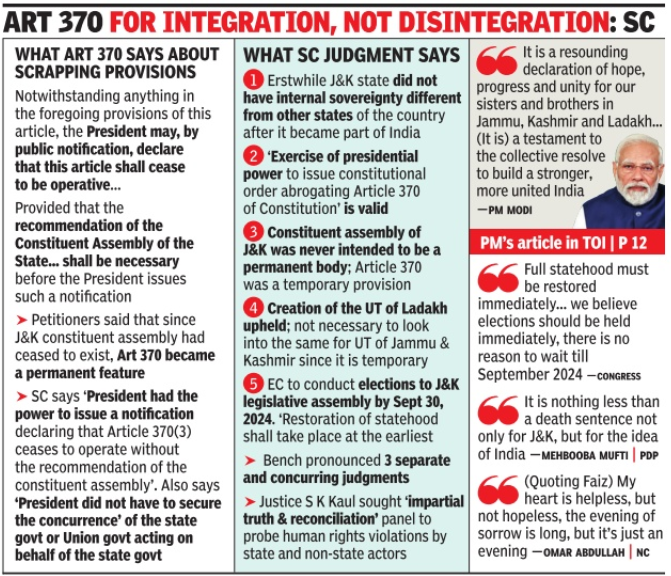
Supreme Court Verdict on Abrogation of Article 370

Context
- < UNK> On Monday, • The Supreme Court in a 5-0 unanimous ruling upheld the Centre’s abrogation of Article 370 of the Constitution.
Key Details:
- A Constitution Bench led by Chief Justice of India (CJI) D Y Chandrachud upheld the constitutional validity of the two Presidential Orders CO (The Constitution (Application To Jammu and Kashmir) Order) 272 and 273 of August 5 and 6, 2019 respectively by which the entire Constitution of India was made applicable to J&K. All provisions of Article 370 were declared inoperative.
- This is what the court said on four key issues in the challenge to the government's decisions.
On the sovereignty of Jammu and Kashmir
- The petitioners had argued that J&K retained an element of sovereignty when it joined the Indian Union in 1947. This arrangement, they argued, was distinct from the relationship with the other princely states that merged with India.
- The court examined the constitutional set-up of the erstwhile state to examine if it retained an element of sovereignty, which would allow Article 370 to operate in “unique circumstances”.
- First, it noted, that Article 1 of the Constitution of India provides that India is a Union of States. Article 1 references “Part III states”, and Jammu and Kashmir were listed as a Part III state (before 2019) in the First Schedule to the Constitution of India.
- Second, Section 3 of the Constitution of Jammu and Kashmir declared that Jammu and Kashmir is an integral part of India. The provision read: “Relationship of the State with the Union of India: The State of Jammu and Kashmir is and shall be an integral part of the Union of India.” Section 147 of the J&K Constitution prohibited any amendment to Section 3.
|
On whether Art 370 is temporary or permanent
- A range of arguments were made before the Court on the permanence (or lack thereof) of Article 370. The petitioners argued that the provision could not be abrogated since it had attained permanence, and as the original part of the Constitution forms the basic structure, which cannot be tinkered with.
- Senior advocate Kapil Sibal argued that since 370(3) prescribes the recommendation of the Constituent Assembly of the State (which has ceased to exist) as a prerequisite to abrogate Article 370, its abrogation is essentially infructuous. This means no constitutional means existed to abrogate Article 370 once the J&K Constituent Assembly had ceased to exist.
- The opinions of both the CJI and Justice Kaul held that Article 370 was always meant to be a “temporary” feature.
- Justice Kaul held that since Article 370 is meant to be a temporary arrangement, it cannot be said that the mechanism under Article 370(3) came to an end after the State Constituent Assembly was dissolved.
|
On the legality of the abrogation of Article 370
- The legal route for the abrogation of Article 370 was twofold. First, on August 5, 2019, then President Ram Nath Kovind issued CO 272, which amended Article 367 of the Constitution. Article 367 deals with the interpretation of the Constitution, and the CO added a new meaning to “Constituent Assembly of Jammu and Kashmir” to mean “legislative assembly of Jammu and Kashmir.
- Then, CO 273 was promulgated seeking the consent of Parliament (which had assumed powers of the J&K legislature) to recommend that “all clauses of the said article 370 shall cease to be operative”.
- While Justice Kaul upheld this process, CJI Chandrachud in his opinion said that the circuitous route of first changing the meaning of the Constituent Assembly of J&K was not needed. Essentially, after the Constituent Assembly of the state ceased to exist, the President could have always unilaterally abrogated Article 370.
- “The power under Article 370 (3) did not cease to exist upon the dissolution of the Constituent Assembly of Jammu and Kashmir. When the Constituent Assembly was dissolved, only the transitional power recognized in the proviso to Article 370 (3) which empowered the Constituent Assembly to make its recommendations ceased to exist. It did not affect the power held by the President under Article 370(3),” the ruling stated.
|
On the action that was taken under the President’s rule
- The petitioners had argued that the Union took “irrevocable” action without the state’s consent when it was under the President’s rule. Here, the challenge was to the extent of powers that can be appropriated when Article 356 is in operation.
- Both the CJI and Justice Kaul cited the 1994 ruling in S R Bommai v Union of India that defined the contours of the proclamation of President’s rule. The Bommai ruling was a nine-judge Bench verdict that is binding on a smaller 5-judge Bench.
- Relying on the Bommai ruling, the court said that the standard to decide the validity of the President’s action was to see whether it was not “mala fide or palpably irrational”, or that the “advisability and necessity of the action was not borne in mind by the President”.
- The court also held that the petitioner and the Union government must show mala fides to the court. The ruling rejected the argument that irrevocable action being taken cannot be accepted as proof of mala fides.
Significance of the Verdict:
- The verdict reaffirms the legality of the government's decision to abrogate Article 370.
- It acknowledges the temporary nature of the reorganization and paves the way for the restoration of statehood and democratic processes in Jammu and Kashmir.
- The recommendation for a Truth and Reconciliation Commission reflects a commitment to addressing human rights concerns in the region.
About Article 370:
- Article 370 of the Indian Constitution, introduced as a "temporary provision" in 1949, granted special status to the region of Jammu and Kashmir. Drafted by N Gopalaswami Ayyangar, a member of the Constituent Assembly of India, it played a pivotal role in shaping the governance of this disputed territory.
Provisions and Autonomy:
- Under Article 370, Jammu and Kashmir had the privilege of maintaining its constitution, flag, and a considerable degree of autonomy. The state enjoyed authority over various matters, excluding defense, foreign affairs, and communications, which remained under the purview of the Indian government.
Historical Context:
- The genesis of Article 370 lies in the Instrument of Accession signed in 1947 by the then-ruler of Jammu and Kashmir, Hari Singh. This instrument facilitated the region's integration into India following an invasion by Pakistan.
Controversy and Abrogation:
- Over the years, Article 370 became a contentious issue, sparking debates and differing opinions. In August 2019, the Indian government, under Prime Minister Narendra Modi, took a historic step by abrogating Article 370. This move revoked the special status previously accorded to Jammu and Kashmir, leading to significant changes in its governance structure.
Why was the Article 370 Abrogated?
- Integration and Development: Article 370 was perceived as a hindrance to the complete integration of Jammu and Kashmir into the Indian Union. Its presence fueled a sense of separatism, impeding the region's overall development.
- The removal of Article 370 was seen as a step towards fostering better integration and providing increased access to resources, infrastructure, and developmental opportunities for the people of Jammu and Kashmir.
- National Security: Article 370 had been exploited by Pakistan to support terrorism and separatist activities in the region. Abrogating the article was viewed as essential for strengthening national security. It allowed the Indian government to exert more control over the region, facilitating a more robust response to terrorist threats and separatist movements.
- Ending Discrimination: Article 370 was criticized for perpetuating discrimination, particularly against women, Dalits, and other marginalized groups in Jammu and Kashmir. Its abrogation aimed to bring these groups under the protective umbrella of Indian laws, ensuring equal rights and opportunities for all residents of the region.
- Transparency and Accountability: The presence of Article 370 contributed to a lack of transparency and accountability in the governance of Jammu and Kashmir. Abrogating the article meant bringing the state under the purview of the Central Vigilance Commission and the Right to Information Act.
- This move was expected to enhance transparency, improve governance, and make authorities more accountable.
- Economic Prosperity: Article 370 was seen as a barrier to economic development in Jammu and Kashmir. Its removal was anticipated to open up the region to greater investment, tourism, and job creation, thereby fostering economic prosperity.
- The expectation was that without the restrictions imposed by Article 370, the region could attract more business and contribute to its overall economic growth.
What has been the Impact of Article 370 Abrogation?
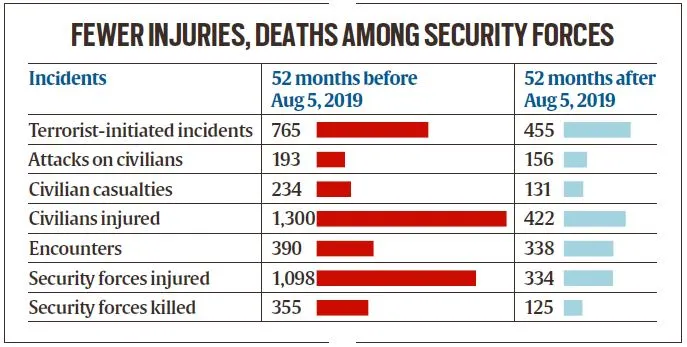
Reduction in Violence:
- There has been a substantial decrease in terrorist incidents, exceeding 50%, and security forces have successfully neutralized over 300 militants.
- These improvements suggest a significant enhancement in the region's security, attributed to heightened security measures, improved intelligence strategies, and a decline in public support for militancy.
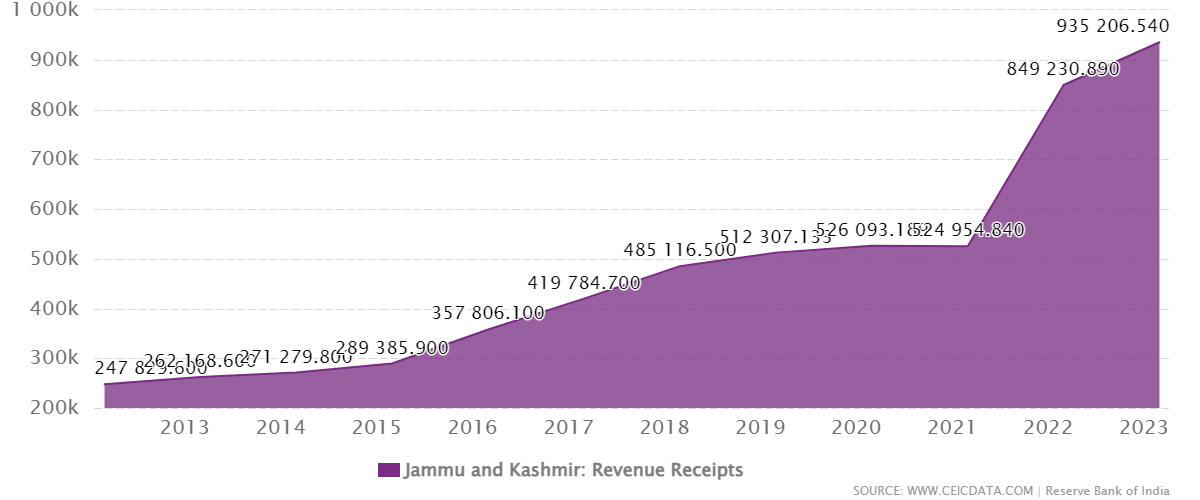
Economic Development Initiatives:
- Government-driven initiatives like the Prime Minister's Development Package (PMDP) and the Industrial Development Scheme (IDS) have played a pivotal role in stimulating economic growth.
- Increased investment, job creation, and a remarkable 31% growth in tax revenue underscore the positive economic impact of these measures.
- The 8% growth in Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) at constant prices during 2022-23, surpassing the national average, highlights the encouraging economic trajectory.
Infrastructure Development:
- Substantial investments in infrastructure, including the construction of roads, bridges, tunnels, and power lines, have enhanced connectivity and accessibility within the region.
- These developments not only facilitate smoother travel but also contribute to a more conducive environment for economic activities.
Tourism Boost:
- Tourist numbers have experienced a notable surge, reaching a historic high of 1.62 crore in 2022. This increase reflects the positive impact on the tourism sector, attributed to enhanced security measures, effective marketing strategies, and the implementation of new tourism initiatives.
- The rise in tourism not only brings economic benefits but also signifies renewed interest in exploring the natural beauty and cultural richness of Jammu and Kashmir.
Closing thoughts
- The Supreme Court's verdict not only validates the constitutional order but also outlines steps for the future, including the restoration of statehood, holding elections, and addressing past grievances through a Truth and Reconciliation Commission.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=people-unanimously-welcome-verdict-of-Supreme-Court-upheld-abrogation-of-Article-370&id=472977#:~:text=people%20unanimously%20welcome%20verdict%20of%20Supreme%20Court%20upheld%20abrogation%20of%20Article%20370,-AIR%20PIC&text=People%20from%20different%20sections%20of,the%20abrogation%20of%20Article%20370.
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1984904
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=BJP-welcomes-SC-verdict-on-abrogation-of-Article-370%2C-terms-it-landmark-decision&id=472992
https://www.outlookindia.com/national/supreme-court-upholds-abrogation-of-article-370-how-did-china-and-pakistan-react--news-336212
https://thefridaytimes.com/13-Dec-2023/article-370-the-indian-supreme-court-judgment-and-pakistan-s-options
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W6WbuXCVybk

Central Universities (Amendment) Bill, 2023
Context
- Parliament has passed the Central Universities (Amendment) Bill, 2023 with Rajya Sabha giving assent to it today. Lok Sabha had passed the Bill last week.
Key features of the bill:
- The Bill will amend the Central Universities Act, of 2009, which establishes central universities for teaching and research in various States.
- The Bill seeks to establish a Central Tribal University in Telangana which will be named ‘Sammakka Sarakka Central Tribal University’.
- It will provide avenues of higher education and research facilities primarily for the tribal population of India.
- The primary objective of the bill is to provide avenues for higher education and research facilities, particularly catering to the tribal population of India. This aligns with the broader goal of improving educational opportunities and outcomes for marginalized communities.
The Legend of Sammakka and Sarakka:
- Sammakka, married to Pagididda Raju, a feudal chief of the Kakatiyas, ruled the Warangal area. She had three children - Sarakka (Saralamma), Nagulamma, and Jampanna.
13th-century Battle:
- In the 13th century, Saralamma died in a battle against local rulers protesting tax imposition, while Sammakka disappeared into the hills. Local Koya tribals believed Sammakka transformed into a vermillion casket.
The Sammakka Saralamma Jatara:
- The Mulugu district in Telangana hosts the biennial Sammakka Saralamma Jatara, known as the Kumbh Mela of tribals. Commemorating the mother-daughter duo's battle against taxes, it's Asia's largest tribal fair, occurring every two years at Medaram village.
Political and Cultural Significance:
- Declared a state festival in 1996, the Jatara attracts political and cultural attention. The Union Ministry of Tribal Affairs and the Telangana state government actively participate.
- Funds are allocated for community shelters and infrastructure. The Ministry of Tourism granted Rs. 75.88 crore for the tribal circuit's development under the Swadesh Darshan Scheme, encompassing Mulugu - Laknavaram - Medavaram - Tadvai - Damaravi - Mallur - Bogatha Waterfalls.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Parliament-passes-Central-Universities-(Amendment)-Bill%2c-2023-paving-way-for-establishing-Sammakka-Sarakka-Central-Tribal-University-in-Telangana&id=473135

28th Conference of the Parties (COP28)
Context
- In Dubai, the 28th Conference of the Parties (COP28) has come to a historic close, marking a turning point in global efforts to combat climate change.
.jpg)
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement is not intended
Details:
- A landmark agreement, aptly named "The UAE Consensus," was reached by 198 participating Parties, outlining an ambitious climate agenda aimed at keeping the goal of limiting global warming to 1.5°C within reach.
Key Achievements:
- Key achievements under the Action Agenda include the launch of ALTÉRRA, a $30 billion catalytic private finance vehicle by the UAE, aiming to mobilize $250 billion for global climate action.
- Additionally, COP28 saw the endorsement of the 'COP28 UAE Declaration on Agriculture, Food, & Climate' by 158 countries, embedding sustainable agriculture and food systems in climate change responses.
- The 'COP28 UAE Declaration on Climate and Health,' endorsed by 144 countries, accelerates the development of climate-resilient, sustainable, and equitable health systems.
- The Global Decarbonization Accelerator (GDA) introduced initiatives such as the Global Renewables and Energy Efficiency Pledge and the Oil and Gas Decarbonization Charter.
- Outside the Global Stocktake, COP28 delivered historic negotiated outcomes, including the operationalization of Loss and Damage, securing $792 million in early pledges, advancing the Global Goal on Adaptation (GGA), and institutionalizing the role of the Youth Climate Champion. Dr. Al Jaber reaffirmed the balanced nature of the COP28 achievements, addressing emissions, adaptation, global finance, and loss and damage.
- The unprecedented consensus reflects a commitment to inclusivity, collaboration, and a determination to accelerate global climate action.
- As COP28 concludes, the focus now shifts to ensuring the agreements are implemented and followed through at COP29 and COP30.
- The COP28 Presidency has signed an agreement with Brazil, the host of COP30, to deepen collaboration and increase climate ambitions, working with Azerbaijan, the hosts of COP29, to ensure ambitious updated climate plans for action in this critical decade.
- COP28 has set a precedent for future conferences, providing a blueprint for ambitious and inclusive climate action on a global scale.
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=COP28-in-Dubai-concludes-with-landmark-UAE-Consensus-to-transition-away-from-fossil-fuels&id=473114
.jpg)
No Shortage of Anti-TB Drugs
Context
- The Government has said that there is no shortage of anti-tuberculosis drugs in the country.

Details
- The Ministry of Health in a statement said that there has been regular supply of Anti-TB drugs to all the States and UTs from the Central level under the National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP) throughout the year.
- It said regular assessments are conducted to evaluate the stock positions at various levels, from Central warehouses to peripheral Health institutes.
- The Ministry added that States and UTs have been provisioned with resources for local procurement for limited quantities as and when required to meet the emergent requirements.
About the National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP):
|
About
|
- The National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP) is a comprehensive initiative launched by the Government of India to combat and eliminate Tuberculosis (TB) in the country.
- TB is a bacterial infection that primarily affects the lungs and poses a significant public health challenge globally.
|
|
Objectives
|
- Early Detection and Diagnosis: NTEP focuses on early detection of TB cases through widespread screening and diagnostic services. This involves identifying and testing individuals who may be at risk of TB infection.
- Effective Treatment: Once diagnosed, the program emphasizes the prompt and effective treatment of TB cases. It involves the administration of appropriate anti-TB medications to ensure a complete cure and prevent the spread of the disease.
- Prevention of Drug Resistance: NTEP aims to prevent the development and spread of drug-resistant TB strains by ensuring that patients adhere to the prescribed treatment regimen. This involves a combination of drugs administered under direct observation.
|
|
Progress and Achievements
|
- The NTEP has made significant strides in reducing TB incidence and mortality rates across the country.
- It has achieved milestones in terms of increased case detection, improved treatment success rates, and the overall decline of TB prevalence.
|
|
Collaboration
|
- NTEP operates through collaboration with various stakeholders, including healthcare providers, non-governmental organizations, and international partners.
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=No-Shortage-of-Anti-TB-Drugs-Confirmed-by-Govt.-Says&id=473173

Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra
Context
- More than 63 lakh people have availed benefits of health camps under the Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra (VBSY) campaign.

Details:
- The Ministry of Information and Broadcasting said that during the Yatra, more than 26 thousand Gram Panchayats have achieved a cent percent saturation of Ayushman Cards to date.
- It added that almost 10 lakh Ayushman Cards have been issued to more than 1.5 lakh people and more than 26 lakh people have been screened for Tuberculosis (TB).
- Over six lakh attendees have been screened for Sickle Cell Disease at the VBSY camps.
- The Ministry added that TB patients under the Nikshay Poshan Yojna are being given financial help through Direct Benefit Transfer.
- It further said that people can also get checked for other diseases such as Hypertension and Diabetes at the camps.
About the Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra:
|
About
|
- The Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra (VBSY) recently presented an enlightening showcase on agricultural development, offering farmers valuable insights to enhance production and productivity.
- The event featured over 120 drone demonstrations and Soil Health Card presentations, coupled with interactive sessions with farmers practicing Natural Farming.
|
|
Government Flagship Schemes Milestones
|
- The Yatra underscored remarkable achievements in the 100% saturation of government flagship schemes.
- Noteworthy statistics include 83 Gram Panchayats achieving 100% Ayushman Card saturation, 89 GPs with 100% Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) saturation, 97 GPs achieving 100% Jan Dhan saturation, and 124 GPs attaining Open Defecation Free Plus status.
|
|
Success Stories and Testimonies
|
- Individual success stories took center stage during the Yatra as over 200 beneficiaries shared their transformational journeys through "Meri Kahani Meri Zubani."
- These testimonies highlighted the tangible impact of government flagship schemes in improving the lives of citizens.
|
|
Largest-Ever Outreach Initiative
|
- Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra stands out as the largest-ever outreach initiative by the Government of India, aligning with the vision of inclusive development.
- The Yatra aims to ensure that the benefits of government schemes reach every corner of the nation, achieving 100% saturation.
- Through extensive outreach, information dissemination, and citizen empowerment, the Yatra plays a pivotal role in making citizens active stakeholders in the country's development.
|
|
Real-Time Monitoring and Data Capture
|
- Ground-level activities undertaken by Information, Education, and Communication (IEC) vans are captured in real-time on a portal developed by the Digital India Corporation of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
- This ensures transparency, accountability, and effective monitoring of the Yatra's impact on the ground.
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Over-63-Lakh-Benefit-from-Health-Camps-in-Viksit-Bharat-Sankalp-Yatra&id=473169








.jpg)

