Successful Injection of ISRO's Aditya-L1 in Halo Orbit to Study Sun

Context
- The successful injection of ISRO's Aditya-L1 in Halo Orbit to study the Sun is a milestone achievement for India and the space science community of the country.
Key Details:
- Nigar Shaji, Project Director of Aditya-L1 in an interview with Akashvani News, said that with the success of this mission, India became the 4th such country that has sent a mission to the Halo Orbit to study the Sun.
- She said space is an upcoming field, and it is a matter of happiness for ISRO and the country that it is contributing to at a large level. Aditya-L1 Project Director said the country has a better hold in the field of space science to be at top levels.
ISRO's Aditya-L1:
| Indian Army is encouraging women officers to join the force by adopting enabling policies for their inclusion. Recent major initiatives are as under: |
- Purpose: Aditya-L1, launched by ISRO, aims to study and observe the Sun comprehensively. It seeks to provide insights into various solar phenomena such as the solar corona, solar wind, charged particles, and eruptions that can impact space weather and technologies on Earth.
Significance of Studying the Sun:
- The Sun's activities impact Earth's atmosphere, climate, and space-based technologies.
- Understanding solar processes like the solar wind, flares, and coronal mass ejections (CMEs) is crucial for space weather predictions.
Aditya-L1's Objectives:
- Observe the ultraviolet radiation emitted from the solar corona to comprehend its behavior and energy dynamics.
- Monitor solar eruptions and the properties of charged particles in the solar wind.
- Provide early warnings of solar eruptions to mitigate potential disruptions to space-based technologies.
Why Aditya-L1 is Positioned at L1 (Lagrangian Point 1)
- About L1: L1, or the first Lagrangian point, is a point of gravitational equilibrium between the Earth and the Sun.
- Advantages of L1 for Aditya-L1:
- Uninterrupted View: Placing Aditya-L1 at L1 ensures an uninterrupted view of the Sun as the spacecraft remains between the Earth and the Sun. It eliminates eclipses or interruptions caused by Earth's movements.
- Observation outside Earth's Atmosphere: Being outside Earth's atmosphere enables Aditya-L1 to observe ultraviolet radiation from the solar corona, which is not possible from Earth due to atmospheric absorption.
- Early Warning System: Continuous monitoring from L1 enables early detection of solar eruptions, allowing preparations to mitigate potential damages caused by these events.
Characteristics of L1
- Stability: L1 offers a relatively stable position due to the gravitational balance between the Earth and the Sun. However, it requires careful orbiting around the L1 point to maintain position.
- Unstable Nature:Despite being a stable point, L1 is fundamentally unstable. A minor disturbance can cause a spacecraft positioned at L1 to drift away, so Aditya-L1 is placed in an orbit around L1 to maintain its position.
- Orbit Duration:Aditya-L1 follows a complex orbit nearly perpendicular to the line joining the Sun and Earth, taking about 178 days to complete one full orbit around L1.
Comparison with Other Lagrange Points (L2)
- L2's Utility:While L1 is ideal for solar observation, L2 is useful for observing distant celestial bodies.
- Usage of L2:Spacecraft positioned at L2, such as the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), Gaia, and Euclid, point away from Earth, enabling observations of deep space without interruptions from Earth's presence.
| Lagrange points, also known as libration points, are specific regions in space where the gravitational forces of two celestial bodies, such as a planet and its moon or a planet and the Sun, create a stable equilibrium. These points were first discovered by Joseph-Louis Lagrange, a mathematician, and physicist, in the late 18th. There are five Lagrange points labeled L1 to L5, each with unique characteristics and properties. |
Position and Characteristics
L1: Located on the line connecting the two massive bodies, closer to the larger body. Objects placed at L1 move in sync with the Earth's orbital motion, making it suitable for space observatories like the James Webb Space Telescope.
L2: On the line connecting the two bodies, beyond the larger body. Objects at L2 enjoy a constant view of the night sky and are used for solar and Earth observations.
L3: Opposite to the larger body, forming a straight line with the two massive bodies. It's unstable, making objects there prone to perturbations and drift.
L4 and L5: Form equilateral triangles with the two massive bodies. Objects at these points tend to accumulate over time due to gravitational forces, forming regions known as Trojan asteroids or Lagrange point clouds.
Aditya-L1: India's Solar Observatory

Launch Details:
- Aditya-L1, India's pioneering space-based observatory dedicated to solar studies, was successfully launched in September 2023. The launch utilized a PSLV-C57 rocket, taking off from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota.
Orbital Placement:
- The satellite strategically orbits the Sun at the L1 Lagrange point, situated approximately 1.5 million km from Earth.
- This location, constituting just 1% of the Earth-Sun distance, allows for continuous solar observation, devoid of occultation or eclipse, providing a unique advantage in monitoring solar activities.
Lagrange Points:
- Lagrange points are gravitational equilibrium positions in space, where the gravitational forces of two massive bodies balance the centripetal force, enabling smaller objects to remain stationary. The L1 Lagrange point, in this case, optimizes fuel efficiency, facilitating the spacecraft's ability to sustain its position effectively.
Scientific Payloads:
- Aditya-L1 carries a suite of seven payloads designed to observe distinct layers of the Sun, including the photosphere (visible surface), chromosphere (the layer between the photosphere and corona), and the corona (outermost layers).
- These payloads play a crucial role in gathering information on coronal heating, coronal mass ejections, space weather dynamics, as well as particle and field propagation.
Objectives:
- The primary mission objectives encompass advancing our understanding of solar phenomena, particularly focusing on coronal activities and their implications on space weather.
- The data collected by Aditya-L1 is expected to contribute significantly to our knowledge of solar processes and enhance our ability to predict and manage space weather events.
Payloads of Aditya L1:
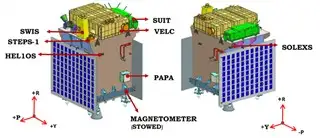
The instruments of Aditya-L1 are tuned to observe the solar atmosphere mainly the chromosphere and corona. In-situ instruments will observe the local environment at L1. There are a total of seven payloads on-board with four of them carrying out remote sensing of the Sun and three of them carrying in-situ observation.
|
Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC)
|
- Corona/Imaging & Spectroscopy.
|
|
Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT)
|
- Photosphere and Chromosphere Imaging- Narrow & Broadband.
|
|
Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS)
|
- Soft X-ray spectrometer: Sun-as-a-star observation.
|
|
High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS)
|
- Hard X-ray spectrometer: Sun-as-a-star observation.
|
|
Aditya Solar Wind Particle Experiment (ASPEX)
|
- Solar wind/Particle Analyzer Protons & Heavier Ions with directions.
|
|
Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA)
|
- Solar wind/Particle Analyzer Electrons and heavier Ions with directions
|
|
Advanced Tri-axial High-Resolution Digital Magnetometers
|
- In-situ magnetic field (Bx, By and Bz).
|
Significance of the Mission:
Advancement in Solar Physics:
- Aditya-L1's observations and data will contribute to advancements in solar physics, plasma dynamics, and magnetism, enriching our understanding of stellar astrophysics.
Space Exploration Endeavors:
- The mission sets a precedent for India's space exploration initiatives, enabling future solar and space-based research missions.
Coronal Heating and Eruption Mechanisms:
- Aditya-L1 aims to uncover the mechanisms behind coronal heating, coronal mass ejections, and solar flares, providing insights into the complex interactions within the Sun's atmosphere.
Space Weather Prediction:
- By studying space weather impacts and solar events, the mission intends to enhance space weather prediction models, offering the potential to mitigate their effects on Earth's technological infrastructure.
Solar Wind and Magnetic Field Studies:
- The mission will contribute to understanding the solar wind's composition, dynamics, and magnetic field topology, shedding light on their roles in driving space weather.
Limitations of the Mission:
Orbital Perturbations:
- While Lagrange points offer stability, they are not completely free from disturbances. Orbital perturbations from other celestial bodies and non-gravitational forces can affect objects stationed at these points.
Energy Requirements:
- Positioning and maintaining objects at Lagrange points require careful fuel management due to the need to counteract gravitational influences and maintain desired orbits.
Closing thoughts
- The Aditya-L1 mission represents India's foray into solar research and exploration, promising valuable insights into the Sun's intricate dynamics and their impacts on our technological environment.
- By studying the Sun's upper atmospheric behavior, space weather phenomena, and solar particle interactions, Aditya-L1 aims to unravel longstanding mysteries while contributing to global scientific knowledge and the advancement of space technology.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Successful-injection-of-ISRO%26%2339%3Bs-Aditya-L1-in-Halo-Orbit-to-study-Sun-is-a-milestone-achievement-for-India%3A-Nigar-Shaji%2C-Project-Director-of-Aditya-L1&id=474736
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=India%E2%80%99s-first-solar-observatory-mission%2C-Aditya-L1%2C-successfully-launched-from-Sriharikota-Space-Centre&id=467119
https://newsonair.com/2023/09/02/aditya-l1-indias-first-space-mission-to-study-sun-to-be-launched-from-sriharikota-this-morning/
https://www.isro.gov.in/Aditya_L1.html
https://www.hindustantimes.com/technology/isro-launch-first-solar-mission-adityal1-study-sun-explained-

55th convocation ceremony of the Indian Institute of Mass Communication
Context
- Former President Ram Nath Kovind has expressed concern over fake news, paid news, and deepfake saying one has to be ready to tackle the challenges arising out due to the emergence of new technology.

Key Details:
- Addressing the 55th convocation ceremony of the Indian Institute of Mass Communication (IIMC) in New Delhi, Mr Kovind said that the wrong information adversely impacts society and there is a need to look into this challenge.
About fake news, paid news, and deep fake:
- Fake news refers to false or misleading information presented as genuine news. It often involves the intentional spread of misinformation to deceive or manipulate public opinion.
- Paid news involves the exchange of money for favorable coverage or the suppression of negative information in news media. It compromises journalistic integrity.
- Deepfake refers to the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning techniques to create realistic but fabricated audio or video content, often featuring individuals saying or doing things they never did.
Impacts:
- Misinformation: Deepfakes can be used to spread false narratives, manipulating public perception and causing reputational harm.
- Privacy Concerns: Individuals may become victims of deepfake manipulation, with potential consequences for personal and professional relationships.
- Trust Issues: The prevalence of deepfakes raises concerns about the reliability of visual and auditory information, leading to a decline in overall trust in media and online content.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Former-President-Ram-Nath-Kovind-expresses-concern-over-fake-news%2c-paid-news-%26-deep-fake%2c-saying-one-has-to-be-ready-to-tackle-challenges-arising-out-of-new-technology&id=474883

World Hindi Day
Context
- World Hindi Day is being observed today. The day is commemorated every year to promote the use of the Hindi language abroad.

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement is not intended
Details:
- On this day in 2006, the First World Hindi Conference was held in Nagpur to promote the language worldwide and since then, every year 10th January has been observed as World Hindi Day.
- The Ministry of External Affairs and Indian Missions abroad also observe the day annually. On the occasion of World Hindi Day, the cultural arm of the High Commission of India in Colombo, Swami Vivekananda Cultural Centre (SVCC) organized a two-day Conference at the Sri Lanka Foundation in Colombo.
About the World Hindi Day:
- Global Celebration: Celebrated worldwide on 10 January to promote Hindi as an international language.
- Awareness: A day dedicated to raising awareness about the significance of Hindi on a global scale.
- Embassy Programs: Special programs organized in Indian embassies around the world to showcase the cultural and linguistic richness of Hindi.
Importance of Hindi Language:
- Global Presence: Hindi is spoken by 61 crore people worldwide, highlighting its widespread global presence.
- Literary Promotion: All India Language Literature Conferences are organized to foster the growth of Hindi literature.
- World Hindi Secretariat: Located in Mauritius since 11 February 2008, this secretariat actively works towards the global promotion of the Hindi language.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=World-Hindi-Day-being-observed-today-to-promote-Hindi-language-abroad&id=474881
South China Sea code
Context
- Indonesia's Foreign Minister Retno Marsudi has said that her country is ready to work with other Southeast Asian nations to finalize a long-delayed code of conduct for the South China Sea, where many of its neighbors have overlapping claims with China.

Details
- Ms Retno said this at a joint press conference with Filipino counterpart Enrique Manalo in Manila, ahead of a visit by Indonesian President Joko Widodo. She said, in the South China Sea, Indonesia is ready to work together with all Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) member states including the Philippines to finalize the Code of Conduct as soon as possible.
About the South China Sea code:
|
About
|
- The South China Sea code typically refers to a Code of Conduct (COC) for the South China Sea. It is an agreement that aims to establish guidelines and behavior for countries with claims and interests in the South China Sea region, which has been a source of territorial disputes.
|
Key Points about the South China Sea Code of Conduct:
- Territorial Disputes: The South China Sea is an area where multiple countries, including China, Vietnam, the Philippines, Malaysia, Brunei, and Taiwan, have territorial claims, leading to tensions and disputes.
- Code of Conduct: The COC is intended to be a set of rules and guidelines to manage and prevent conflicts in the South China Sea. It aims to establish a framework for peaceful resolution and cooperation among the involved nations.
- Negotiations: The development of the COC involves negotiations between the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and China. ASEAN member states play a crucial role in shaping the agreement.
- Timeline: Discussions and negotiations on the COC have been ongoing for several years. While progress has been made, reaching a comprehensive and mutually agreeable code has proven to be a complex and time-consuming process.
- Contentious Issues: Issues such as freedom of navigation, resource exploitation, and the handling of maritime incidents are often key points of contention in the negotiations.
- International Significance: The South China Sea is of strategic importance due to its role in global trade routes and its natural resources. The development of a COC is closely watched by the international community.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Indonesia-ready-to-work-with-countries-to-finalise-South-China-Sea-code&id=474888
.jpg)
Dubai secures top spot in 2024 Tripadvisor Travellers’ Choice Awards
Context
- Dubai has clinched the prestigious title of the No.1 global destination in the Tripadvisor Travellers’ Choice Best of the Best Destinations Awards 2024, marking its third consecutive win.

Details:
- This achievement sets a historic milestone, making Dubai the first city to accomplish such a feat in succession. The announcement coincides with the first anniversary of the Dubai Economic Agenda, D33, which strives to solidify Dubai’s standing as a leading global city for both business and leisure.
About the Tripadvisor Travellers’ Choice Awards:
|
Tripadvisor's Traveler's Choice Award 2023
|
- The prestigious Tripadvisor Traveler's Choice Award for 2023, based on millions of traveler reviews, has once again crowned Dubai as the world's favorite destination.
- This recognition, covering 12 months from October 1, 2022, to September 30, 2023, is a testament to the city's exceptional offerings in hotels, restaurants, and experiences.
- Dubai's allure is amplified by the resounding praise from the global travel community, solidifying its position as a premier destination.
|
|
Dubai's Global Recognition
|
- Dubai continues to captivate the world as it secures the coveted second spot in Euromonitor International's prestigious Top 100 City Destinations Index for the year 2023.
- This recognition reflects the sustained appeal of Dubai, underpinned by a harmonious blend of top-notch infrastructure, exceptional service, and a diverse array of offerings.
- The city's ability to consistently attract global attention reaffirms its standing as a premier international destination.
|
|
Global Power City Index
|
- According to a report from the Mori Memorial Foundation’s Institute for Urban Strategies in Japan, Dubai has earned a place among the top 10 cities in the Global Power City Index.
- This recognition underscores Dubai's significance on the global stage, with a dynamic combination of local talent and international investment.
- The city's rise in this index is a testament to its evolving influence and prominence as a major global hub.
|
|
Safety and Liveability
|
- Dubai's appeal extends beyond its tourist attractions, as the United Arab Emirates (UAE), the home of Dubai, is acknowledged as the second safest country globally in 2023 according to Numbeo.
- This recognition reinforces Dubai's position as a top global liveability hub, offering a unique lifestyle and maintaining high safety standards for travelers.
- The city's commitment to safety adds another layer to its allure, making it an attractive destination for residents and visitors alike.
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Dubai-secures-top-spot-in-2024-Tripadvisor-Travellers%e2%80%99-Choice-Awards-for-third-consecutive-year&id=474895










