Increasing Participation of Women in Indian Armed Forces and Paramilitary Forces

Context
- In the Indian Armed Forces, there is no distinction in the deployment and working conditions of male and female officers in the Arms and Services in which they serve.
Key Details:
- The postings are as per organizational requirements. Training, postings, promotions, terms of engagement, etc. are common for both women and men.
- The rules regarding employability in Indian Armed Forces are gender-neutral and provide equal opportunities to men and women.
Indian Army:
| Indian Army is encouraging women officers to join the force by adopting enabling policies for their inclusion. Recent major initiatives are as under: |
- Permanent Commission (PC) is being granted to Women Officers (WOs) in 12 Arms and services (in addition to the Army Medical Corps, Army Dental Corps, and Military Nursing Service) where they are commissioned.
- The Indian Army has ensured parity amongst WOs and their male counterparts with a complete gender-neutral environment existing in the 12 Arms/ Services they are presently serving in. A special board to screen all affected WOs has been held and the results have been declassified.
- In regular boards also, WOs are being considered for grant of PC along with their male counterparts.
- The Armed Forces have opened entry for women candidates in the National Defence Academy (NDA) with 19 cadets including 10 for the Indian Army joining the academy every six months. First, Second, and Third batches of women cadets started training in NDA with effect from July 2022, January 2023, and July 2023 respectively.
- The organization is ensuring inclusive measures to carry out all necessary administrative, training, and policy changes to enable the same.
- The Indian Army has also opened avenues for WOs to serve as pilots in the Corps of Army Aviation.
- WOs are also being considered for Colonel (Select Grade) ranks and are being given command appointments. Certain waivers have also been given to WOs to rule out any impediment in the career progression of those who could not undergo mandatory career courses during the transition period.
- Provision for enrolment of women as Other Ranks (ORs) in the Corps of Military Police in the Indian Army has been introduced in 2019. Under the scheme, 1,700 women are targeted to be inducted into the Indian Army in a phased manner (approximately 100 per year).
Evolution of Women’s Participation in India’s Armed Forces
- Opening Doors in 1992: Traditionally perceived as a male-dominated domain, the Indian Armed Forces initiated the inclusion of women in 1992, when the Air Force welcomed its first batch.
- Limited Combat Roles: Progressing cautiously, the military granted permanent commissions in 2008 to women in streams like Judge Advocate General (JAG) and Army Education Corps. In 2015, combat air force roles expanded to include women as fighter pilots within the Air Force. However, similar roles in the Army and navy are yet to be fully realized.
Significance of Women’s Induction in Defence Forces in India
- Equal Opportunity: Allowing women officers to contribute equally to the nation's defense efforts is a pivotal step in promoting gender equality within the armed forces.
- Challenging Stereotypes: Breaking the conventional mindset that has restricted women from combat roles challenges stereotypes and fosters a more inclusive environment.
- Fulfilling Career Paths: Providing women with diverse roles and career options not only enhances the capabilities of the armed forces but also offers women a more challenging and fulfilling career.
- Changing Regressive Mindsets: Inclusion challenges the regressive mindset that has perpetuated the notion that domestic obligations solely rest on women, fostering a more progressive outlook.
Challenges in Integrating Women into Combat Roles
- Operational, Practical, and Cultural Concerns: The universal perception within the military is that integrating women into combat roles may pose operational, practical, and cultural challenges.
- Privacy Issues: Combat branches often involve close quarters, raising privacy concerns, a potential issue for female officers.
- Living Conditions: Maintaining suitable living conditions for women in combat situations proves challenging, particularly in adherence to prevailing social norms in India.
- Social Expectations and Absence: Society often perceives challenges for women to meet service requirements due to concerns about prolonged absence during pregnancy, motherhood, and domestic responsibilities.
The Way Ahead for Women in the Armed Forces
- Role Models: Women in the Armed Forces serve as inspiring role models for others. Both the Supreme Court and the Indian Government have played instrumental roles in pushing for gender inclusion.
- Proactive Approach: The Armed Forces should proactively champion gender equality, taking the lead in creating an environment that is inclusive and supportive, without waiting for legal interventions.
Recent developments for women in the armed forces
- Leadership Advancements for Women in the Armed Forces:
- The military is making significant strides in promoting gender equality by allowing women to command teams on par with their male counterparts.
- A Special Number 3 Selection Board, convened in January 2023, screened 108 female officers for promotion to the rank of Colonel, marking a historic move towards equal opportunities for leadership roles.
- Parity in Permanent Commission and Promotion:
- Following a Supreme Court decision advocating for parity in permanent commission and promotion, a one-time solution was implemented through the Special Number 3 Selection Board.
- This initiative aims to clear the backlog and ensure that women have equal opportunities for career advancement within the armed forces. Future selection panels are expected to adopt a gender-neutral approach.
- Expansion of Access to Different Military Branches:
- Progress has been made in expanding access for women within various military branches.
- Direct admittance as officers through the National Defence Academy, and enlistment in the Corps of Military Police, and Assam Rifles have been initiated, albeit at a slow pace. Access to the artillery, a prominent fighting branch, has also been granted.
- Training Achievements:
- Six female officers have completed the prestigious Defense Services Staff Course (DSSC) and Defense Services Technical Staff Course (DSTSC), showcasing their competence and dedication.
- Notably, the first female officer is currently stationed at the challenging Siachen Glacier, breaking barriers in traditionally male-dominated environments.
- Agnipath Program and Enlistment:
- The Agnipath program has facilitated the enlistment of women in the military, reflecting a commitment to inclusivity.
- This initiative demonstrates a proactive approach to encourage more women to join the armed forces and contribute to national defense.
- Remaining Challenges in Inclusion:
- Despite the positive developments, challenges persist as women are still barred from joining certain fighting forces, including the Armoured Corps, Infantry/Mechanized Infantry, Special Forces, and merit-driven competitive entry.
- The current entry pathway for women remains vacancy-based, hindering their ability to join the military on equal footing with men.
- Addressing these barriers is crucial for achieving comprehensive gender equality in the armed forces.
What are the advantages of Women joining the Armed Forces?
- The recruitment of military personnel should be based on qualifications rather than gender.
- In modern warfare, technical expertise and decision-making skills are more crucial than physical strength.
- Breaking Gender Stereotypes:
- Women in the armed forces can challenge traditional gender norms and promote equality.
- Encourages society to recognize and appreciate women's capabilities beyond stereotypical roles.
- Upholding the Right to Equality:
- The Constitution (Articles 14, 15, 16, and 19) emphasizes equality and non-discrimination.
- Denying eligible women the opportunity violates these constitutional values.
- Mixed-gender forces contribute to a robust and ready military.
- Addresses recruitment and retention challenges faced by the armed forces.
- Inclusion of women expands the recruitment pool, fostering a more diverse military.
- Allows for a representative and versatile armed forces.
- Women, often trained from childhood, excel in collaborative leadership.
- Encourages participation, power-sharing, and adaptability in various situations.
|
Prominent examples of Women in the Indian Armed Forces
Gunjan Saxena – She is a former IAF officer who became the first woman to fly in a combat zone during the 1999 Kargil War between India and Pakistan.
Padmavathy Bandopadhyay – She became the first woman Air Marshal of the Indian Air Force in 2004.
Bhawana Kanth – In 2016, she became the first woman to be inducted into the fighter stream of the Indian Air Force (IAF).
Tania Shergill – She became the first woman Parade Adjutant for the Republic Day parade in 2020, leading an all-male contingent of the Indian Army.
|
Closing thoughts
- The landscape of warfare is evolving, and tapping into the diverse skill sets of women is crucial for the future effectiveness of armed forces. Emphasizing meritocracy ensures that the most capable individuals, regardless of gender, are selected for key roles.
- This not only enhances the overall competency of the armed forces but also promotes a fair and inclusive environment where talent is recognized and utilized to its fullest potential.
- In a rapidly changing and technologically advanced world, merit-based selection becomes a strategic imperative for maintaining a strong and adaptable defense apparatus.
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1945707
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/women-india-republic-day-parade-explained-8596861/
https://static.mygov.in/indiancc/2021/07/mygov-10000000001255937422.pdf
https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/india/only-3-69-women-as-central-armed-police-forces-struggle-to-meet-quota-target/articleshow/95411009.cms
https://indianexpress.com/article/opinion/columns/international-womens-day-gender-equality-rajnath-singh-girl-education-women-indian-army-6305736/
https://www.india.gov.in/spotlight/career-defence-and-paramilitary-forces
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1908062
https://www.wionews.com/opinions-blogs/opinion-changing-role-of-women-in-the-indian-armed-forces-391292

PM Modi launches development projects at Kavaratti Island
Context
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi today said that the government is fully committed to ensuring the sustainable development of Lakshadweep.
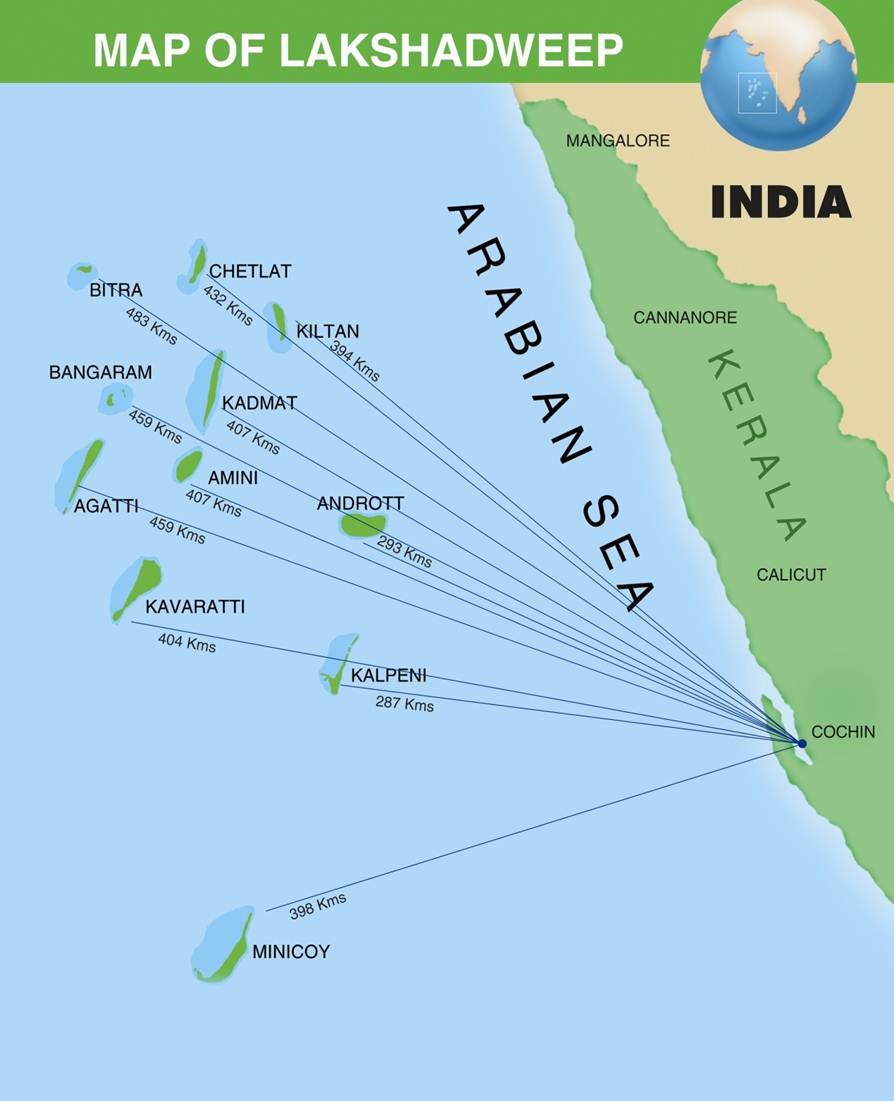
Key Details:
- Modi was addressing a function to mark the launching and laying the foundation stone of development projects worth 1156 crore rupees at Kavaratti island in Lakshadweep.
- He said all efforts are being made by the government to bring Lakshadweep to the forefront of the international tourism map.
- Lakshadweep hosting one of the G20 meetings has helped the island group to establish its identity as a tourism destination.
- He said construction of water villa projects is currently underway at the Kadamat and Suheli islands. Noting that tourists' arrival in Lakshadweep has increased fivefold in recent years, the Prime Minister appealed to those embarking on tours to visit beaches abroad should first visit Lakshadweep.
About Lakshadweep:
- Lakshadweep is a tropical archipelago of 36 atolls and coral reefs in the Laccadive Sea, 280 km to 480 km off the coast of Kerala. 11 are inhabited.
- But currently, there are 35 islands, as the Parali 1 island is submerged in water due to sea erosion.
- Lakshadweep means "one lakh islands" in Malayalam, the official as well as the widely spoken native language in the territory. Fishing is the most important industry.
- The islands form the smallest union territory of India and their total surface area is just 32 km square.
- Kavaratti serves as the capital of the Union Territory and the region comes under the jurisdiction of Kerala High Court. It is a uni-district Union Territory.
- The principal languages of Lakshadweep are Malayalam, Jeseri (Dweep Bhasha) and Mahl.
- These islands were earlier known as Laccadive, Minicoy, and Amindivi Islands.
- The name Lakshadweep was adopted on 1st November 1973.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=PM-Modi-launches-development-projects-at-Kavaratti-Island-in-Lakshadweep%3b-Says%2c-all-efforts-being-made-by-Govt-to-bring-Lakshadweep-on-international-tourism-map&id=474425
.jpg)
Special Investigation Team (SIT)
Context
- The Supreme Court has refused to order a Special Investigation Team (SIT) probe into the Adani-Hindenburg controversy.
.jpg)
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement is not intended
Details:
- Rejecting the plea to transfer the probe from the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) to SIT, a bench comprising Chief Justice DY Chandrachud and justices JB Pardiwala and Manoj Misra said, the market regulator has not been lackadaisical in the investigation.
- In a major relief to Adani Group, the Supreme Court said it can't enter into the domain of the regulatory regime and the report of Hindenburg or anything like that cannot become the basis of ordering a separate probe.
About the Special Investigation Team (SIT):
- SIT, or Special Investigation Team primarily deals with cases of significant gravity where the existing system proves inadequate. These often involve high-profile incidents, such as the Gujarat riots and the 1984 anti-Sikh riots.
- Work Procedure of SIT: The establishment of an SIT can be initiated by either the Supreme Court or the state government. Led by a single individual, the team thoroughly investigates the matter and compiles a report for the court's consideration.
- The court reviews the report at multiple levels of appeal, either accepting or rejecting it. In case of rejection, the appellate court takes charge of deciding the case.
- SIT Members: Comprising mainly retired High Court or Supreme Court justices, SIT members play a crucial role in maintaining law and order.
- The team may also include other members as per the Code of Criminal Procedure, with the investigating officer being an integral part.
- The transparent and honest judgments of these members, often utilizing the experience of retiring judges, contribute significantly to resolving complex situations.
Significance of SIT:
- In the pursuit of justice and the maintenance of law and order, SIT proves to be a crucial entity. Its members, guided by the expertise of retired judges, provide valuable recommendations and assistance to individuals facing challenging circumstances.
- The court's authority to accept or reject SIT reports ensures a thorough review process, with the appellate court being the final arbiter in case of rejection.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=SC-refuses-to-order-a-Special-Investigation-Team-probe-into-Adani-Hindenburg-controversy&id=474440
7th meeting of India-Nepal Joint Commission
Context
- External Affairs Minister Dr. S Jaishankar will be on a two-day visit to Nepal beginning tomorrow.

Details
- The visit will be at the invitation of the Foreign Minister of Nepal, P. Saud for co-chairing the 7th meeting of the India-Nepal Joint Commission in Kathmandu.
- The India-Nepal Joint Commission was established in 1987 and provides a platform for both Ministers to review all aspects of the bilateral partnership.
- During the visit, Jaishankar will also call on the leadership of Nepal and meet prominent political figures.
About the India-Nepal relations:
|
About
|
- Nepal is an important neighbor of India and occupies a special significance in its foreign policy because of the geographic, historical, cultural, and economic linkages/ties that span centuries.
- India and Nepal share similar ties in terms of Hinduism and Buddhism with Buddha’s birthplace Lumbini located in present-day Nepal.
- The India-Nepal Treaty of Peace and Friendship of 1950 forms the bedrock of the special relations that exist between India and Nepal.
- India is Nepal’s largest trade partner and the largest source of foreign investments, besides providing transit for almost the entire third-country trade of Nepal.
- India-Nepal has undertaken various connectivity programs to enhance people-to-people linkages and promote economic growth and development.
- Bilateral defense cooperation includes assistance to the Nepalese Army in its modernization through the provision of equipment and training.
- India has signed three sister-city agreements for twinning Kathmandu-Varanasi, Lumbini-Bodhgaya and Janakpur-Ayodhya.
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=EAM-Dr-Jaishankar-to-be-on-two-day-visit-to-Kathmandu-to-co-chair-7th-meeting-of-India-Nepal-Joint-Commission&id=474451

India and UAE Joint Military Exercise ‘DESERT CYCLONE’
Context
- India and UAE began a joint military exercise called ‘DESERT CYCLONE’ in Mahajan, Rajasthan yesterday.

Details:
- The exercise will conclude on January 15. The UAE contingent comprising 45 personnel is being represented by troops from the Zayed First Brigade while the Indian Army contingent comprising 45 personnel is being represented mainly by a Battalion from the Mechanised Infantry Regiment.
About the ‘DESERT CYCLONE’:
|
Objective
|
- The primary goal of Exercise 'DESERT CYCLONE' is to augment interoperability in sub-conventional operations, specifically focusing on Fighting in Built-Up Areas (FIBUA) in desert and semi-desert terrain.
- This aligns with the principles outlined in the United Nations Charter on Peacekeeping Operations.
|
|
Cooperation and Interoperability in Peacekeeping Operations
|
- A key aspect of the drill is to enhance cooperation and interoperability between the participating sides in the context of Peacekeeping Operations.
- By fostering a shared understanding and coordinated approach, the exercise seeks to optimize the effectiveness of joint efforts in maintaining peace.
|
|
Promotion of Collaborative Partnership
|
- Exercise 'DESERT CYCLONE' serves as a platform for fostering collaborative partnerships between India and the UAE.
- Through joint military exercises, the participating nations aim to strengthen bonds of friendship and trust, laying the foundation for future collaborative endeavors.
|
|
Sharing Best Practices
|
- The drill emphasizes the exchange of best practices between the Indian and UAE forces.
- This knowledge-sharing initiative is crucial in refining operational strategies, tactics, and methodologies, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency of the participating units.
|
|
Significance of 'DESERT CYCLONE' in Bilateral Relations
|
- The exercise symbolizes a significant step towards further strengthening the bilateral relations between India and the UAE.
- By aligning security objectives, both nations aim to fortify their partnership, contributing to regional stability and peace.
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=India-and-UAE-Joint-Military-Exercise-%e2%80%98DESERT-CYCLONE%e2%80%99-begins-in-Mahajan%2c-Rajasthan&id=474422






.jpg)

