



Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: INDIAN EXPRESS
India and the EU have finalized an FTA to boost trade. However, the main hurdle for Indian exporters is navigating the EU's complex and strict Non-Tariff Barriers (NTBs).
|
Read all about: India European Union Relations l India-EU Free Trade Agreement: Significance, Challenges, Way Forward l India-EU FTA Explained: Opportunities and Challenges |
Top Trading Partner
The EU is one of India's largest trading partners, with total bilateral trade in goods and services growing steadily, reaching roughly $136.5 billion for 2024-25. (Source: PIB)
Investment Hub
The EU is a leading foreign investor in India, with investment stock reaching €140.1 billion in 2023. Over 6,000 European companies operate in India, supporting nearly 7 million direct and indirect jobs. (Source: DD News)
Strategic Trade Deal (2026)
The finalized Free Trade Agreement provides India with preferential access to European markets. It includes immediate duty elimination for key labor-intensive sectors such as textiles, leather, and footwear, while reducing duties on machinery and pharmaceuticals.
Geopolitical Realignment
The partnership acts as a crucial alternative to US/China markets, enhancing economic sovereignty and supply chain resilience amidst global tensions.
Broadened Cooperation
Beyond goods, the partnership covers services, technology, and migration; to manage skilled worker flows.
What is India-EU Free Trade Agreement?
The India-EU Free Trade Agreement (FTA), also dubbed the "Mother of All Deals," is a comprehensive trade and investment pact between India and the 27-member European Union, to create a free trade zone of 2 billion people, covering nearly 25% of global GDP.
Key Highlights of the Agreement
Market Access: The EU will eliminate tariffs on 99.5% of Indian exports (by value) over seven years, with most duties dropping to zero immediately. India will liberalise about 97.5% of its traded value with the EU.
Major Beneficiaries (India): Labour-intensive sectors like textiles, apparel, leather, footwear, marine products, and gems and jewellery will gain duty-free access, enhancing their global competitiveness.
Major Beneficiaries (EU): EU exporters will see tariff cuts on high-tech goods, machinery, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals.
Consumer Impacts in India:
Services & Mobility: India secured access to 144 services subsectors in the EU, along with a comprehensive mobility framework for skilled professionals and students.
Strategic & Defence: Alongside the trade deal, a separate Security and Defence Partnership was signed to cooperate on maritime security, cyber threats, and space.
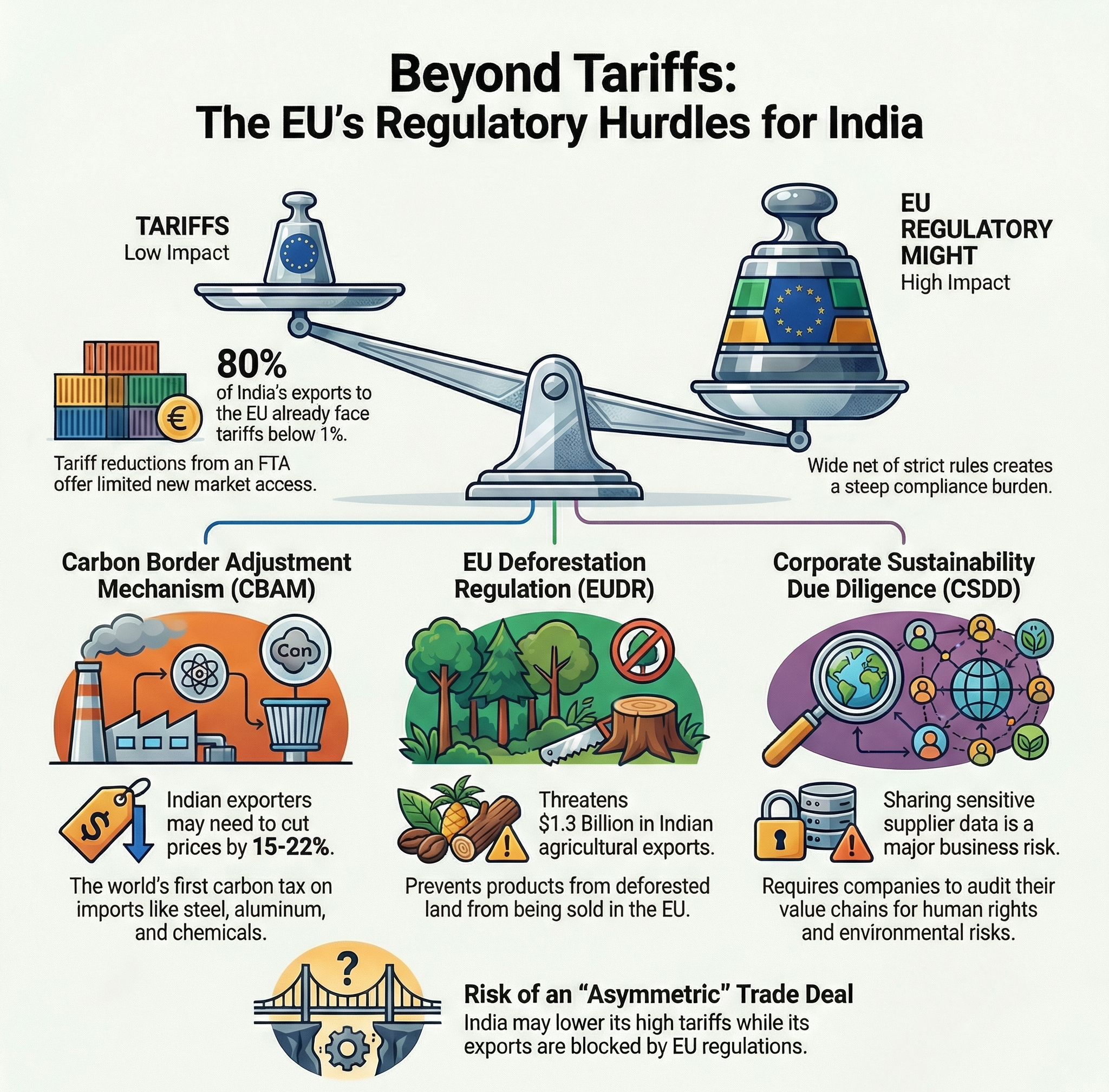
Despite these benefits, experts note that nearly 80% of India’s exports to the EU already face minimal tariffs. Therefore, the real test lies in overcoming the EU's powerful regulatory framework, which acts as a trade barrier.
Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)
What is it? CBAM is the world's first carbon tax on imports. It imposes a levy on goods from countries with less strict climate policies to prevent "carbon leakage." It targets carbon-intensive sectors like steel, aluminum, cement, and fertilizers.
Impact on India:
EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR)
What is it? This regulation prohibits the sale of products in the EU that originate from land deforested after December 31, 2020. Its implementation has been extended to December 2026.
Impact on India:
Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDD)
What is it? Effective from 2027, the CSDD mandates that companies identify and mitigate adverse human rights and environmental impacts throughout their entire value chains.
Impact on India:
 Way Forward For India
Way Forward For India
To ensure the Free Trade Agreement (FTA) is beneficial, it must include strong provisions to tackle non-tariff barriers, using the agreement's legal framework.
Establish a Robust Regulatory Dialogue
Create a formal mechanism for regular consultation on upcoming EU regulations. This would allow India to provide input during the drafting stage, not after the laws are passed.
Pursue Mutual Recognition Agreements (MRAs)
Negotiate to recognize Indian standards and certifications as equivalent to its own. This would eliminate the need for costly and duplicative testing processes.
Demand Technical and Financial Assistance
The FTA should include binding commitments from the EU to help Indian SMEs upgrade their technology and processes to meet European standards, ensuring compliance costs are not prohibitive.
Negotiate for Proportionality
Argue for compliance requirements to be adjusted based on the size of the business. Securing exemptions or phased implementation timelines for SMEs is crucial.
Utilize a Strong Dispute Settlement Mechanism
A fair and efficient dispute resolution body within the FTA is essential to legally challenge any EU regulations that act as protectionism and violate the spirit of the agreement.
The success of the India-EU FTA depends on proactively removing non-tariff barriers and balancing the EU's regulatory standards with India's developmental needs to ensure mutual benefits.
Source: INDIAN EXPRESS
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. "Non-tariff barriers are the new tariffs in the 21st century." Evaluate this statement in the context of India-EU trade relations. (150 words) |
The India-EU Free Trade Agreement (FTA) is a comprehensive economic pact between India and the 27-member European Union. Often dubbed the "Mother of All Deals," it establishes a massive free trade zone covering nearly 2 billion people and accounting for approximately 25% of global GDP.
CBAM is a carbon tax imposed by the EU on imported goods from sectors like steel, aluminium, and cement from countries with weaker climate policies. It directly impacts India's key exports in these sectors, potentially making them less competitive by requiring exporters to bear additional costs or reduce prices.
The EU Deforestation-Free Regulation (EUDR) is projected to affect about $1.3 billion of India's annual agricultural exports. Although the regulation aims to tackle climate change, it introduces substantial administrative and financial challenges for Indian industries that are highly dependent on European markets.
© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved