Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The Union government partially relaxed the indefinite ban on onion exports, allowing for the immediate export of 2,000 tonnes of white onions grown in Gujarat from three designated ports.
White Onion
- White onions, a cultivar of dry onion, have a mild flavor profile.
- They are low in sulphur and high in sugar, making them less pungent.
- Commonly used raw in salads and sandwiches for a light, fresh taste.
- Used in stews and fermented dishes for a mild, cohesive flavor.
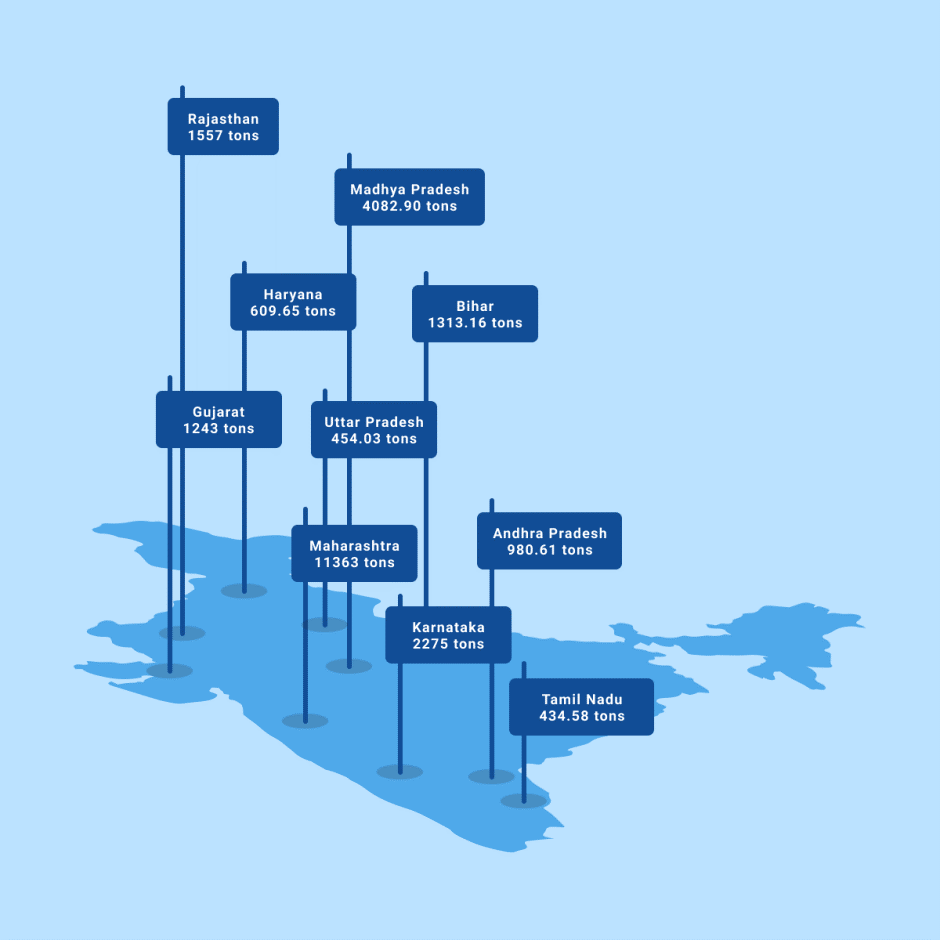
Production of White Onion in India
- India is the world’s second-largest producer of onions, behind China.
- Indian farmers grow red and white onions, but white onions are more prevalent in some parts of the country.
- White onion farming in India is concentrated in Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Maharashtra is India’s leading producer of white onions, accounting for nearly 40% of the country’s total production. The state’s climate is well-suited for onion cultivation, and the sandy soil in many parts of Maharashtra is ideal for growing onions. Farmers in Maharashtra typically use irrigation to water their crops, as rainfall is unpredictable in the region.
- Karnataka is India’s second-largest producer of white onions, with a production share of about 20%. The state has a moderate climate that is conducive to onion cultivation.
- Andhra Pradesh is India’s third largest producer of white onions, with a production share of about 15%. The state has a hot climate that is ideal for growing onions. Farmers in Andhra Pradesh typically use drip irrigation to water.
- Gujarat is the predominant producer and exporter of white onions in the country, with districts like Bhavnagar and Amreli accounting for a large part of the produce.
Diseases Affecting White Onions
Onion Smudge
- Caused by the fungus Colletotrichum circinans.
- Thrives in damp soil above 20°C, impacting crop yield and quality.
- Damages outer scale leaves, reducing market value.
- Can infect entire crops if left untreated.
Onion White Rot
- Caused by the fungus Sclerotium cepivorum.
- Survives in soil for over 20 years as hardened fungal mass.
- Spreads through floodwater, agricultural equipment, and wind-blown plant scales.
- Identified by yellowing and wilting of leaves, leading to reduced bulb size.
Botrytis Leaf Blight
- Caused by the fungus Botrytis squamosa.
- Affects leaves, causing lesions, dieback, and blighting.
- Survives winter as sclerotia, infecting leaves and bulbs.
- Thrives in wet and cold conditions.
Onion Downy Mildew
- Caused by the oomycete Peronospora destructor.
- Causes pale green, then tan, brown, or yellow leaves that collapse.
- Spreads through spores released at night in cold, moist conditions.
- Overwinters in live hosts and releases spores in humid climates.

Planting Methods for White Onions
- Onion Transplants
- Seedlings started in the current growing period are bought and planted.
- Yields quick bulb growth but plants are more vulnerable to disease in maturity.
- Onion Sets
- Small bulbs from the previous harvest are not allowed to mature and are dried.
- These bulbs are used in the current season, growing quickly and producing larger bulbs.
- Onion Seeds
- Seeds of the white onion are planted into sets in late Spring.
- This method has the longest grow time (up to 4 months for mature bulbs), but produces onions least susceptible to disease.
Varieties and Cultivation Timing
- Short-day onions form bulbs with 10 to 12 hours of sunlight a day.
- Intermediate-day onions form mature bulbs with 12 to 14 hours of sunlight a day.
- Long-day onions form bulbs with 14 to 16 hours of sunlight a day.
Soil pH and Nutrient Supply
- For most white onion varieties, a soil pH of 6-7 is optimal.
- Below pH 5.5, magnesium and molybdenum supply are inadequate.
- Above pH 6.5, zinc, manganese, and iron are less present in the soil.
|
TYPES OF ONION
There are many different types of onions, each with its unique flavor and texture. Here are just some of the most popular varieties:
- White onions: These are the most common type of onion grown across the globe and have a sharp, spicy flavor. They’re often used in salads, as they don’t overwhelm other flavors.
- Red onions: These onions are slightly sweeter than white onions and have a deep purple hue. They’re often used in cooked dishes, as their sweetness mellows out when heated.
- Yellow onions: These have a rich, golden color and a milder flavor than other onions. They’re versatile and used in both cooked and raw dishes.
- Green onions: Also known as scallions, these onions usually have a milder flavor than other types of onion. They’re often used as a garnish or in stir-fries.
|
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. How many of the following statements about white onion farming in India are correct?
1. India is the largest producer of white onions in the world.
2. Maharashtra accounts for approximately 40% of India's total white onion production.
3. White onions are low in sulphur and high in sugar.
Choose the correct code from the options given below.
A) Only one
B) Only two
C) All
D) None
|










