Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context:
- The government of Switzerland announced that it will host a major summit on June 15-16 as a “first step” for lasting peace in Ukraine following Russia’s invasion in February 2022.
Details:
- Switzerland announced it will host a summit on June 15-16 aimed at achieving lasting peace in Ukraine after Russia's invasion in February 2022.
- Over 100 countries, including India, have been invited, but Russia's participation is uncertain.
- The summit will follow a plan discussed by Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy and Swiss Foreign Minister Ignazio Cassis.
- Ukraine has stated that it will not participate in peace talks unless Russian hostilities cease, and Russia returns the territories it gained in the war.
Attempts to negotiate the deal in the past
Various attempts have been made for peace since 2022.
- Turkey was able to negotiate the movement of grains from Ukraine through the Black Sea, given Ukraine’s significance as a major producer of wheat and corn, for global trade and food security.
- In December 2022, Ukraine suggested a 10-point plan that focused on “restoring Ukraine’s territorial integrity”, “withdrawal of Russian troops and cessation of hostilities”, and “restoration of Ukraine’s state borders with Russia”, among other issues related to the release of prisoners and food security. Russia rejected this plan.
- The Chinese plan emphasized ending hostilities and protecting civilians but did not mention Russia's returning territory.
The Russia-Ukraine conflict is complex and has various underlying reasons :
- Historical and Cultural Factors: Ukraine has a long history of being culturally, ethnically, and linguistically distinct from Russia, but it was part of the Soviet Union until its dissolution in 1991. This historical connection and subsequent independence have created tensions between the two countries.
- Geopolitical Struggle: Ukraine's strategic location between Russia and Europe has made it a focal point in the geopolitical struggle between Russia and the West, particularly the European Union and NATO. Russia sees Ukraine as part of its sphere of influence and is wary of NATO expansion into the region.
- Russian Minority in Ukraine: A significant portion of Ukraine's population, particularly in the eastern regions, identifies as ethnically Russian. Russia has expressed concern about the rights and well-being of these Russian-speaking populations, using it as a pretext for intervention.
- Energy Transit: Ukraine serves as a crucial transit route for Russian natural gas exports to Europe. Disputes over gas prices and transit fees have often led to tensions between the two countries.
- Desire for Greater Autonomy and Integration: Ukraine's desire for closer integration with the European Union and NATO, particularly evident during the Euromaidan protests in 2013-2014, has been viewed unfavorably by Russia, which sees it as a threat to its influence in the region.
- Annexation of Crimea: In 2014, Russia annexed Crimea following a controversial referendum. This move was widely condemned by the international community and further escalated tensions between Russia and Ukraine.
- Conflict in Eastern Ukraine: Since 2014, pro-Russian separatist movements in eastern Ukraine, particularly in the Donetsk and Luhansk regions, have led to ongoing conflict. Russia has been accused of providing military support to these separatist groups, exacerbating the situation.
- Strategic Military Objectives: For Russia, maintaining influence over Ukraine provides strategic military advantages, including access to warm-water ports in Crimea and a buffer zone between Russia and NATO-aligned countries.
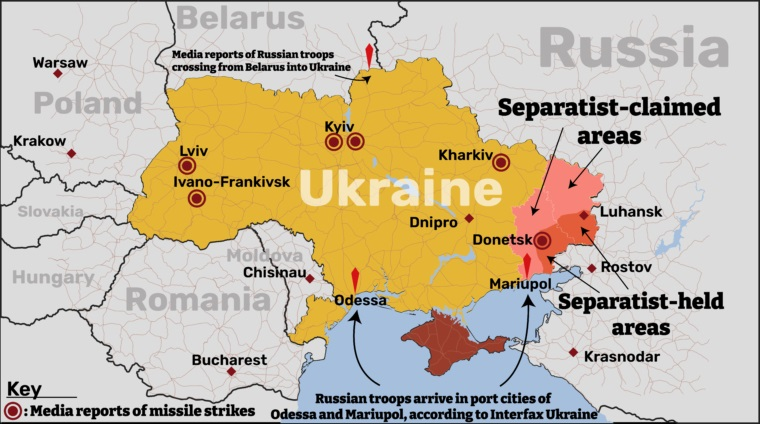
Resolving the tensions between Russia and Ukraine requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses the underlying issues fueling the conflict. The Following Are Ways ahead:
- Diplomatic Dialogue: Direct and sustained diplomatic dialogue between Russia and Ukraine, facilitated by neutral mediators or international organizations, can help build trust and find mutually acceptable solutions.
- International Mediation: Engaging international mediators, such as the United Nations or the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), can provide impartial facilitation and support for negotiations.
- Peace Negotiations: Renewed efforts for peace negotiations, based on previously agreed-upon frameworks like the Minsk agreements, can provide a foundation for addressing key issues such as ceasefire arrangements, withdrawal of troops, and political reforms.
- Humanitarian Assistance: Providing humanitarian assistance to populations affected by the conflict, especially in eastern Ukraine, can help alleviate suffering and build confidence in the peace process.
- Respect for Sovereignty: Upholding the principles of sovereignty and territorial integrity is essential. Any solution to the conflict must respect Ukraine's sovereignty and the rights of its citizens to determine their future.
- Security Guarantees: Providing security guarantees to all parties involved, including assurances against military aggression and respect for existing borders, can help create a stable environment for negotiations.
- De-escalation Measures: Implementing confidence-building measures, such as troop withdrawals, demilitarized zones, and arms control agreements, can reduce the risk of further escalation and build momentum for peace.
- Reconciliation and Dialogue: Promoting reconciliation efforts at the grassroots level, including people-to-people exchanges, cultural initiatives, and educational programs, can foster understanding and trust between Russian and Ukrainian communities.
- Long-Term Political Solutions: Addressing underlying political grievances and promoting inclusive governance structures that accommodate diverse interests within Ukraine can help address the root causes of the conflict and prevent future escalation.
India’s Stand on Russia Russia-Ukraine War
- Neutrality: India has refrained from taking sides in the conflict and has emphasized the need for a peaceful resolution through dialogue and diplomacy. India's traditional policy of non-alignment and its commitment to sovereign equality underpin its neutral stance.
- Support for Diplomacy: India has consistently called for the resolution of the conflict through diplomatic means, including dialogue between Russia and Ukraine. India has supported efforts by the international community, including the United Nations and the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), to facilitate negotiations.
- Respect for Sovereignty and Territorial Integrity: India has reiterated its commitment to the principles of sovereignty and territorial integrity, emphasizing the importance of upholding international law and respecting the borders of all nations, including Ukraine.
- Humanitarian Concerns: India has expressed concern about the humanitarian impact of the conflict, particularly on civilians in eastern Ukraine. India has called for the protection of civilians and the provision of humanitarian assistance to those affected by the conflict.
- Economic Considerations: India has sought to balance its diplomatic stance with its economic interests. India maintains economic ties with both Russia and Ukraine and has sought to minimize any adverse impacts on its trade and investment interests.
- Engagement with Both Parties: India has maintained diplomatic engagement with both Russia and Ukraine. Indian leaders have held discussions with their counterparts from both countries to express India's concerns and promote dialogue.
Source
https://www.thehindu.com/news/international/indias-jagjit-pavadia-re-elected-for-a-third-term-to-the-international-narcotics-control-board/article68049269.ece
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Which of the following statements regarding the Russia-Ukraine conflict is/are correct?
Statement I: The conflict escalated significantly following Russia's annexation of Crimea in 2014.
Statement II: The conflict primarily revolves around ethnic tensions between Russians and Ukrainians in Eastern Ukraine.
Statement III: The Minsk agreements have successfully brokered a lasting ceasefire and resolution to the conflict.
a) Only Statement I
b) Statements I and II
c) Statements I and III
d) All of the above
Correct answer: c)
|









