Description
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://foammagazine.com/swell/
Context: The Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) predicted hazardous swell waves to hit coastal areas in several Indian states and union territories, suggesting precaution and suspending activity near beaches.
|
The Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) was founded in 1998 to act as an integrated centre for Indian Ocean-related data collecting, research, and service supply. It is an autonomous body under the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
|
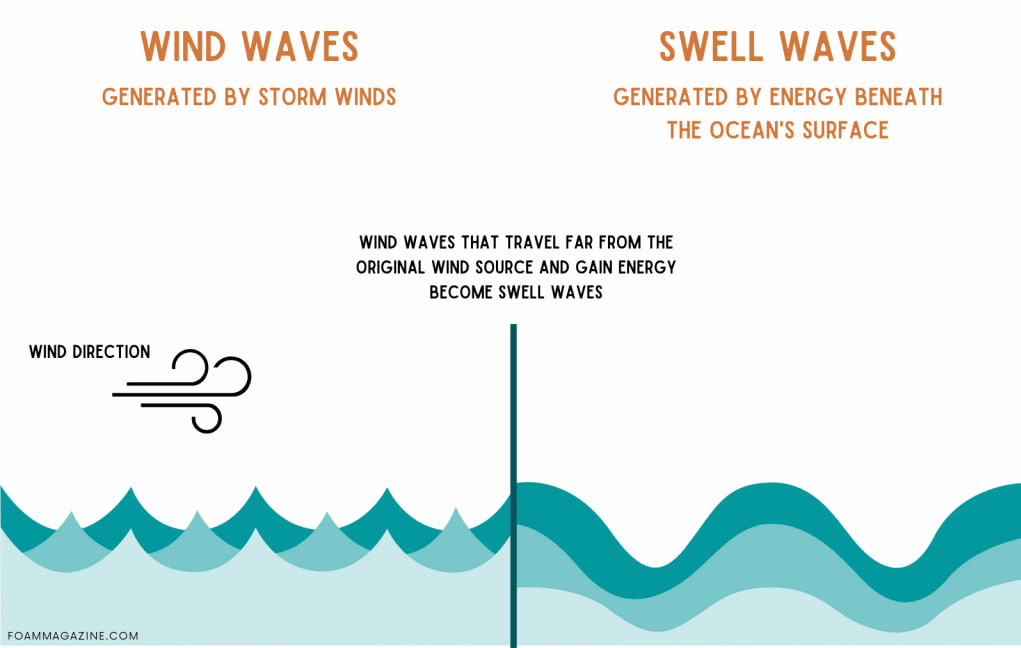
Swell Waves
- Swell waves are a type of ocean wave that originates from distant storms, such as hurricanes or strong gale winds, rather than from local winds.
- These waves are characterized by their large size and long wavelengths, and they can travel across vast distances over the ocean surface until they reach coastal areas.
Key points about swell waves
- Swell waves are formed when strong winds over large ocean expanses transfer energy to the water surface. This energy transfer can occur over thousands of kilometres from the storm centre.
- During storms like hurricanes or prolonged gale winds, significant energy is transferred from the atmosphere to the ocean, creating large and powerful waves known as swells.
- Swell waves can travel long distances, maintaining their energy and size as they move across the ocean. They often travel for days before reaching coastal regions.
- Swell waves generally have a uniform and regular appearance with long wavelengths and large amplitudes. They are distinct from locally generated wind waves, which have shorter wavelengths and are affected by local wind conditions.
- When swell waves reach coastal areas, they can cause significant impacts, including coastal erosion, flooding, and damage to infrastructure.

|
The Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) has developed the Swell Surge Forecast System to predict the occurrence of swell waves. This system helps in issuing advance warnings to coastal populations and authorities about potential high sea waves and associated risks.
|
Difference between Swell Waves and Tsunamis
Cause
- Swell waves are generated by distant storms like hurricanes or intense gale winds that transfer energy from the atmosphere to the ocean surface. They are not directly associated with underwater disturbances.
- Tsunamis are caused by underwater disturbances, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, landslides, or meteorite impacts that displace large volumes of water rapidly.
Size and Nature
- Swell waves are regular, rhythmic waves that travel across the ocean surface over long distances. They are relatively slower-moving and have a predictable pattern.
- Tsunamis consist of a series of enormous waves with very long wavelengths and travel at high speeds across the ocean. They are characterized by their immense energy and volume of water displaced.
Speed
- Swell waves travel at speeds that depend on their wavelength and ocean depth but are generally much slower compared to tsunamis.
- Tsunamis are extremely fast-moving in deep ocean waters, travelling at speeds ranging from 500 to 800 km/h.
Impact on Land
- Swell waves can increase in height and intensity as they approach the coastline but typically do not cause significant damage or flooding upon landfall.
- Tsunamis can cause devastating impacts when they reach the coastline due to their speed, volume, and energy. They can lead to widespread flooding, destruction of coastal infrastructure, and loss of life.
Behavior near Coast
- Swell waves gradually slow down and decrease in height as they approach shallow waters near the coast.
- Tsunamis slow down considerably as they reach shallow coastal regions, causing the waves to increase in height dramatically before making landfall.

Summary
- Swell waves are large waves generated by distant storms like hurricanes or intense gale winds, transferring energy from the air into the water. Unlike tsunamis, which are rapid waves caused by underwater disturbances like earthquakes, swell waves travel slower and can be forecasted in advance using systems like INCOIS's Swell Surge Forecast System.
Must Read Articles:
Indian National Centre For Ocean Information Services (INCOIS)
Kallakkadal
Source:
Indian Express
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Which of the following statements about swell surge is true?
A) Swell surge is caused by underwater earthquakes.
B) Swell surge occurs due to sudden changes in wind direction.
C) Swell surge is a gradual rise in ocean water levels caused by distant weather disturbances.
D) Swell surge only affects coastal areas during typhoons.
Answer: C
|












